The pH Scale and Indicators + 6.3
advertisement

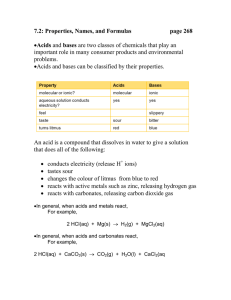
6.2 - The pH Scale and Indicators The ______________ is a numerical scale, ranging from _____________, that is used to classify solutions as _________________, __________________, or _____________________. The pHs of a variety of solutions (pool water, foods and beverages, and solutions from industrial processes) are regularly monitored. Acidic: ___________ Basic: _______________ Neutral: ______________ A pH (__________________________) value relates to the _____________________________________ in a solution. Values __________________ or _________________ exponentially (by a _________________) as you move up or down the scale. Determining the pH of a Solution ____________________________ are substances that change colour to show the concentration of hydrogen ions (_______) and hydroxide ions (________) in a solution. ______________________ have a sensor or probe that electronically produces a ______________________ (real time) reading of the pH of a solution that is displayed digitally on the meter. ______________________________________________________ – chemically treated indicator paper. Acids _________ Blue ______________ Red. Bases _________ Red _______________ Blue. This simple indicator can determine whether a solution is acidic, basic, or neutral. _________________________ and ________________ are composed of a mixture of indicators that change to different colours under different pH conditions. These indicators cover the ________ pH range from 0-14. Other pH Indicators 1 pH Indicators in Nature - A variety of plants contain juices that can act as natural acid-base indicators. A few of these are listed below. Acids and Bases: Similarities and Differences 2 6.3 - Reactions of Acids and Bases __________________________ is the reaction of an acid and a base to form a ________ and ___________. ___________(aq) + _____________(aq) ____________(l) + ____________(aq) Neutralizing Stomach Acid ________________ such as those shown below (e.g. tums) are taken to ________________ excess acid produced in the dark pits of the ____________ lining shown on the right. This excess acid leads to a _______________ sensation called ______________. Neutralizing Acid Spills The environmental damage caused by accidental acid spills like the one from the train derailment shown below can be reduced by __________________________________________________________________ ________________ (aq) + ________________(aq) _______________(aq) + ______________ (l) Acid Precipitation _____________________________ (a.k.a. _________________) is rain that has a pH lower than that of normal rain (which is around ________________). Acid precipitation is primarily caused by emissions of ___________________ and ____________________ that combine with _________ and other gases in the atmosphere to produce _________ and _____________ Sulfure oxide emissions: __________ (g) + __________(l) _____________ (aq) Nitrogen oxide emissions: __________ (g) + __________(l) _____________ (aq) Effects of Acid Precipitation Changes in the pH of water can be __________________ when a rapid snowmelt in the spring releases __________________amounts of acid __________________________________. ____________ changes in the pH of waterways can reduce _________ and ________________ populations dramatically. Food that these animals rely on _________________, and low pH levels have a ___________________ effect on ________________________. Renewing Acidified Lakes One strategy for reversing the effects of acid precipitation is to _________________________________ to neutralize the acid in lakes. _____________________________ involves the application of basic materials, typically __________________________, to renew acidified lakes and regions. Homework Read Pages 229-235 and Answer Q’s 1-4 on Page 235 and Read Pages 236-246 and do Q`s 1,2,4 3 DATE: NAME: CHAPTER 6 Section 6.2 Review (Alternative Format) CLASS: BLM 6-8 1. What is the general pattern in chemical formulas that allows one to determine if a substance is an acid or a base? Provide examples. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is a pH scale and what is the main purpose for its use? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What does pH stand for? _________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Draw a pH scale and place these substances on the scale: baking soda human blood battery acid Milk of Magnesia® bleach tomatoes drain cleaner vinegar gastric juice water 5. Fill in the blanks. a. __________ substances have a pH of less than 7. b. __________ substances have a pH of 7. c. __________ substances have a pH of more than 7. 6. A solution has a pH of 5. Explain how the number of hydroxide ions in the solution compares to the number of hydrogen ions. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 4 7. How much more acidic is a solution with a pH of 4.5 than a solution with a pH of 6.5? Explain. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 8. What is an indicator? List different types of indicators: 3 natural and 3 chemical. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 9. How does a universal indicator differ from other types of indicators? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Use a Venn diagram to compare the properties of acids and bases. Section 6.3 Review (Alternative Format) Use the words below to complete questions 1 through 10. You can use words more than once. salt metals neutralization nitric acid ores increasing limestone OH– water destroyed lowered H2O tailing magnesium hydroxide pH H2SO4 precipitation antacids non-metal oxides heartburn neutralize bases sulfur dioxide 1 double displacement AB gastric BC digestion NO2 hydrogen ions H+ acidic hydrochloric acid 1. An acid reacts with a base to produce ______________________ and ________________________. 2. This type of reaction is called ______________________________. 3. In the reaction (H+) _________________ _________________ combine with (____) hydroxide ions to form (HOH or _________________) water molecules. ________ + OH- → H2O 4. The word neutralization is used because the acid and base properties of H+ and OH- are _________________ or neutralized. 5 5. Neutralization is a type of ___________________ ___________________ reaction where _____ + CD → AD + ______. 6. Neutralization can also occur in the body. Your stomach contains a solution of _________________ _________________ called _________________ juice that has a pH of about _________________. 7. The gastric juice is important to break down food particles during the process of _________________. Too much acid may damage the lining of the stomach and cause pain. A common treatment for _________________ is the use of _________________. They are designed to _________________ the acid because they are _________________ containing (Mg(OH)2) _________________ _________________ and (Al(OH)3) aluminum hydroxide. 8. Acid _________________ forms when _________________ such as nitrogen dioxide (_________________) and _________________ _________________ (SO2) dissolve in water. This reaction creates _________________ solutions such as ________________ _________________ (HNO3) and sulfuric acid (_________________). 9. Acid precipitation damages rivers and lakes because the _________________ of the water source is _________________. Lakes may be renewed by adding _________________ to _________________ the pH of the water. This process helps to _________________ the acid and raise the pH. 10. Acids are used in industry for extracting _________________ such as copper, gold, and nickel from _________________. This process sometimes causes contamination of the _________________ materials. 11. Explain if it is reasonable for a chemist to use the following reaction to produce solid silver. K(s) + Ag(NO3)(aq) _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 6