Monetary Policy—Review Questions
advertisement

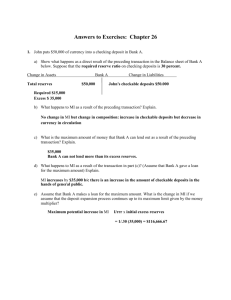
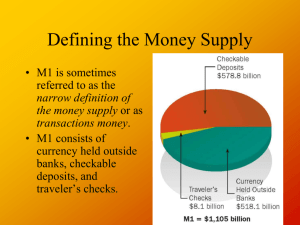
1 Monetary Policy—Review Questions You may write directly on this sheet 1. What does it mean to say that money is a unit of account? 2. The use of money makes the consumption of additional leisure possible. Explain. 3. What gives money value? 4. What does the M1 money supply equal? 5. What does the M2 money supply equal? 6. Since credit cards are widely accepted for purposes of exchange, why aren’t they considered money? 7. What do a bank’s reserves consist of? 8. How many people sit on the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System? 9. How many Federal Reserve districts exist? 10. What is the most important responsibility of the Fed? 11. Explain how an Open Market purchase increases the money supply. 12. Explain how an Open Market sale decreases the money supply. 2 13. Explain how lowering the discount rate increases the money supply. 14. What does the demand for money have to do with the opportunity cost of holding money? 15. What is an expansionary/loose monetary policy? What is a Contractionary/tight monetary policy? 16. Explain how expansionary monetary is supposed to remove an economy from a recessionary gap. 17. Explain how a Contractionary policy is supposed to remove an economy from a inflationary gap. 18. Fill in the blanks in the table: Required-reserve ratio Simple deposit multiplier .10 .12 .09 19. Fill in the blanks in the table: Currency Checkable Deposits $200 b $500 b $100 b $300 Traveler’s Checks M1 Money Supply $8 b $9 b $10 b $700 b $500 20. Fill in the blanks in the table: Checkable RequiredRequiredDeposits reserve ratio Reserves $400 .10 $500 .15 $872 .12 Reserves $60 $80 $200 Excess Reserves 3 21. Fill in the blanks in the table: Fed Action… Money Supply (rises, falls, remains unchanged) Conducts an open market purchase Lowers required-reserve ratio Conducts an open market sale Raises the discount rate to a level higher than the federal funds rate Raises the required-reserve ratio What is the Question? 22. Medium of exchange, unit of account, store of value. 23. Deposits on which checks can be written. 24. An asset that can easily and quickly be turned into cash. 25. The central bank of the United States. 26. The difference between reserves and required reserves. 27. 1 divided by the required-reserve ratio. 28. This group conducts open market operations. 29. These are sold to raise funds to pay the government’s bills. 30. The Fed buys and sells government securities. 4 Multiple Choice 31. Money is valuable because a. it is backed by gold. b. The government says it is valuable. c. People are willing to accept it as payment for goods and services. d. It is backed by silver. 32. M1 is comprised of a. Currency, checkable deposits, Visa and MasterCard b. Currency, checkable deposits, traveler’s checks. c. Currency and checkable deposits. d. Currency, checkable deposits, savings deposits. 33. A credit card is a. considered money. b. not considered money. c. under certain circumstances considered money. d. the same as a repurchase agreement. e. none of the above. 34. If deposits in Bank A total $15 million and the required-reserve ration is 10 percent, then excess reserves equal _____. a. $13.5 million b. $1.5 million c. $10.5 million d. $2.5 million e. none of the above. 35. Which of the following required-reserve ration would allow a bank the least amount of loanable funds? a. 5 percent b. 10 percent c. 12 percent d. 15 percent 36. The banking system increases the money supply by a. Printing its own currency b. Creating checkable deposits c. Creating demand deposits and currency d. Creating Federal Reserve notes 37. The simple deposit multiplier is a. the required-reserve ratio. b. Always 1 c. The reciprocal of the required-reserve ration d. None of the above 38. An open market purchase occurs when a. one bank busy government securities from another bank. b. A bank buys government securities from the Fed c. The Fed busy government securities from a bank. d. The Fed raises the discount rate.