F. Fundamentals of Financial Management
advertisement

Computer Lab - Practical Question Bank FACULTY OF COMMERCE, OSMANIA UNIVERSITY ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------B.Com (All Streams) III Year W.E.F.2010-11 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Time: 60 Minutes Record : 10 Skill Test : 20 Total Marks : 30 Note: Problems are to be solved by using computers (Excel/Accounting package). 1. If you invest Rs.10,000 in a bank at simple interest of 7% per annum, what will be the amount at the end of three years ? 2. Rs.2,000 is deposited in a bank for two years at simple interest of 6%. How much will be the balance at the end of 2 years ? 3. Find the rate of interest if the amount owed after 6 months is Rs.1,050, borrowed amount being Rs.1,000. 4. Determine the compound interest for an investment of Rs.7,500 at 6% compounded halfyearly. 5. Rs.2,000 is invested at annual rate of interest of 10%. What is the amount after 2 years if the compounding is done. 6. Determine the compound amount and compound interest on Rs.1,000 at 6% compounded semi-annually for 6 years. 7. What annual rate of interest compounded annually doubles an investment in 7 years? Read the following and answer Q.8 to Q.10. *A person opened an account on April, 2005 with a deposit of Rs.800. The account paid 6% interest compounded quarterly. On October 1, 2005 he closed the account and added enough additional money to invest in a 6-month Time Deposit for Rs. 1,000 earning 6 % compounded monthly. 8. How much additional amount did the person invest on October, 1 ? 9. What was the maturity value of his Time Deposit on April 1, 2006 ? 10. How much total interest was earned ? 11. The interest is 10% payable quarterly, find the effective rate of interest. 12. What is the present value of Re.1 to be received after 2 years compounded annually at 10% ? 13. Find the present value of Rs.10,000 to be required after 5 years if the interest rate be 9 per cent. 14. Find out the present value of Rs.2,000 received after in 10 years hence , if discount rate is 8%. 15. What is the present value of Rs.50,000 to be received after 10 years at 10 percent compounded annually. 16. Find the amount of an annuity if payment of Rs.500 is made annually for 7 years at interest rate of 14% compounded annually. 1 17. A person is required to pay four equal annual payments of Rs.5,000 each in his deposit account that pays 8% interest per year. Find out the future value of annuity at the end of 4 years. 18. Rs.200 is invested at the end of each month in an account paying interest 6% per year compounded monthly. What is the amount of this annuity after 10th payment ? 19. Find out the present value of a 4 year annuity of Rs.20,000 discounted at 10 percent. 20. Y bought a TV costing Rs. 13,000 by making a down payment of Rs. 3,000 and agreeing to make equal annual payment for 4 years. How much would be each payment if the interest on unpaid amount to be 14% compounded annually? 21. Determine the present value of Rs. 7,000 each paid at the end of each of the next six years. Assume an 8 percent of interest. 22. Determine the present value of Rs. 700 each paid at the end of each of the next six years. Assume an 8 percent of interest. 23. Ramesh wants to retire and receive Rs. 3,000 a month. He wants to pass this monthly payment to future generations after his death. He can earn an interest of 8% compounded annually. How much will he need to set aside to achieve his perpetuity goal? 24. How much amount is required to be invested every year so as to accumulate Rs. 30,000 at the end of 10 years if the interest is compounded annually at 10%? 25. A makes a deposit of Rs. 10,000 in a bank which pays 10% interest compounded annually for 6 years.You are required to find out the amount to be received after 5 years. 26. Management is considering a Rs. 1,00,000 investment in a project with a 5 year life and no residual value. If the total income from the project is expected to be Rs. 60,000 and recognition is given to the effect of straight line depreciation on the investment. What is average rate of return? 27. Assume cash outflow equals Rs. 1,20,000 followed by cash inflows of Rs. 25,000 per year for 8 years and a cost of capital of 11%. What is the Net present value? 28. What is the internal rate of return for a project having cash flows of Rs. 40,000 per year for 10 years and a cost of Rs. 2,26,009? 29. You are required to calculate the total present value of inflow at rate of discount of 12% of following data. Year end Cash inflows: Rs.2,30,000; Rs.2,28,000; Rs.2,78,000; Rs.2,83,000; Rs.2,73,000; Rs.80,000 (scrap value). 30. A company issued 10,000 10% debentures of Rs.100 each on 1.4.2006 to be matured on 1.4.2011. If the market price of debentures is Rs.80, compute the cost of debt assuming 35% tax rate. 31. Five years ago, Sona Limited issued 12 per cent irredeemable debentures at Rs.103, a Rs.3 premium to their par value of Rs.100. The current market price of these debentures is Rs.94. If the company pays corporate tax at a rate of 35 per cent what is its current cost of debenture capital. 32. XYZ & Co. issues 2,000 10% preference shares of Rs.100 each at Rs.95 each. Calculate the cost of preference shares. 