Remediation Unit 3
advertisement

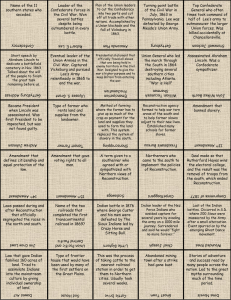
Remediation Unit 3 I. Causes of the Civil War (List the Key Details and Main Effects) a. Wilmot Proviso 1846 i. Details – ii. Effects – Tensions between the North and the South continued to rise. b. Compromise of 1850 i. Details- ii. Effects- For a short time tensions in the country appeared to lessen. c. Kansas-Nebraska Acti. Details- ii. Effects- Thousands of people rushed to Kansas from the North and South, hoping to make it either slave or free; Republican Party forms d. “Bleeding Kansas” 1856 i. Details- ii. Effects- Violence poured over into Congress (Brooks-Sumner Incident); All previous compromises on the question of slavery were becoming ineffective e. Dred Scott v. Sandford 1857 i. Details- ii. Effects- Missouri Compromise unconstitutional; Congress could not restrict slavery in the territories; Northerners became more determined to stop the spread of slavery f. Uncle Tom’s Cabin published by Harriet Beecher Stowe i. Details- ii. Effects- more Northerners firmly oppose slavery g. Election of 1860 i. Detailsii. Effects- South Carolina became the first state to secede from the Union (Dec. 20, 1860) Multiple Choice Questions Causes of the Civil War 1. Which answer best outlines the Wilmot Proviso? a. A proposal to buy part of present day New Mexico b. A proposal to outlaw the spread of slavery into territories gained by the Mexican war c. A proposal to cut off funding for the Mexican War d. A resolution praising heroism of those killed in the raid at Harper’s Ferry 2. What was the main effect of the Dred Scott decision? a. The Supreme Court shocked the nation by ruling that slavery was immoral and unconstitutional. b. The Supreme Court ruled that slaves were not citizens, that they had no rights, and that Congress had no power to halt the spread of slavery. c. Proslavery advocates became discouraged and flocked to the Republican Party. d. Scott was declared a free man. 3. Which part of the Compromise of 1850 received the greatest support from southern farmers? a. the admission of California as a free state b. the passage of a strict fugitive slave law c. the end of the slave trade in Washington, D.C. d. the allowance of popular sovereignty in new territories II. The Civil War (Turning Points, Key Details, and Significance to Outcome) a. First Battle of Bull Run (1861) i. Key Detailsii. Significance – Lincoln prepares for a long conflict b. Battle of Antietam (1862) i. Key Details- General Lee attacked into the Union (Maryland); Union Army defeated Lee and drove Confederate Army back into the South. ii. Significance- c. The Emancipation Proclamation (January 1, 1863) i. Key Detailsii. Significance- gave the war a deeper moral purpose beyond saving the union; allowed free blacks to serve in the Union Army; angered the Confederate States d. Battle of Gettysburg (1863) i. Key Details- ii. Significance- turning point battle of the war; from this point on, Lee and the Confederates were on the defensive e. Grant wins at Vicksburg (1863) i. Key Details- Confederate fort along the Mississippi River surrenders after a long siege ii. Significancef. Sherman’s March to the Sea (1864-1865) i. Key Detailsii. Significance- “Total War”, Sherman fights not only Confederate Army but the people of the South who support the war; adds to the South’s discouragement and anger g. Lee surrenders to Grant at Appomattox Court House (April 9, 1865) i. Key Details- After pursuing Lee for months, Grant’s forces finally trap Lee’s army and force them to surrender. ii. SignificanceMultiple Choice Civil War 1. Which statement best describes “Sherman’s March to the Sea”? a. The battle that defeated New Orleans b. The Union Army’s destruction of wide of a wide area of Georgia and South Carolina c. A symbolic gesture, made to encourage recently freed slaves d. A Confederate attempt to seize Washington D.C. 2. Why can the Emancipation Proclamation be seen as a diplomatic document? a. It made it hard for foreign nations to recognize and support the Confederacy. b. It warned European nations to stay out of affairs in the Western Hemisphere. c. It called on England and France to sell weapons to the Union army. d. It encouraged France to sell the Louisiana Territory to the United States. 2. Which battle was considered the turning point of the Civil War? a. Battle of Bull Run b. Battle of Gettysburg c. Battle of Chancellorsville d. Appomattox Courthouse III. Reconstruction a. Lincoln’s Plan i. Main Pointsii. Why Congress did not like? b. Johnson’s Plan i. Main Pointsii. Why Congress did not like? c. Congressional Reconstruction (Radical Republican Reconstruction) i. Main Pointsii. What was the military’s role? d. The End of Reconstruction i. What ended Reconstruction?ii. What happened to the South after Reconstruction? e. Reconstruction Amendments i. 13th Amendmentii. 14th Amendment iii. 15th Amendment Multiple Choice 1. Which action abolished slavery in the United States? a. suspension of habeas corpus b. passage of the Thirteenth Amendment c. passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1866 d. delivery of the Gettysburg Address 2. Which of these is the strongest evidence of the federal government showing its power over state governments during the Reconstruction period? a. the creation of the sharecropping system b. the migration of carpetbaggers into southern states c. the military occupation of former Confederate states d. the creation of the Freedmen’s Bureau 3. Why did the House of Representatives impeach Andrew Johnson? a. The president refused to follow Lincoln’s Reconstruction plan. b. The president violated the Tenure of Office Act. c. Congress wanted to test the Fifteenth Amendment. d The Supreme Court supported separation of powers.