COURSE TITLE
advertisement

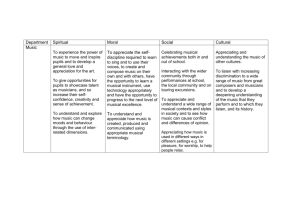
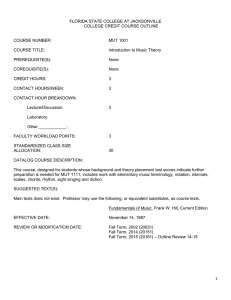
MUSIC THEORY 2009-2010 CURRICULUM COURSE DESCRIPTION Students taking this course develop skills in the analysis of music and theoretical concepts. Students: (1) develop ear training and dictation skills, (2) compose works that illustrate mastered concepts, (3) understand choral and harmonic structures and analysis, (4) understand modes and scales, (5) study a wide variety of musical styles, (6) study traditional and nontraditional music notation and sound sources as tools for musical composition, and (7) receive detailed instruction in other basic elements of music. Students have the opportunity to experience live performances, by professionals, during and outside of the school day. COURSE OBJECTIVES 1. Develop ear training and dictation skills 2. Compose works that illustrate mastered concepts 3. Understand choral and harmonic structures and analysis 4. Understand modes and scales 5. Study a wide variety of musical styles 6. Study traditional and nontraditional music notation and sound sources as tools for musical composition 7. Receive detailed instruction in other basic elements of music ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What are the mechanics of music? What is the Western Civilization scale and notation system? INDIANA STATE STANDARDS DESIRED RESULTS Students will be able to: H.2.1 Play melodic, rhythmic, and harmonic patterns on keyboard, percussion, or other instruments. H.2.2 Play simple melodies and accompaniments that use primary chord progressions. H.4.1 Compose simple melodies that demonstrate the principles of unity, variety, repetition, contrast, form, and melodic contour. H.4.2 Arrange music for different instruments or voices than originally written including transposing instruments. H.5.1 Follow traditional and non-standard notation in musical scores while listening to aural examples. H.5.2 Identify symbols found in a musical score. H.6.2 Use correct terminology when describing musical events, musical devices, or instruments used within an example from a musical work. H.6.4 Use correct terminology to identify elements and compositional devices in aural examples such as form, texture, meter, cadences, harmonic progressions, non-harmonic tones, and key changes. H.8.1 Identify concepts and terms used in the creative process in music and compare their use in other disciplines. KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS Western Civilization scale system, Intervals, Chord Structure, Part-writing, Dictation APPLICATIONS OF TECHNOLOGY www.musictheory.net, Smart music program, audio recordings UNITS OF INSTRUCTION (STATE STANDARDS) Basic Elements – Standard 2 Intervals – Standard 2, 4 Scales – Standard 2, 4, 5 Meters – Standard 2, 4, 5 Triads and Chords – Standards 2, 4, 5, 6 Cadences – Standards 2, 4, 5, 6, Arranging and Composing – Standards 2, 4, 5, 6, 8 COURSE ASSESSMENTS WRITTEN TESTS AND QUIZZES TIMELINE Week 1 – basic elements of music notation Week 2 – intervals Week 3 – major scales Week 4 – minor scales Week 5 – rhythms and meters Week 6 - triads Week 7 - triads Week 8 – chords Week 9 - chords Week 10 – cadences Week 11 – arranging for other instruments Week 12 – composing and review COURSE MATERIALS: MAJOR TEXTS, PRINCIPAL MATERIALS AND FILMS KEY TEXTS: Master Theory Workbook, Theoretical Foundations of Music, and Church Hymnals SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS: Choral anthems, Function chorales