Unit Flashcards
advertisement

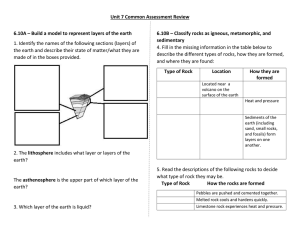
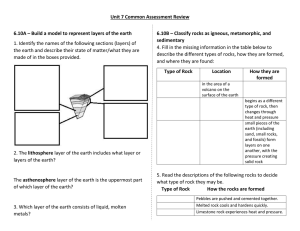
s3o3o4 Earth’s History Flashcards 1 sedimentation 2 accumulation 3 layer 4 deposition 5 relative age 6 absolute age 7 law of superposition 8 intrusion 9 fault 10 law of crosscutting relationships 11 unconformity 12 fold 13 uniformitarianism 14 index fossil 16 inference 17 evidence 19 paleontologist 22 recent 25 seismic wave 15 over turned fold 18 paleontology 20 fossil 21 paleoenvironment 23 volcano 24 earthquake 26 mechanical energy 27 potential mechanical energy 28 heat energy 29 magma chamber 30 plate tectonics 31 lithosphere 32 asthenosphere 33 convection current/cell 34 convergent plate boundary 35 transverse plate boundary 36 divergent plate boundary 37 uplift 38 gradual 39 erosion 41 42 40 rate 43 44 46 47 1 2 The process of The slow piling up small pieces of of sediments into a rocks settling down layer. and being left behind in layers. 4 A synonym for sedimentation. 7 States the oldest rock layer is at the bottom if the rocks have not been disturbed. 5 The age of a rock compared to other rocks. 8 A mass of igneous that cooled inside the earth. 45 48 3 A distinct package of sediments with similar properties. 6 The number of years since a rock formed. 9 A break in the earth’s crust. 11 10 A surface that States that anything represents lots of 12 that cuts across or erosion and A wrinkle, twist, or into something is missing time. Older bend in rock layers. younger than the than the layers on thing it cuts across top of it. or into. 13 States that processes that happen today probably happened in the past. 16 A conclusion based on evidence. 19 A scientist that studies ancient things. 22 The opposite of long ago. 14 Fossils that are widely distributed around the world and are useful in determining the relative age of rock layers. 15 A bend in layers that shows older rocks on top of younger rocks. Formed from extreme pressure. 17 Factual data that cannot be argued. 18 The study of ancient things. 20 Any evidence of a once living organism. 21 An ancient environment. 23 A hill like structure that has a crater at the top where gas, ash, and lava can escape. 24 What is felt on the surface of the Earth after two stuck plates release stored energy. 25 The mechanical wave released from two tectonic plates rupturing. 28 The amount of thermal energy stored in a substance. 31 The hard, outermost , rocky layer of the Earth 26 Energy due to motion. 29 A huge glob-like mass of molten rock inside the earth. 32 The weak, ductile, gooey layer that plates ride on. 35 34 Two tectonic plates Two tectonic plates that slide past each coming together other 37 A process caused 38 by plate tectonics A synonym of that create slowly mountains. 41 40 Layers of How fast or slow sedimentary rocks something should be happens. horizontal unless something has happened to them 27 Mechanical energy that is stored and can be released. 30 The idea that huge plates in the lithosphere float around on the asthenosphere. 33 The cyclic rising and falling of molted rock that makes tectonic plates move. 36 Two plates that move away from each other. 39 The process of removing weathered material 42