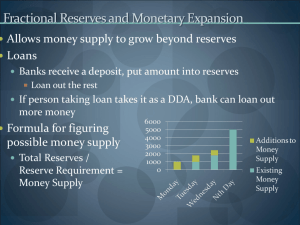
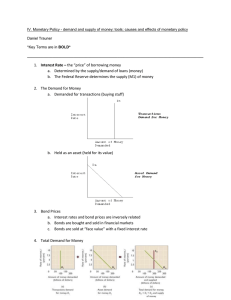
Problem Set 3
advertisement

University of Bahrain College of Business Administration Department of Economics and Finance Econ 341 - Monetary Economics Problem Set 3 (Chapter 17) AlShawa 1. Open market sales will a. raise the monetary base and increase the money supply b. raise the monetary base and decrease the money supply c. lower the monetary base and increase the money supply d. lower the monetary base and decrease the money supply 2. If the Fed wants to temporarily increase reserves in the banking system, it will engage in a. dynamic open market purchase. b. dynamic open market sale. c. defensive open market purchase. d. defensive open market sale. 3. To lower interest rates, the Fed could a. buy government securities. b. sell government securities. c. lower the discount rate. d. only (a) and (c) of the above. 4. Which of the following statements is correct? a. Elimination of discount operations would increase fluctuations in the monetary base. b. Elimination of discount operations would reduce fluctuations in the money multiplier. c. Elimination of discount operations would prevent the Fed from acting as lender-of-last resort. d. All of the above statements are correct. 5. Discount operations affect the money supply by affecting a. reserves b. the money multiplier c. the monetary base d. (a) and (c) of the above. 6. The most important advantage of the Fed's lending operations is that it allows the Fed to a. signal its intentions about future monetary policy. b. act as lender-of-last resort. c. control the money supply. d. punish banks that have low reserves. 2 7. A financial panic was averted in October 1987 following "Black Monday" when the Fed announced that a. it was lowering the discount rate. b. it would provide discount loans to any bank that would make loans to the security industry. c. it stood ready to purchase common stocks to prevent a further slide in stock prices. d. all of the above. 8. Open market operations as a monetary policy tool have the advantages that a. they are flexible and precise. b. they can be implemented quickly without administrative delays. c. they are not easily reversed. d. only (a) and (b) of the above. 9. The Fed is reluctant to use reserve requirements to control the money supply because a. of their powerful impact on the money supply. b. they have the potential to create liquidity problems for banks with low excess reserves. c. frequent changes in reserve requirements complicate liquidity management for banks. d. of all of the above. 10. The global reduction in reserve requirements a. increases bank costs. b. decreases bank profits. c. increases bank competitiveness. d. increases moral hazard. 11. In the channel/corridor system for setting interest rates used in Canada, a. control of the overnight interest rate is impossible. b. reserve requirements are essential for monetary control. c. the overnight rate always equals the bank rate. d. allows for monetary control with no required reserves. 12. In the channel/corridor system for setting interest rates used in Canada, a. the bank rate sets a cap on the overnight rate. b. banks can borrow unlimited amounts at the bank rate. c. the rate on reserves sets a floor for the overnight rate. d. all of the above.