NAME: Fill-in-the-Blank Word Bank Ecology Food Web Population
advertisement

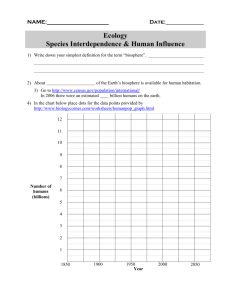
NAME: ________________________________ Fill-in-the-Blank Word Bank Ecology Food Web Population Biomass Ecosystem Transpiration Biosphere Community Nutrient Species Evaporation Food Chain Autotroph Consumer Organism (Some words many be used more than once or not at all.) 1. Species a group of organisms so similar to one another that they fertile offspring. Biome Trophic Level Limiting Nutrient can breed and produce 2. Community assemblages of different populations that live together in a defined area. 3. Food Chain a series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten. 4. Biomass the total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level. 5. Nutrient all the chemical substances that an organism needs to sustain life. 6. Evaporation process by which water changes from a liquid form to an atmospheric gas. 7. Ecosystem a collection of all the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving, or physical, environment. 8. Food Web feeding relationships among the various organisms in an ecosystem form a network of complex interactions. 9. Ecology the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings. 10. Population groups of individuals that belong to the same species and in the same area. 11. Biosphere contains the combined portions of the planet in which all of life exists, including land, water, and air, or atmosphere. 12. Trophic Level each step in a food chain or food web. 13. Biome a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities. Multiple Choice ,True/False, Short Answer (Circle the ENTIRE answer, NOT JUST THE LETTER) 14. What are the three fundamental approaches ecological researchers use to study the living world? a. b. c. d. e. f. Observing Experimenting Modeling All the above None of the above Only a and b 15. True or False: Organisms and their environment are not interdependent of each other? a. True b. False 16. The study of ecology ranges from the study of individual organisms to populations, communities, ecosystems, biomes, and finally entire ecosystems. The picture below is of levels of organization, Write the level next to the appropriate letter? (Community, Biosphere, Population, Ecosystem, Individual, and Biome) A. Individual B. Population C. Community D. Ecosystem E. Biome F. Biosphere 17. What is the main energy source for life on Earth? a. b. c. d. Water Air/Atmosphere Sunlight Food 18. True or False: Matter can cycle through the biosphere because biological systems do not use up matter, they transform it? a. True b. False 19. An Autotroph is defined as an organism that captures energy from the sunlight or chemicals and uses that energy to produce food. What is another name for an Autotroph? a. b. c. d. Consumer Producer Decomposer Parasite 20. What is the difference between Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis? Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis are processes both used by autotrophs. The difference is photosynthesis uses light energy to power chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and energy-rich carbohydrates such as sugars and starches. And with Chemosynthesis autotrophs rely on energy within the chemical bonds of inorganic molecules such as hydrogen sulfide to produce energy. 21. Food chains show the one-way flow of energy. Put the food chain in the appropriate order of energy flow? a. b. c. d. Algae Small Fish Zooplankton Shark Squid Zooplankton Small Fish Algae Shark Squid Algae Zooplankton Small Fish Squid Shark Algae Zooplankton Small Fish Shark Squid 22. True or False: The Carbon Cycle, Nitrogen Cycle, and Phosphorus Cycle are three examples of biogeochemical cycles? a. True b. False 23. Below is a picture of the water cycle, correctly place the appropriate words to complete the cycle in the correct order? (Evaporation, Transpiration, Precipitation, Condensation (use twice), Surface Runoff) A. Condensation C. Precipitation B. Transpiration D. Surface Runoff E. Condensation F. Evaporation 24. What are the three types of ecological pyramids? Energy Pyramid Biomass Pyramid Pyramid of Numbers 25. The process where nitrogen is converted into ammonia is known as? a. b. c. d. Nitrogen fixation Denitrification Decomposition None of the above 26. Heterotrophs otherwise known as consumers are organisms that rely on other organisms for their energy and food supply. There are five different types of heterotrophs write the correct type of heterotroph next to the animal’s picture? and also state what that organism eats. Herbivore — Only Plants Omnivore – Both Plants and Animals Decomposer – Breaks down organic matter Carnivore – Only Animals Detritivore – Plant and Animal remains and other dead matter. 27. True or False: There are four main types of processes that move carbon through its cycle? a. True b. False Essay 28. With the animals listed below draw a simple food web? (Do not have to use all animals, but must have at least 6 steps)? Extra points for any food web that is 9 or more steps, must be correct though. Algae (diatoms), Zooplankton, Blue gill, Largemouth Bass, Great Blue Heron, Bullfrog, Mallard Duck, Grasshopper, Grass, Red-Winged Blackbird, Eastern Water Snake, Field Mouse, Bald Eagle. 29. The graph above shows the relationship between the wolf and moose population on Isle Royale. Looking at the graph especially between the years of 1970 to 1990, tell me what is the relationship between the wolves and the moose? (Meaning tell me why does one go down causing the other to go down, and also why does one go up while the other continues to go down) And what does it mean when the lines are almost parallel to do other? (Like around 1982). Also what is it called when one population is decreasing causing the other to decrease too? When you look at the graph you will see a decrease in the population of the moose, which leads to some of the wolves to starve to death causing their population to decrease too. You will see that the moose population slowly starts to increase while the wolf population is still decreasing, because there are still not enough moose to feed a growing population wolves causing some of them to still starve. Finally if the lines are pretty much parallel the populations are at an equilibrium which means the same number of wolves and moose are dying every year, causing the populations to stay in check. When the moose are decreasing causing the wolf population to decrease the moose would be a Limiting Nutrient Bonus Question: 30. What is the goal of NASA’s Sea-viewing Wide Field-of-view Sensor (SeaWiFS) Project? The project’s goal is to study factors that affect global change and to assess the ocean’s role in the global carbon cycle, as well as other chemical cycles.