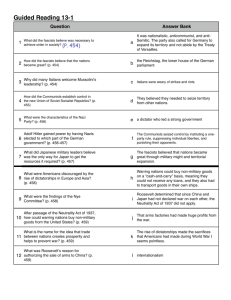
KEY_Glencoe Reading
advertisement
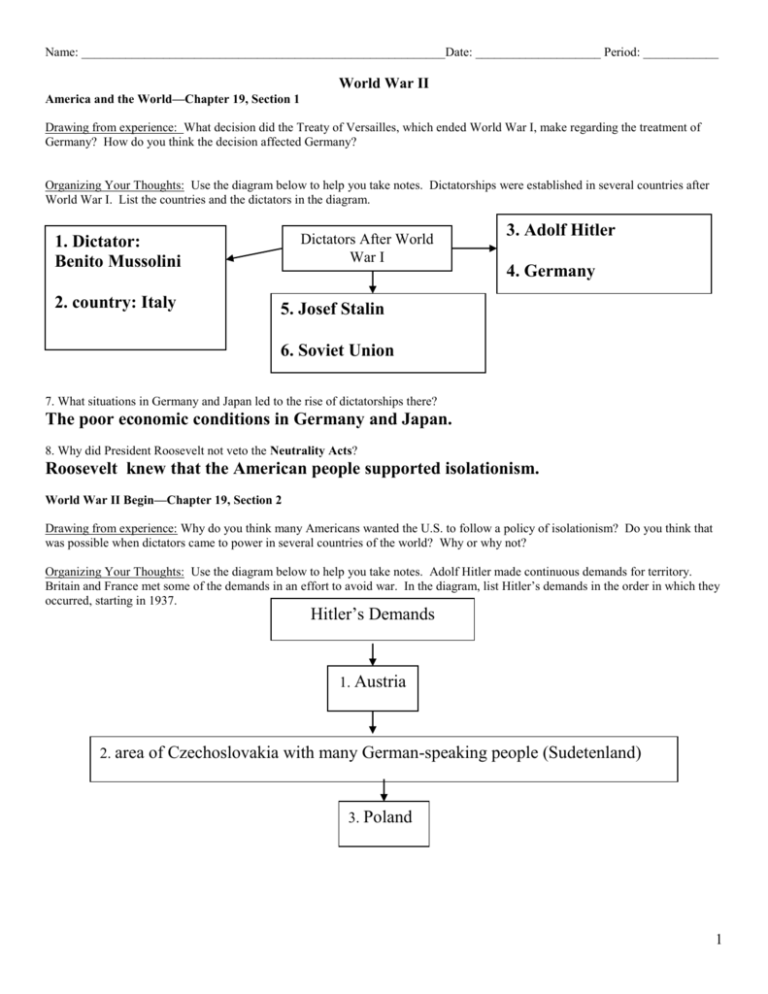
Name: __________________________________________________________Date: ____________________ Period: ____________ World War II America and the World—Chapter 19, Section 1 Drawing from experience: What decision did the Treaty of Versailles, which ended World War I, make regarding the treatment of Germany? How do you think the decision affected Germany? Organizing Your Thoughts: Use the diagram below to help you take notes. Dictatorships were established in several countries after World War I. List the countries and the dictators in the diagram. Dictators After World War I 1. Dictator: Benito Mussolini 2. country: Italy 3. Adolf Hitler 4. Germany 5. Josef Stalin 6. Soviet Union 7. What situations in Germany and Japan led to the rise of dictatorships there? The poor economic conditions in Germany and Japan. 8. Why did President Roosevelt not veto the Neutrality Acts? Roosevelt knew that the American people supported isolationism. World War II Begin—Chapter 19, Section 2 Drawing from experience: Why do you think many Americans wanted the U.S. to follow a policy of isolationism? Do you think that was possible when dictators came to power in several countries of the world? Why or why not? Organizing Your Thoughts: Use the diagram below to help you take notes. Adolf Hitler made continuous demands for territory. Britain and France met some of the demands in an effort to avoid war. In the diagram, list Hitler’s demands in the order in which they occurred, starting in 1937. Hitler’s Demands 1. Austria 2. area of Czechoslovakia with many German-speaking people (Sudetenland) 3. Poland 1 4. Why did Britain and France agree to a policy of appeasement toward Hitler? They hoped that appeasement would avoid war. 5. Why did the evacuation at Dunkirk make it almost impossible for Britain to defend itself against Hitler? --because the British left most of their military equipment in Dunkirk. 6. Why helped Britain prevent a German invasion? The British royal Air Force, with the use of radar, was able to inflict more losses on the Germans than they endured. The Holocaust—Chapter 19, Section 3: Drawing from experience: What is the Holocaust? Have you seen movies or read books about the Holocaust? What was the focus of the movie or the book? Organizing your thoughts: Use the chart below to help you take notes. Historians have considered several factors that could have led to an event such as the Holocaust to occur. List these factors in the chart. Factors that Contributed to the Holocaust 1. German people’s harsh treatment by the treaty that ended World War I. 2. Germany’s severe economic problems 3. the strong hold that Hitler had on Germany 4. the lack of a strong representative government in Germany 5. Germans’ fear of Hitler’s secret police 6. a long history of anti-Jewish prejudice and discrimination in Europe 7. Why was the U.S. reluctant to accept Jewish immigrants? -they were reluctant because laws prohibited immigration by people who might need financial assistance -high unemployment rates in the U.S. made immigration unpopular -immigration quotas limited the number of immigrants that were allowed to come from each country. 8. Why was the purpose of the Wannsee Conference? Nazi leaders called the meeting to decide the “final solution of the Jewish question.” America Enters the War—Chapter 19, Section 4 Drawing from experience: Imagine that you are living in the U.S. in 1940. How do you think you would have felt about the nation becoming involved in the war overseas? Organizing you thoughts: Use the diagram below to help you take notes. President Roosevelt was determined to help Britain while keeping the U.S. neutral. List these ways in the diagram. 