short-answer questions - Iowa State University
advertisement

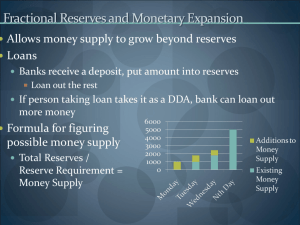
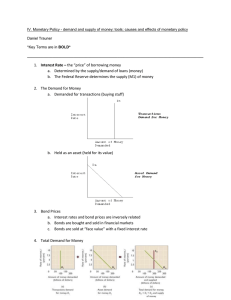
Iowa State University Department of Economics Econ353: Section 2 Spring 2003 Sample Test 3: Short Questions Chapter 9: The Banking Firm and the Management of Financial Institutions Questions and Problems: Questions 11, 12, 13, 14 and 15 on pages 246 and 247 of your textbook. Chapter 15: Multiple Deposit Creation and the Money Supply Process Question 1: Using T-accounts for both the banking system and the Fed for part (a) and the nonbank public, the banking system and the Fed for parts (b) and (c), show: a) how a Federal Reserve sale of $100 of government bonds to banks will affect the monetary base and reserves b) how a Federal Reserve sale of $100 of government bonds to the nonbank public will affect the monetary base and reserves if the nonbank public pays for the bonds in checks c) how a Federal Reserve sale of $100 of government bonds to the nonbank public will affect the monetary base ad reserves if the nonbank public pays for the bonds in currency d) how does the answer in part (c) differ from those in parts (a) and (b). Question 2: Using T-accounts for the First National Bank and the Fed, show a) What happens when the Fed sells $100,000 of T-bills to the First National Bank; what has happened to reserves in the banking system? b) What happens if the First National Bank pays off a $100,000 discount loan; what has happened to reserves in the banking system? Question 3: a) Assume that the required reserve ratio is 0.20 and that the Fed purchases $1000 in government bonds from the First State Bank of Bozeman, which, in turn, lends the $1000 of reserves it has just acquired to a customer for the purchase of a used car. If the used car dealer deposits the proceeds from the sale in Bank A, how much in additional loans can Bank A make? What is the change in the money supply after Bank A lends this amount? b) Assume a similar process occurs for Bank B, Bank C, and Bank D. Complete the following table for these banks (see Table 3, page 405 in the text for an example) and the totals for all banks. Bank A B C D . . . Total All banks Change in Deposits + $1000.00 + $800.00 __________ __________ Change in Loans + $800.00 + $640.00 _________ _________ Change in Reserves + $200.00 + $160.00 _________ _________ __________ _________ _________ Question 4: a) Write down the formula for the simple deposit multiplier. b) Assuming that the required reserve ratio is 0.20, what is the change in reserves when the Fed sells $10 billion of government bonds and extends discount loans of $5 billion to commercial banks? c) Using the simple deposit multiplier formula, calculate the resulting change in checkable deposits. Chapter 17: Tools of Monetary Policy Question 1: Using the supply and demand in the market for reserves and starting from the point of equilibrium (see Figure 1 on page 436 of your textbook), show what happens to the demand and/or the supply curves (i.e., shifts) and what happens to the federal funds rate if: a) the Fed purchases U.S. Treasury securities, b) the Fed lowers the discount rate. Question 2: a) Why is open market operations the most important monetary policy tool? b) What are the two types of open market operations? c) List the advantages of open market operations? d) List the three types of discount loans. e) Why might it be important to have a lender of last resort even with the existence of deposit insurance? f) List two reasons why changes in reserve requirements are rarely used as a policy tool to conduct monetary policy. Chapter 18: Conduct of Monetary Policy: Goals and Targets Question 1: a) Although there is some ambiguity as to whether a particular variable is better categorized as an intermediate target or an operating target, list three variables generally thought to be intermediate targets and two variables generally thought to be operating targets. b) Selecting an intermediate target requires careful thought by members of the Federal Open Market Committee. The wrong choice can mean adverse consequences for the economy. Debate has tended to center around the choice between targeting a monetary aggregate or an interest rate. List the three criteria for choosing one variable as an intermediate target over another. Question 2: For the information given, use the Taylor rule to determine the appropriate setting of the federal funds rate under the assumption that the Fed uses the Taylor rule to determine the appropriate federal funds interest rate. Inflation Rate Equilibrium Federal Funds Rate Inflation Target 3% 4% 4% 4% 4% 5% 1% 1% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% Percentage Deviation of Real GDP from Potential GDP 1% 1% 2% -1% -2% 1% -2% 1% Federal Funds Rate