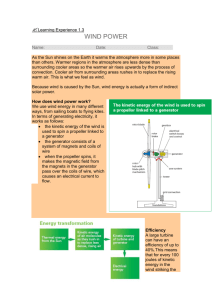
Electronics and Windmills Part 1
advertisement

Electronics and Windmills Part 2: Harnessing the Wind Objective(s): 1. Students should describe the factors that cause the wind to blow. 2. Students should identify and describe the differences between renewable and nonrenewable natural resources. 3. Students should describe a relationship between electromagnets and electric motors. 4. Students should describe how a turbine (as in a wind turbine) can generate electricity. Standard(s): National Science Standards: Grades 5-8 INT-A: 2.a. Different kinds of questions require different kinds of scientific investigations, including observing and describing, collecting, experimentation, research, discovery, and making models. INT-E: 1.a. Identify appropriate problems for technological design. INT-E: 1.b. Design a solution or product. INT-E: 1.c. Implement a proposed design. INT-E: 1.d. Evaluate completed technological designs or products. INT-E: 1.e. Communicate the process of technological design. Illinois State Learning Standards – Science 11.A.2a Formulate questions on a specific science topic and choose the steps needed to answer the questions. 11.A.3b Conduct scientific experiments that control all but one variable. 11.A.4b Conduct controlled experiments or simulations to test hypotheses. 11.A.3c Collect and record data accurately using consistent measuring and recording techniques and media. 11.A.4c Collect, organize and analyze data accurately and precisely. YAAYS 2008 - Star Energy to Earth Yerkes Astrophysics Academy for Young Scientists Page 1 of 8 11.B.2a Identify a design problem and propose possible solutions. 11.B.3a Identify an actual design problem and establish criteria for determining the success of a solution. 12.C.1a Identify and compare sources of energy (e.g., batteries, the sun). 12.C.2a Describe and compare types of energy including light, heat, sound, electrical and mechanical. 12.E.2a Identify and explain natural cycles of the Earth’s land, water and atmospheric systems (e.g., rock cycle, water cycle, weather patterns). 13.A.3c Explain what is similar and different about observational and experimental investigations. 13.A.4c Describe how scientific knowledge, explanations and technological designs may change with new information over time (e.g., the understanding of DNA, the design of computers). 13.A.4d Explain how peer review helps to assure the accurate use of data and improves the scientific process. 13.B.3e Identify advantages and disadvantages of natural resource conservation and management programs. Anticipatory Set: In Electronics and Windmills Part 1, students created electrical circuits. They discussed the differences between series and parallel circuits and saw the use of resistors. Students should be able to explain that electricity is a flow of electrons but that flow needs a power source to push that flow. Instructional Strategies, Methods, Activities: 1. Begin session with a review of circuits. Draw 4 sample circuits on the board with only one that is correct. Have students volunteer to describe why each one is either correct or incorrect. Include in this discussion a sample light bulb circuit and have a student draw lines to represent wires to complete the circuit correctly. YAAYS 2008 - Star Energy to Earth Yerkes Astrophysics Academy for Young Scientists Page 2 of 8 2. Students should be directed to create an electromagnet. Students will place a D cell battery in the battery holder. Then, a wire should be connected to one terminal of the battery holder. The rest of the wire should be wrapped around a nail 20 times and the end of the wire should be connected to the other terminal of the battery holder. Students should test the strength of their electromagnet by counting the number of washers or paper clips the electromagnet will pick up. The students should test the strength of the electromagnets by increasing the number of times the wire is wrapped around the nail. Students should compare the original 20 wraps with 30 and 40 wraps of the wire around the nail and report their results of the number of objects held by the electromagnet. YAAYS 2008 - Star Energy to Earth Yerkes Astrophysics Academy for Young Scientists Page 3 of 8 3. Review with the students that a coiled wire spinning around a magnet or a magnet spinning around a coiled wire generates electricity which generates a movement of electrons. This is how electric motors work and how electricity can be generated. 