Guided Reading 13-1
advertisement
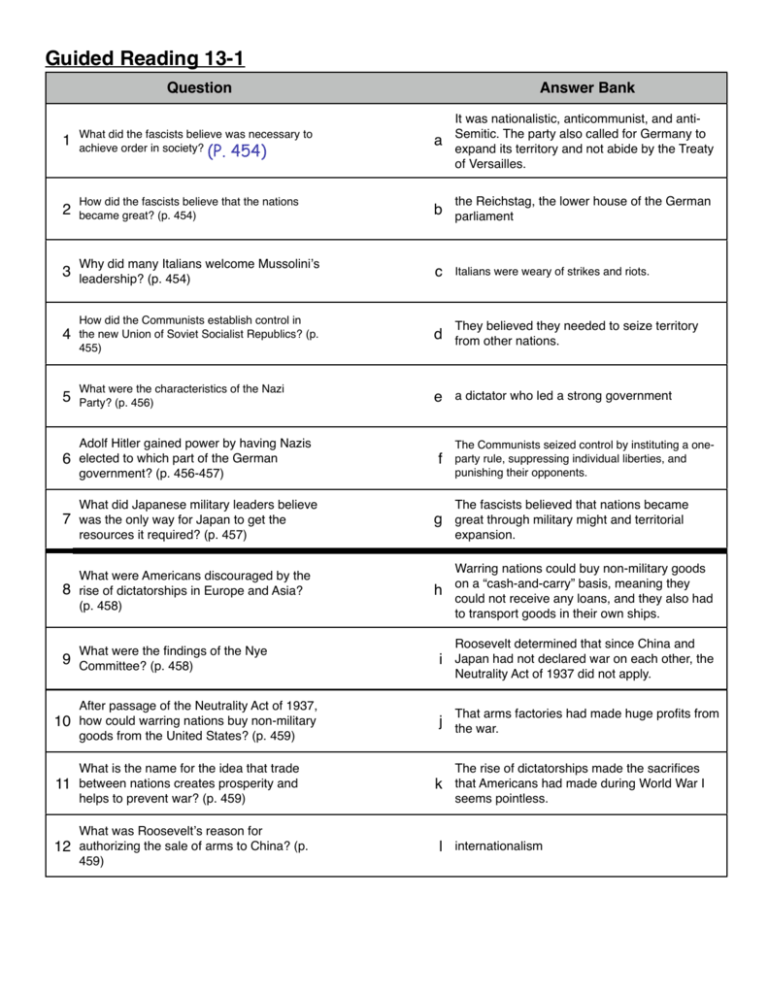
Guided Reading 13-1 Question Answer Bank It was nationalistic, anticommunist, and antiSemitic. The party also called for Germany to expand its territory and not abide by the Treaty of Versailles. 1 What did the fascists believe was necessary to achieve order in society? (P. 454) a 2 How did the fascists believe that the nations became great? (p. 454) b parliament Why did many Italians welcome Mussoliniʼs 3 leadership? (p. 454) the Reichstag, the lower house of the German c Italians were weary of strikes and riots. 4 How did the Communists establish control in the new Union of Soviet Socialist Republics? (p. 455) d from other nations. 5 What were the characteristics of the Nazi Party? (p. 456) e a dictator who led a strong government They believed they needed to seize territory Adolf Hitler gained power by having Nazis 6 elected to which part of the German f government? (p. 456-457) What did Japanese military leaders believe 7 was the only way for Japan to get the 8 The Communists seized control by instituting a oneparty rule, suppressing individual liberties, and punishing their opponents. The fascists believed that nations became g great through military might and territorial resources it required? (p. 457) expansion. What were Americans discouraged by the rise of dictatorships in Europe and Asia? (p. 458) Warring nations could buy non-military goods on a “cash-and-carry” basis, meaning they could not receive any loans, and they also had to transport goods in their own ships. What were the findings of the Nye 9 Committee? (p. 458) After passage of the Neutrality Act of 1937, 10 how could warring nations buy non-military goods from the United States? (p. 459) What is the name for the idea that trade 11 between nations creates prosperity and helps to prevent war? (p. 459) h Roosevelt determined that since China and i Japan had not declared war on each other, the Neutrality Act of 1937 did not apply. That arms factories had made huge profits from j the war. The rise of dictatorships made the sacrifices k that Americans had made during World War I seems pointless. What was Rooseveltʼs reason for 12 authorizing the sale of arms to China? (p. 459) l internationalism p. 466 p. 466 p. 467 p. 468 p. 468 p. 468 p. 469 p. 470 p. 470 p. 470 p. 471 p. 471 WORD BANK a. Nuremberg Laws d. 350,000 g. four dollars j. 1,600,000 (1.6 million) b. 20,000 e. catastrophe h. World War I k. gas chambers c. Cuba; Florida f. Kristallnacht, or "night of broken glass" i. slave laborers l. concentration camps p. 460 p. 461 p. 461 p. 462 p. 462 p. 462 p. 462 p. 462 p. 463 p. 464 p. 464 p. 465 p. 465 p. 465 p. 465 WORD BANK a. capitalist b. blitzkrieg d. unification e. Maginot Line g. army h. Sudetenland j. bravery k. Britain; France m. Battle of Britain o. the Netherlands; Belgium c. radar f. English Channel i. appeasement l. 338,000 n. puppet government ! Guided Reading 13-4 Question Answer Bank It allowed warring countries to buy arms from the 1 How was the Neutrality Act of 1939 different from its earlier version? (p. 474) a United States, but only on a “cash and carry” basis. 