Seeing Things in Plane (Flat) Mirrors (Optics Lesson 2)
advertisement
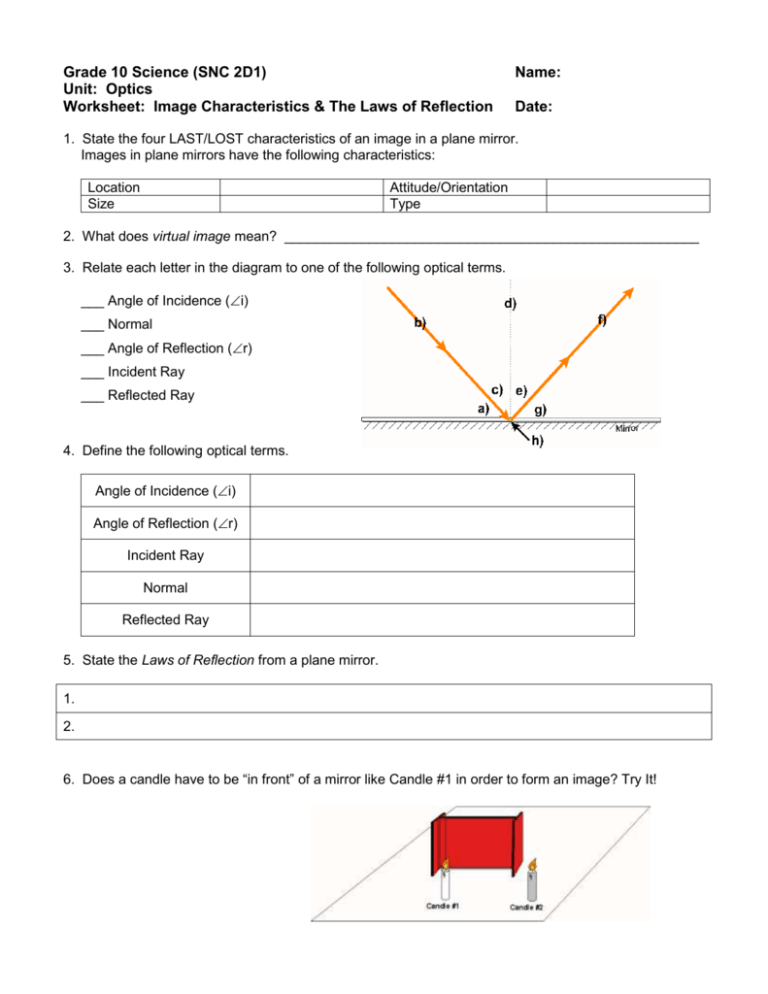
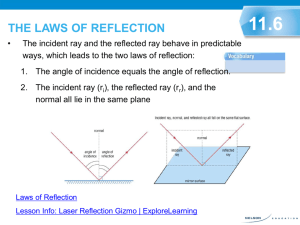
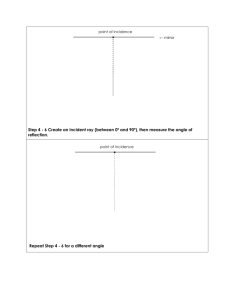
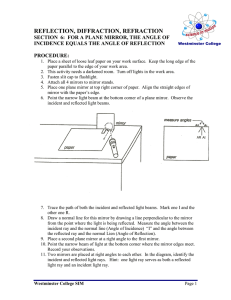
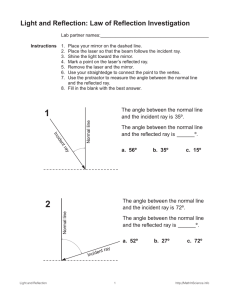
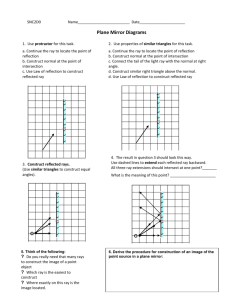
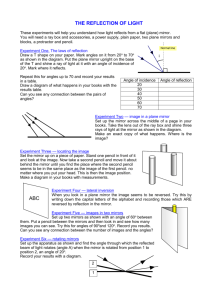
Grade 10 Science (SNC 2D1) Unit: Optics Worksheet: Image Characteristics & The Laws of Reflection Name: Date: 1. State the four LAST/LOST characteristics of an image in a plane mirror. Images in plane mirrors have the following characteristics: Location Size Attitude/Orientation Type 2. What does virtual image mean? ______________________________________________________ 3. Relate each letter in the diagram to one of the following optical terms. ___ Angle of Incidence (i) ___ Normal ___ Angle of Reflection (r) ___ Incident Ray ___ Reflected Ray 4. Define the following optical terms. Angle of Incidence (i) Angle of Reflection (r) Incident Ray Normal Reflected Ray 5. State the Laws of Reflection from a plane mirror. 1. 2. 6. Does a candle have to be “in front” of a mirror like Candle #1 in order to form an image? Try It! 7. a) Show where the images of the candles are located. b) Which eye-brain can see the top of: image of candle #1? image of candle #2? 8. What determines whether an eye-brain observer can see an image or not? _________________________________________________________________________________ In the following diagrams, use arrows for the images in order to ease drawing. 9. Use the Laws of Reflection to show how the eye-brain sees the top and bottom of a candle in a periscope. 10. Use the Laws of Reflection to show how the eye-brain sees the top and bottom of a candle if the top mirror is rotated to face backwards. 11. Use the Laws of Reflection and geometry to prove light is reflected back, parallel to the Incident Ray from two mirrors at right angles. Draw two more incident rays to prove the law.