Questions
advertisement

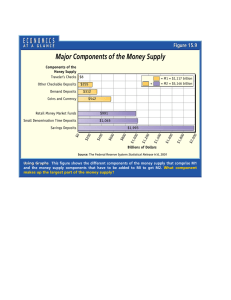
Questions Which of the functions of money distinguish it from any other asset . o Medium of exchange o Store of value (wealth) o Unit of account o Standard of deferred payment. Wealth = Assets(Money, stocks, bonds, art, houses, jewelery,….) The government can make anything it wants to be money? Does it require a government to make something money? The Fed can measure money precisely. What is commodity money? How does money create efficiency compared to a barter economy? What is fiat money? What advantages do checks have over currency. Which of the following are components of M1 o Currency o Coins o Checkable deposits o Savings deposits o Time deposits o NOW accounts o Travelers checks o Negotiable CD’s Will we ever move to a (mostly) paperless system of money? What will make us tend to move in that direction? 4. (End of Chapter question in text )Why were people in the United States in the nineteenth century sometimes willing to be paid by check rather than with gold, even though they knew there was a possibility that the check might bounce? Because a check was so much easier to transport than gold, people would frequently rather be paid by check even if there was a possibility that the check might bounce. In other words the lower transaction costs involved in handling checks made people more willing to accept them. It was also the case the thieves might be more easily tempted by gold than by a check. 5. (End of Chapter question in text) In ancient Greece why was gold a more likely candidate for use as money than wine was? Wine is more difficult to transport than gold and is also more perishable. Gold is thus a better store of value than wine and also leads to lower transactions cost. It is therefore a better candidate for use as money. 7. Rank the following assets from the most liquid to the least liquid. a. Checking account deposits b. Houses c. Currency d. Washing machines e. Savings deposits f. Common stocks. The ranking is (a) and (c) the most liquid; then, in descending order of liquidity, (e), (f), (b), and (d). 8. Explain how money makes trade more efficient than it would be in a barter economy.