Computers and Networks

Software for Personal
Computing
A course overview
1
Goal
• To provide you with the knowledge and skills needed to use computers effectively.
– Learn about Windows XP
– Learn to navigate in a Unix environment
– Use electronic mail
– Work with a word processor
– Work with a web browser
– Work with spreadsheets
– Connect to remote computers
– Transfer files between computers
– Compress and uncompress files
– Search and retrieve files
– Read and compose email messages
2
Computers and their uses
•
Personal Computer (PC)
– Windows XP
–
Unix
– Mac OS
• In this class:
Windows XP
Word Processing
Spreadsheets
Database
Slide Presentations
Telnet and ftp
Drawing Tools
File Compression
Web browser and creating web pages
Unix
Basic usage
3
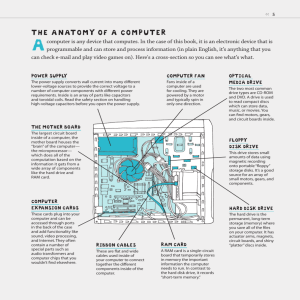
The Main Components of your PC
• Hard Drive
• RAM
• CPU (Central Processing Unit)
– Processor, sort of
• Mouse
• Keyboard
• Monitor
• Software
• Anything else???
4
The Motherboard
• A motherboard is the central or primary circuit board making up a modern computer.
• It is also known as a mainboard , baseboard , system board, or, on Apple computers, a logic board .
• Is to provide the electrical and logical connections by which the other components of the system communicate.
5
The Hard Drive
• This is where every program and file on your computer is stored.
• When you start a program or open a file, that program/file is copied into memory from the hard drive.
• Because all of your files/programs are located on your hard drive, you need to have more storage space than memory.
• Current hard drive sizes are in excess of
200
GB and are growing fast.
6
Random Access Memory (RAM)
• Any data to be processed must be stored in memory rather than on the hard drive.
• This makes access much faster since the RAM can be accessed quicker than the hard drive.
• When you start a program, the program and the data it needs are loaded from the hard drive into memory.
• When a computer does not have enough memory, information must be swapped from RAM to the hard drive, which slows down the computer a great deal.
• You can add additional RAM chips to gain more memory for your PC. A currently acceptable amount of RAM is 1~2 GB .
7
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
• The “brains” of your computer. If you have a 2.8 GHz CPU, then your processor can handle 2.8 billion commands a second.
• One Hertz (Hz) means the frequency of
<some event> is 1/second.
8
Read Only Optical Storage
Media
•
ROM means Read only Memory. Discs labeled as ROM can only be read.
• CD-ROM s can hold about 700 MB, or the equivalent of 486 floppies.
• DVD s (Digital Video Disk) have multiple capacities, ranging from ~5-10 GB.
• BlueRay is gaining popularity, and can store over 50 GB.
9
CDs
• CD players’ read speed is measured with an X, or the number of times greater than 150 Kilobytes per second the speed of the first CD reader. So a
48X reader can read at 150 KB * 48 per second.
• CD-R discs can be written to once. Files deleted from a CD-R before the disc is finalized are NOT deleted. They are simply no longer accessible.
10
DVDs
• High capacity optical or laser disc.
• One layer can hold 4.7 GB of data.
• Most commercial DVDs are dual layer. Each layer can be written to. As a result, dual layer dvds can hold up to
8.5 GB of data, twice as much as a regular DVD.
• DVD-R can be written to just once.
• There are many dual layer burners on the market. They require blank dual layer DVD R discs.
• There are two competing technologies: DVD+R and
DVD-R. Some drives can only read or write one format, although most drives work with both formats.
11
Software
• Software is another name for programs
Instructions that tell the computer how to process data
• Two kinds of software
System software – what the computer uses
Operating Systems
Application software – what you use
12
Personal Operating Systems
Mac OS and Linux
• Mac OS is the operating system for today’s Apple
Computers . Its GUI is similar to Windows, but the differences are large enough that people tend to pick one or the other.