33. A company has paid dividend of Rs.1 per share (of face value of Rs.10 each) last year and it is expected to grow @ 10% next year. Calculate the cost of equity if the market price of share is Rs.55. 34. 35. ABC Company provides the following details: Do=Rs.4.19 Po=Rs.50 G=5% Calculate the cost of retained earnings based on DCF method. 2 36. Amar Ltd. Provides the following details: Rf=7% b=1.20 Rm-Rf=6% Calculate the cost of retained earnings based on CAPM method. 36. A person is required to pay four equal annual payments of Rs.4,000 each in his Deposit account that pays 10 per cent interest per year. Find out the future value of annuity at the end of 4 years. 37. A company issues Rs.10,00,000 12% debentures of Rs.100 each. The debentures are redeemable after the expiry of fixed period of 7 years. The Company is in 35% tax bracket. Calculate the cost of debt after tax. 38. Consider the following information for Strong Ltd: EBIT Rs.1,120 lakh PBT Rs. 320 lakh Fixed cost Rs. 700 lakh Calculate the percentage of change in earnings per share, if sales increased by 5 per cent. 39. Consider the following information for Omega Ltd: Rs. In lakhs EBIT (Earnings before Interest and Tax) 15,750 EBT (Earnings before Tax) 7,000 Fixed Operating costs: 1,575 Calculate percentage change in earnings per share, if sales increase by 5%. 40. Sudha Ltd is expecting annual earnings before the payment of interest and tax of Rs.2 lacs. The company in its capital structure has Rs.8 lacks in 10% debentures. The cost of equity or capitalisation rate is 12.5%. You are required to calculate the value of firm according to NI Approach. Also compute the overall cost of capital. 41. Radha Ltd is expecting annual earnings before the payment of interest and tax of Rs.2 lacs. The company in its capital structure has Rs.10 lacks in 10% debentures. The cost of equity or capitalisation rate is 12.5%. You are required to calculate the value of firm according to NI Approach. Also compute the overall cost of capital. 42. XYZ Ltd. Sells 2000 units @ Rs. 10 per unit. The variable cost of production is Rs. 7 and fixed cost is Rs. 1000. The company raised the required funds by issue of 100, 10% debentures @ Rs. 100 each and 2000 equity shares @ Rs. 10 per share. The sales of XYZ Ltd. Is expected to increase by 20%. Assume tax rate of company is 50%. You are required to calculate the impact of increase in sales on earning per share. 43. A publishing house purchases 72,000 rims of a special type paper per annum at cost Rs. 90 per rim. Ordering cost per order is Rs. 500 and the carrying cost is 5 percent per year of the inventory cost. Normal lead time is 20 days and safety stock is NIL. Assume 300 working days in a year: You are required to calculate the Economic Order Quantity(E.O.Q). 44. A publishing house purchases 72,000 rims of a special type paper per annum at cost Rs. 90 per rim. Ordering cost per order is Rs. 500 and the carrying cost is 5 percent per year of the inventory cost. Normal lead time is 20 days and safety stock is NIL. Assume 300 working days in a year: You are required to calculate the Reorder Inventory Level. 45. A firm is considering offering 30-day credit to its customers. The film likes to charge them an annualized rate of 24%. The firm wants to structure the credit in terms of a cash discount for immediate payment. How much would the discount rate have to be? 3 46. Modi vanaspathi Ltd. Is capitalised with Rs.10,00,000 divided into 1,00,000 equity shares of Rs.10 each. The management wishes to raise another Rs.10,00,000 for the financing of a major expansion programme. The management may finance with (i)all equity shares,(ii) Rs.5,00,000 by equity shares and Rs.5,00,000 by 5% debentures, (iii) all by 6% debentures. The company’s existing earnings before interest and taxes amounted to Rs.1,20,000. Its is expected that the company will maintain its same rate of return after the expansion programme. Tax rate is assumed to be 50% . Calculate earnings on equity shares under the above proposal (i), (ii) and (iii). 47. The capital employed in a business is: Capital Rs.6,00,000; Net working capital Rs.4,00,000 Total: Rs.10,00,000. This has been finance by Equity share capital Rs.3,00,000; Reserves Rs.1,00,000; 6% Debentures Rs.4,00,000; 7% Preference share capital Rs.2,00,000; The company earned a profit of Rs.2,00,000 before interest and tax whose tax rate is 50%. Work out gearing ratio. 48. The total capitalisation of Gupta Steels Ltd; is Rs.40,00,000 and its alternatives are given below: Alternatives I II III IV Equity Share Capital Rs. 25,00,000 27,00,000 31,00,000 38,00,000 8% Prefer.Shares 5,00,000 7,00,000 7,00,000 2,00,000 10% Debentures 10,00,000 6,00,000 2,00,000 --The company earns before interest and tax Rs.8,00,0000 and rate of tax is 50%. Calculate the normal rate of return, capital gearing ration and income percentage to equity shareholders. 49. Draw a chart showing the factors influencing dividend policy of a company. 50. Present Operating Cycle for working capital of an organisation. ***** 4

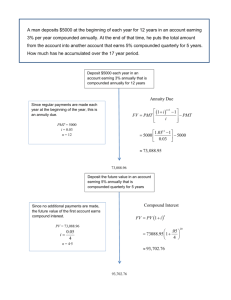




![Practice Quiz Compound Interest [with answers]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008331665_1-e5f9ad7c540d78db3115f167e25be91a-300x300.png)
