HSI 2.06 Respiratory Review
advertisement

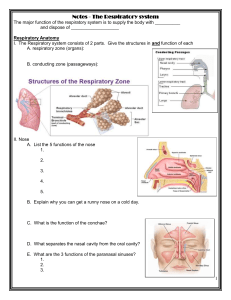
RESPIRATORY REVIEW 1. What is the name of the cartilage flap that covers the larynx when you swallow? ____________________________ 2. The respiratory system ends in millions of tiny, thin-walled sacs called: ____________________________________ 3. Where would you find a person’s larynx?____________________________________________________________ 4. What covers the outer surface of the lungs and lines the inner surface of the rib cage?_______________________ 5. The windpipe is referred to as the: __________________________________________________________________ 6. The walls of the trachea are made more rigid by the presence of: ________________________________________ 7. Each lung is divided into two or three parts called:_____________________________________________________ 8. Structures that produce mucous for the respiratory tract and are located in the skull are the: __________________ 9. When the trachea divides to enter both lungs, the tubes that are formed are called: _________________________ 10. The partition that separates the nose into right and left cavities is the: ___________________________________ 11. The medical name for the throat is the: _______________________________________________________________ 12. Surfactant is a fatty substance in the lungs that prevents:_______________________________________________ 13. Which structure of the respiratory system is responsible for voice production?_______________________________ 14. What is initially sensed by the brain to control breathing? ______________________________________________ 15. Cilia located in the nasal epithelium perform the function of: _____________________________________________ 16. Coughing is the body’s attempt to: ________________________________________________________________ 17. The part of respiration that involves taking air into the lungs is called:_______________________________________ 18. Moving air out of the lungs is called: _________________________________________________________________ 19. Collectively, taking air into then moving air out of the lungs is called:_______________________________________ 20. The normal number of breaths an adult takes each minute at rest is about: ________________________________ 21. List the correct pathway of air into the lungs: ______________, _____________, ________________, ______________ 22. What function is made possible by fibrous plates contained within the cartilage of the larynx?___________________ 23. When you sleep, do respirations increase or decrease? ________________ Exercise?__________________________ DISORDERS 1. Influenza is caused by a:___________________________________________________________________________ 2.The most common cause of chronic bronchitis is: _______________________________________________________ 3. Katlin comes to the office with wheezing, dyspnea, and tightness in the chest. She is experiencing: _______________ 4. Due to the increases in illegal immigration, homelessness, and AIDS, the incidence of what disease is increasing in the United States? __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. The two main causes of pneumonia are: ____________________ and ______________________________________ 6. What is dyspnea? ________________________________________________________________________________ 7. In what disease does dyspnea worsen as the disease progresses? _________________________________________ 8. Cough, low grade fever in the afternoon, weight loss, and night sweats are symptoms of what respiratory disease? _________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. What disorder is characterized by overdilated alveoli that have lost their elasticity? ____________________________ 10. Kim experienced hoarseness for two days and loss of voice for three days. She most likely suffers from:_____________________________________________________________________________________ THINGS TO REMEMBER: • The respiratory center is located in the brain, the medulla oblongata. • Phrenic nerves are motor nerves which lead to the diaphragm and the intercostal • muscles. • An increase of carbon dioxide or lack of oxygen in the blood will trigger the respiratory center. • Nerve pathways carry sensory impulses from the nose, larynx, lungs, skin, and abdominal organs via the vagus nerve in the medulla Chemical regulators of respiration (chemoreceptors) are found in the carotid arteries and the aorta. As the arterial blood flows around_ these structures, the chemoreceptors are particularly sensitive to the amount of oxygen present. If the level becomes low, impulses are sent from these structures to the respiratory center which will stimulate the rate and depth of respiration.