Enlightenment
advertisement

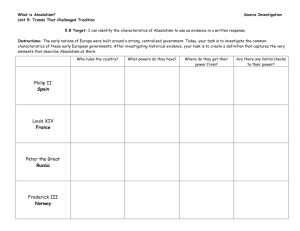
Y4 Enlightenment Lesson 1 Part A Revolution Part B Key questions 1. What was European society like in 1600? 2. Which type of people ruled European societies in 1600 in comparison with 1900? 3. How did parliamentary government differ from rule by “divine monarchs?(pg 90) 4. What were the changes that took place in this periods and what impact did they have outside of Europe? 5. What caused these changes? 6. How were these changes connected? 7. Did the same changes occur in all European countries? Part A Absolutism: Consolidation of power with the monarch, rise of state power and the decreased influence of nobility. Examples: Louis XIII, Louis XIV and Ivan the Terrible. Parliamentarism: < Parliament: national legislative body, normally elected by popular vote. Its role is to pass legislation and keep a check on the activities of the government or executive. In the UK: Parliament is constituted by the House of Lords and the elected House of Commons. (see photocopy) Origins ________________________________________________________ Enlightenment Definition: ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Enlightened Absolutism: Same basic principle as above including rulers’ belief that they held the right to govern by birth and divine right, but rulers followed principles of rationality, religious toleration, freedom of speech and press and encouraged the arts and education. Examples: Holy Roman Emperor Joseph II 1765-1790, Frederick the Great of Prussia 1740-1786. What about Spain? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________