2 How did Roosevelt manage to give Churchill the destroyers that he requested? (p. 474) b office. What did Churchill give to Roosevelt for the 3 destroyers instead of cash? (p. 474) 4 How did most Americans feel about Rooseveltʼs destroyers-for-bases deal? (p. 475) 5 What did the Fight for Freedom Committee promote? (p. 475) Who were some of the members of the America 6 First committee? (p. 475) What organization pressed for increased 7 American aid to the Allies, but not armed intervention? (p. 475) was unprecedented about Rooseveltʼs 8 What decision to run for president in 1940? (p. 475) How did Roosevelt get around the cash-and- 9 carry requirement of the Neutrality Act when Britain ran out of funds? (p. 476) What was the purpose of the hemispheric 10 defense zone? (p. 476) What was included in the text of the Atlantic 11 Charter? (p. 477) Which “strategic materials” did Roosevelt refuse 12 to sell to the Japanese? (p. 478) What was the Japanese response to Rooseveltʼs 13 actions? (p. 479) Why did Hitler aid the Japanese after the attack 14 on Pearl Harbor? (p. 479) No previous president had served more than 2 terms in c Hitler hoped that German assistance to the Japanese would lead to Japanʼs support for Germany, and against the Soviet Union. isolationists, including Charles Lindbergh and Senator d Gerald Nye e f the right to build American bases on British-controlled Newfoundland, Bermuda, and British islands in the Caribbean He used a loophole in the Neutrality Act, creating an “exchange” (aka a trade) instead of a “sale.” He created the Lend-Lease Act, which allowed the g United States to send arms to Britain if they promised to return or pay rent for them after the war. h The Committee to Defend America by Aiding the Allies For the United States to protect British supply ships in i the Atlantic, while still remaining neutral. They signed an alliance with Germany and Italy, and j became a member of the Axis Powers. Most Americans accepted it, since they favored k offering limited aid to the Allies. It committed the United States and Britain to a postwar l world of democracy, nonaggression, free trade, economic advancement, and freedom of the seas. the repeal of all neutrality laws and stronger action m against Germany. n airplane fuel, scrap iron ***OK TO USE LETTER ABBREVIATIONS*** A D F B C K H L E G I J ***OK TO USE LETTER ABBREVIATIONS IN CHART*** M