3.2 Notes ws
advertisement

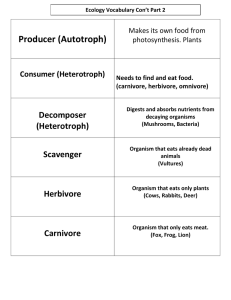
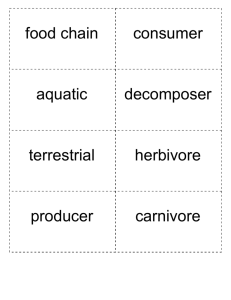
Name Class Date 3.2 Energy, Producers, and Consumers Lesson Objectives Define primary producers. Describe how consumers obtain energy and nutrients. Primary Producers 1. What do autotrophs do during photosynthesis? Consumers 2. Complete the table about types of heterotrophs. Types of Heterotrophs Type Definition Herbivore Examples cows, rabbits Heterotroph that eats animals humans, bears, pigs Omnivore Detritivore Decomposer Heterotroph that consumes the carcasses of dead animals but does not typically kill them itself 3. What is a consumer? 4. How would you categorize a consumer that usually catches and eats prey, but also eats dead animal carcasses? Concept Map The concept map below shows the relationships between different types of organisms in this lesson. decomposer photosynthesis detritivore chemosynthesis heterotroph omnivore herbivore scavenger carnivore primary producer also called autotroph uses solar energy for the process of is ingested by a uses chemical energy for the process of also called a consumer meat-eating plant-eating detritus detritus producing feeding Follow the directions. 5. List each of the terms in the concept map that is a type of consumer. plant & meat-eating