4. Electricity needs a power source. A review of energy sources is conducted. The list generated should include renewable resources such as wood, solar (sun), wind and moving water and nonrenewable resources such as coal, oil, and natural gas (fossil fuels). Students should be able to explain the reasons and caveats of why each source is renewable or nonrenewable. 5. The discussion turns to wind power and what causes the wind to blow. A diagram on the board shows how the sun heats the earth unevenly creating areas that are warm creating warm air currents that rise and areas that are cooler where the cool air sinks. The warm air rises because it is less dense and the cool air sinks because it is more dense. The movement of air parallel to the ground is the resulting wind. YAAYS 2008 - Star Energy to Earth Yerkes Astrophysics Academy for Young Scientists Page 4 of 8 This can be demonstrated with a convection chamber. It should be reminded that the main source of this movement of air is the Sun. 6. A demonstration of a wind turbine is conducted. First, the formula for power generated by the turbine is explained. The formula is: Power = ½ ρ π r2 v3 where ρ = density of the air (rho) r = radius of the blade area v = wind velocity YAAYS 2008 - Star Energy to Earth Yerkes Astrophysics Academy for Young Scientists Page 5 of 8 A multimeter is then connected to the wires from the turbine and a box fan is started to move the blades. The experimentation that follows adjusts the variables of speed of fan, pitch of turbine blades, number of blades, and the size of blades. The result should show that there is an optimal amount of blades and pitch of blades to generate the highest voltage. A small Christmas tree light bulb is then attached to the turbine clips to demonstrate that the current is strong enough to light the light bulb. YAAYS 2008 - Star Energy to Earth Yerkes Astrophysics Academy for Young Scientists Page 6 of 8 Assessment: Students should be able to diagram the workings of a complete light bulb circuit, an electromagnet, and the flow of air to create wind. Students should be able to recognize how energy sources are either renewable or nonrenewable. Vocabulary Terms: battery, filament, tungsten, electricity, magnetism, conductor, insulator, renewable resource, nonrenewable resource, electromagnet, parallel circuit, series circuit, turbine Resources: KidWind Project (source to purchase wind turbine kit and more). http://www.kidwind.org/ Building the Basic PVC Wind Turbine – site includes a pdf file for basics on the pvc wind turbine http://www.eere.energy.gov/education/lessonplans/plan.cfm/lpid=291 Electronic Snap Kits (we used the Electronics 202 Snap-Kit Model: 28-287, Catalog #: 28-287) http://www.radioshack.com/sm-electronics-202-snap-kit--pi-2102915.html Convection of Gas Apparatus http://www.fishersci.com/ Catalog number: S41795 Wind Power Project Curriculum from the Mathematics, Science and Technology Education (MSTE), University of Illinois. http://www.mste.uiuc.edu/projects/wind/ Wind – a kid friendly site that illustrates the basics of winds. http://www.weatherwizkids.com/wind1.htm Wind – Dan’s Wild Weather. http://www.wildwildweather.com/wind.htm Wind Power. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wind_power How a Wind Turbine Works. http://www1.eere.energy.gov/windandhydro/wind_how.html Modern Marvels: Magnets (DVD) From everyday products to cutting-edge laboratories, see how magnetic attraction shapes the world. http://store.aetv.com YAAYS 2008 - Star Energy to Earth Yerkes Astrophysics Academy for Young Scientists Page 7 of 8 Pod’s Mission – Circuit Breaker A fun interactive assessment tool for circuits http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/podsmission/electricity/annie03.shtml# Wind Power – good graphic for the pieces and parts inside a turbine http://www.powerhousekids.com/stellent2/groups/public/documents/pub/phk_ee_re_001 502.hcsp Wind Power Online Wind Quiz http://www.powerhousekids.com/stellent2/groups/public/documents/pub/phk_fg_og_002 656.hcsp#P-4_0 YAAYS 2008 - Star Energy to Earth Yerkes Astrophysics Academy for Young Scientists Page 8 of 8