Name - NHS Anatomy
advertisement

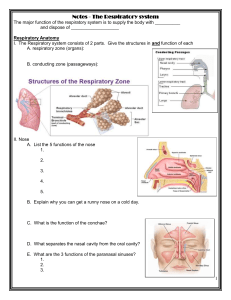
Name: ______________________________ Pd: _____ Date: ___________________ Ch 8 Respiratory System Handout Functional Anatomy The following questions refer to the primary bronchi. In the spaces provided, insert the letter R to indicate the right primary bronchi and the letter L to indicate the left primary bronchi. 1. _____ Which of the primary bronchi is larger in diameter? 2. _____ Which of the primary bronchi is more horizontal? 3. _____ Which of the primary bronchi is the most common site for lodging of a foreign object that has entered the respiratory system? Respiratory System Parts 4. Directions: Using the key choices, select the terms identified in the following descriptions by inserting the appropriate term or letter in the answer blanks. KEY TERMS 1. ________ Smallest conducting respiratory passageways A. Alveoli H. Phrenic Nerve 2. ________ Separates the oral and nasal cavities B. Bronchioles I. Conchae 3. ________ Major nerve, stimulating the diaphragm C. Epiglottis J. Trachea 4. ________ Food passageway posterior to trachea D. Esophagus K. Visceral Pleura 5. ________ Closes off the larynx during swallowing E. Glottis 6. ________ Windpipe F. Palate 7. ________ Actual site of gas exchanges G. Parietal Pleura 8. ________ Pleural layer covering the thorax walls 9. ________ Pleural layer covering the lungs 10. ________ Fleshy lobes in the nasal cavity which increase its surface area 11. ________ Opening between vocal folds 5. Figure 13-2 is a diagram of the larynx and associated structures. A. On the figure, identify each of the structures listed below. B. Select different colors for each and use them to color in the coding circles and the corresponding structures on the figure. C. Then, answer the questions following the diagram. D. What are the 3 functions of the larynx? ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ E. What type of cartilage forms the epiglottis? ____________________________________ ____________________________________ F. What type of cartilage forms the other 8 laryngeal cartilages? __________________________________________ __________________________________________ 6. 6. Color the Diagram Label the Leader Lines KEY WORDS Circoid Cartilage Conchae Epiglottis Esophagus Frontal Sinus Hard Palate Hyoid Bone Laryngopharynx Lingual Tonsils Nasal Cavity Nasopharynx Opening of Auditory Tube Oral Cavity Oropharynx Palatine Tonsil Pharyngeal Tonsil Soft Palate Sphenoid Sinus Thyroid Cartilage Trachea Vocal Folds of Larynx Yellow Book Pg 386 Name: ____________________________Pd: ______________ Figure 13-4 illustrates the gross anatomy of the lower respiratory system. Intact structures are shown on the left; respiratory passages are shown on the right. Select a different color for each of the structures listed below and use it to color in the coding circles and the corresponding structures on the figure. Then, use the Key Terms to label the leader lines. KEY TERMS (to label the lines) Pleural Space Diaphragm COLORING TERMS Mediastinum Clavicle Apex of right Lung Base of the right lung 7. Many changes occur within the lungs as the diaphragm contract and then relax. These changes lead to the flow of air into and out of the lungs. The activity of the diaphragm is given in the left column of the following table. Several changes in condition are listed in the column heads to the right. Complete the table by checking the appropriate column to correctly identify the change that would be occurring relative to the diaphragm’s activity in each case. Internal Volume of the Thorax I = Increased D = Decreased I D Internal Pressure in thorax I D Direction of Air Flow Size of the Lungs I D Out of Lung Into Lung Contracted, Moves downward Relaxed, Moves Superiorly 8. Use the key terms to respond to the following descriptions. Insert the correct term or letter in the answer blanks. Key Terms A. External Respiration B. Expiration C. Inspiration D. Internal Respiration E. Ventilation (Breathing) 1. ______ Period of breathing when air enters the lungs. 2. ______ Exchanges of gases between the systemic capillary blood and body cells. 3. ______ Alternate flushing of air into and out of lungs. 4. ______ Exchange of gases between alveolar air and pulmonary capillary blood. 9. Four non-respiratory movements are described here. Identify each by inserting your answers in the spaces provided. Key Terms A. Coughing B. Laughing C. Sneezing D. Yawning E. Hiccups 1. _____________________ Sudden inspiration, resulting from spasms of the diaphragm. 2. _____________________ A deep breath is taken, the glottis is closed, and air is forced out of the lungs against the glottis; clears lower respiratory passageways. 3. _____________________ As just described, but clears the upper respiratory passageways. 4. _____________________ Increases ventilation of the lungs; may be initiated by a need to increase oxygen levels in the blood.