Hints Chaps. 1-2
advertisement

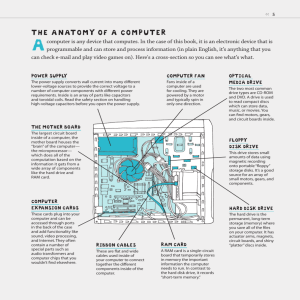
M Elias Hints Chaps. 1-2 michael.elias2@wilkes.edu Analytical Engine – A device planned but never built by Charles Babbage. This device was supposed to solve mathematical problems after being “programmed” such that as long as data sets were entered, the Analytical Engine would grind out answers. In fact, this device was to act similarly to today’s computers, but Babbage was ahead of his time in that although his theory was sound, technology at his time wasn’t sufficient to allow his device to properly function. Bit (b) – A binary digit, the smallest amount of data the hardware can record, represented to humans as a "0 or 1", and as a " or " to show the 2 binary states. BUS – An internal (inside the box) data path between components such as CPU-RAM, RAMhard disk, RAM-monitor port, etc. Byte (B) – A unit of computer storage, 8 bits, needed to normally record 1 character of data. DATA – Raw facts and figures input into a computer system, usually for processing later. Gigahertz (GHz) – Units measuring the processing speed of the CPU in billions per second. This is only one of several overall situations which determine a computer’s overall speed. HARDWARE – Physical pieces of computer equipment, i.e. “the stuff you can kick.” INFORMATION – Processed data output from the computer as answers for us. INTERNET – The numerous paths used to connect a computer with a connection to the Internet to any other computer with a connection to the Internet, i.e., the “superhighway.” Megabytes (MB), Gigabytes (GB), & Terrabytes (TB) – Units of data for memory & storage. NETWORK – The connecting together of 2 or more computers for sharing of data, information, and hardware (such as disk storage and printers). The Wilkes lab computers are networked to each other, as well as to the Wilkes mainframe. An Internet connection is a type of network. Operating System (OS) – Systems software (Windows, etc) which must be present in order for a computer to function. A skeleton version of the full system gets loaded during POST. POST – Power On Self Test, an operation performed every time a computer is started from the off condition (does a “cold boot”). During the POST the computer checks its RAM, checks for all peripherals, and loads a subset of the OS into RAM. RAM – Random Access Memory (volatile), the computer’s workspace or “desktop.” This is a temporary storage area from which the CPU must call data it is processing, If the RAM size isn’t large enough to hold all needed data, then the computer must “page” data by moving what’s in RAM to another spot such as the hard disk while other data is then copied into RAM. The more paging there is, the slower the computer seems to produce answers. ROM – Read Only Memory (non-volatile), usually a “chip” permanently written on containing never-changing data such as how to do a POST and how to load the OS from a hard drive. SOFTWARE – Applications (programs) that instruct the computer hardware in how and when to perform actions such as word processing, spreadsheets, games, music, photo-editing, etc. Thomas J. Watson, Sr. – CEO of IBM who led that company into becoming the largest computer manufacturing company in the world. He was succeeded as IBM’s CEO by his son Thomas J. Watson, Jr. URL (uniform resource locator) – The unique address or location of any one individual site on the Internet, a member of the world wide web. M Elias Hints Chaps. 1-2 michael.elias2@wilkes.edu What Computers Do – Many believe that computers perform but 4 functions, but seem to do many more because of the multitude of ways these four may be combined. They are 1) Receive input 2) Process information 3) Produce output 4) Store information WORLD WIDE WEB (www) – Collection of all computers with a connection to the Internet. These are all the places (sites) one may visit when surfing the ‘net.