2 1. Neutrality Acts were revised 2. Destroyers-for- 3. Lend-Lease Act Ways to Provide Aid to Britain While Remaining Neutral bases agreement with Britain 4. setting up the hemispheric defense zone 5. What did the revised Neutrality Act provide? The revised act allowed countries at war to buy weapons as long as they paid cash and carried the arms away on their own ships. 6. Why did President Roosevelt decide to run for a third term as president? He believed that a change in leadership might not be in the country’s best interest during the war. 7. What was the Lend-Lease Act? It allowed for the U.S. to send weapons to Britain if Britain promised to return or pay rent for them after the war. 8. What led Congress to declare war on Japan? the Japanese attach on Pearl Harbor Mobilizing for War—Chapter 20, Section 1 Drawing from experience: Imagine that you are living in the U.S. on December 7, 1941. How do you think that you would have felt about the war after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor? Organizing your thoughts: Use the diagram below to help you take notes. Even before the attack on Pearl Harbor, the U.S. government mobilized the nation for war. List two ways it did so. Ways of Mobilizing for War the Uproduction .S. Entered the War toBefore wartime 1._Using incentives—the gov’t switched industries 2. It began to build up the nation’s military. 3. What was the effect of the cost-plus system on production? the system helped get things produced quickly. 4. What was the advantage of making welding rather than riveted ships? Welded ships were cheaper and easier to build and harder to sink. 5. How did women’s role in the military change during World War II? -the army enlisted women for the first time, although they were banned from combat -women in the army had administrative and clerical jobs, freeing men for combat -the army, Coast Guard, the navy, and marines set up their own women’s organizations The Early Battles—Chapter 20, Section 2: Drawing from experience: Have you ever seen a movie about World War II? What was the movie about? How did it portray conditions during the war? 3 Organizing your thoughts: Use the chart below to help you take notes. Several battles occurred in the early years of World War II. Explain the result of each of the battles listed in the chart. Battle Battle of Bataan Peninsula Result Battle of Midway 2. stopped Japanese advance in the Pacific Allied invasion of North Africa 3. Germany surrendered North Africa to the Allies Battle of Stalingrad 4. The battle put Germany on the defensive. 1. the Philippines fell to Japn 5. How were Americans able to know about Japanese plans against the U.S. in the Pacific? The U.S. military used code breakers, who alerted it about planned Japanese operations. 6. Why was the Battle of Stalingrad a turning point in the war? The battle put Germany on the defensive for the first time since the war began. Life on the Home Front—Chapter 20, Section 3 Drawing from experience: During WWII, some local governments banned a certain style of dressing. Do you think a government should have the right to do that in certain circumstances? Why do you think so? Organizing your thoughts: Use the diagram below to help you take notes. During WWII, the American people supported the war effort at home. Describe how they did so. 1. rationing (food, gas, Ways Americans Supported the War Effort at Home etc.) 3. buying E bonds 2. planting victory gardens 4. What was the purpose of the Fair Employment Practices Commission? It was set up to enforce the order that banned discrimination in hiring workers in defense industries. 