Respiratory System Overview Nasal Cavity
advertisement

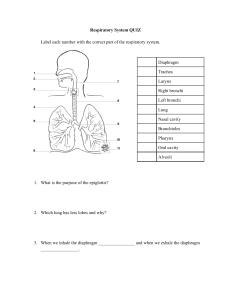
Respiratory System Overview Nasal Cavity • Warms and moistens air so that it doesn’t damage the respiratory tract. • Dust and debris is also removed by short hairs and mucous. Pharynx • “Back of the throat” • Shared by both the respiratory tract and digestive tract • Leads to the esophagus and larynx Larynx • “Voice box” • Contains the glottis (the opening to the larynx and trachea) • Protected by a piece of cartilage called the epiglottis, which closes during swallowing. • The opening is lined by elastic tendons called vocal cords; small muscles change the tension in these tendons. Larynx Larynx Trachea • “Windpipe” • Tough, flexible tube that branches into the right and left bronchi of each lung. • Carries air from the throat to the lungs • The walls of the trachea are supported by tracheal cartilage (“C” shaped cartilage that prevents the trachea from collapsing) Trachea Bronchi • Conducts air into lungs. • The right and left primary bronchi divide into smaller passageways called secondary and tertiary bronchi. These divide into even smaller passageways called bronchioles. • Tubes supported by cartilage. Bronchi Alveoli • The end of the respiratory tract where gas exchange between blood and air takes place. Diaphragm • Skeletal muscle that divides the thoracic and abdominal cavities. • Contraction of the diaphragm causes air to into the lungs (inhalation). Relaxation of diaphragm causes air to exit lungs (exhalation). Diaphragm