• Linux is an open source operating system. It’s used mostly with high end workstations and network servers.
13
History of Operating Systems
By Microsoft
• Microsoft has been making OS software utilizing graphical user interfaces since around 1985.
– Windows 3.1
– Windows 95
– Windows 98
– Windows ME
– Windows XP
– Windows NT and Windows XP Professional both are personal operating systems when used as stand alone machines but can be considered network operating systems when connected to a network.
14
Windows
• Graphical User Interface (GUI)
– perform tasks by clicking or dragging a mouse
– access programs and documents with the Start button
– related files are grouped in a window
– each program is represented by an icon
– menus and toolbars provided additional functionality
– buttons and scroll bars are used to manipulate a window
• Mouse usage is essential for using Windows!
15
Required Mouse Skills
• Pointing
• Clicking
• Right Clicking
• Double Clicking
• Dragging
• Right Dragging
16
Menu
Windows XP
Minimize button Close button
Maximize/Restore button
Start menu Taskbar
Desktop icon
Disk Drives
Removable Drives
18
Word Processing
• Microsoft Word
– create and edit text
– format text (bold, italics, underline, font, font size)
– orient text on a page (center, left-justified, right-justified)
– bullets, borders and shading
– word wrap
– spell checker
– insert graphical image in document
– tables
– Word Art
19
20
Spreadsheets
• Microsoft Excel
– insert text, numbers, formulas or functions into a cell
– format a range of cells
– place a border around a range of cells
– change text or background color
– copy a formula to a range of cells
– develop a chart from the data
– macros (automate a sequence of keypresses)
21
22
Web Browsers
• Examples
– Internet Explorer
– Mozilla Firefox
– Opera?
• Uses
– view multimedia from the World Wide Web (WWW)
– search and retrieve information
– download software
– download multimedia
23
24
25
Connect to remote computers
(using Telnet)
• Telnet to UNIX
(i.e., unixs.cis.pitt.edu)
• Telnet to VMS
(i.e., vms,cis.pitt.edu)
• Telnet to remote computer
(i.e., archie.rutgers.edu)
26
Connect to UNIX
27
UNIX OS
• UNIX environment
– type a command to perform a task or start a program
– at login, you are sitting in your root directory
– you can move to a different directory
– you can copy or move a file
– you can rename or delete a file
– you can create or remove a directory
– you can create or edit a text file
– you can send email
28
enter a unix command
29
Transfer files between computers
(using FTP)
• WS_FTP or Rapid Filer
– transfer a text file
– transfer a binary file
– change directory
– delete a file
– rename a file
• Smart FTP
30
Transferring Files
31
Electronic Mail
• Client programs (installed on computer)
– MS Outlook
– Mozilla Thunderbird
• Web-based:
– Pitt mail
– Gmail (Google email)
• Uses
• Compose and send a message
• Receive and read a message
•
Send or receive attachments
•
Create your own personal signature
• Save a message
• Insert files into messages
•
Create an address book
•
Delete messages
32
Reading Email
33
Key Terms
• application software
• browser
• chassis
• compact disc (CD)
• computer competency
• computer network
• connectivity
• data
• database file
• database management systems
• desktop computer
• digital versatile (or video) disc (DVD)
34
Key Terms cont.
• document file
• end user
• floppy disk
• handheld computer
• hard disk
• hardware
• information
• information system
• information technology
• input device
• internet
• keyboard
• Hertz
35
Key Terms cont.
• mainframe computer
• memory
• microcomputer
• microprocessor
• midrange computer
• minicomputer
• monitor
• mouse
• notebook computer
• operating system
• optical disk
• output device
• palmtop computer
• people
36
Key Terms cont.
• personal digital assistant (PDA)
• presentation file
• presentation graphics
• primary storage
• printer
• procedures
• program
• random access memory (RAM)
• secondary storage devices
• software
• spreadsheet
• supercomputer
37
Key Terms cont.
• system cabinet
• system software
• system unit
• video display screen
• Web
• wireless revolution
• word processors
• worksheet file
• World Wide Web
(WWW)
38