5. How did racism and discrimination affect Japanese Americans during World War II? The loyalty of the Japanese Americans was questioned and the government relocated them to internment camps. 6. Why did the OPA (Office of Price Administration) introduce rationing during World War II? It rationed many consumer products to make sure that there were enough supplies for military use. 4 Pushing the Axis Back—Chapter 20, Section 4: Drawing from experience: Do you know anyone who fought in or lived through WWII? What are their recollections about the battles fought during the war? How did they get information about the war? Organizing your thoughts: Use the chart below to help you take notes. The Allies fought the Axis in Europe and in the Pacific. List the results of the battles that are listed in the chart. Location of Battle Sicily Outcome Normandy 2. American troops broke through Germany defenses. 3. Japan retreated. Leyte Gulf 1. Germany was defeated. 4. What agreements were reached at the conference in Casablanca? Roosevelt and Churchill decided to increase the bombing of Germany and to invade Sicily. 5. What agreements were reached at the conference in Tehran? -Stalin promised to attack the Germans when the Allies invaded France -the Allied leaders agreed that Germany would be broken up after the war -Stalin promised to help the U.S. defeat Japan and the support an international organization to keep peace after the war 6. Why did the invasion of France (Normandy) have to begin at night? to hide the ships carrying the men and equipment across the English Channel from Great Britain 7. How did the geography of the Pacific affect American plans to defeat Japan? Many of the islands of the Pacific were coral reef atolls and the water over them was not always deep enough—as a result, several ships ran aground, causing the troops to wade to shore and become targets for the Japanese. 5 The War Ends—Chapter 20, Section 5: Drawing from experience: What is the United Nations? Do you think the United Nations serves a necessary purpose? Why or why not? Organizing your thoughts: Use the diagram on the next page to take notes. Several events occurred during 1945—the last year of World War II. List the event that occurred on the date shown in each box. 1945 Events February 19 1. U.S. Marines land on Iwo Jima April1 2. American troops land on Okinawa April 12 3. President Roosevelt dies April 25 4. Representatives meet at San Francisco to organize the United Nations May 8 5. V-E Day (Victory in Europe Day)—Germany surrenders August 6 6. atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima August 9 7. atomic bomb dropped on Nagasaki August 15 8. V-J Day—Japan surrenders 9. What was the importance of the Allied victory at the Battle of the Bulge? It left the Germans with very little left (men/equipment) to prevent the Allies from entering Germany. 10. Why did President Truman decide to use the atomic bomb against Japan? Truman wanted to prevent the huge numbers of American casualties that would have resulted from an invasion of Japan. 11. Why did President Roosevelt want to establish an international organization? He wanted to find a way to prevent a future world war. 6