Geog3.1 key
advertisement

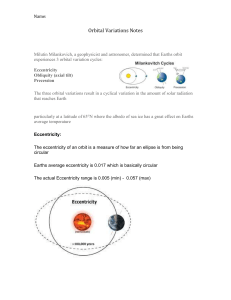
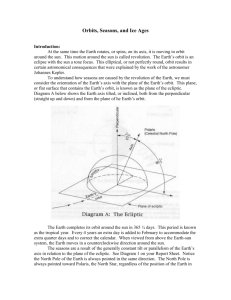
Geography 12 Worksheet 3.1 Chapter 3 Objectives: The Earth In Motion Read pages 38 – 43 of Planet Earth: A Physical Geography. Answer the following questions: Vocabulary (1 mark each) /21 Revolution: the earth orbiting the sun Aphelion: the point in the orbit of the earth where it is farthest from the sun Perihelion: the point in the orbit of the earth where it is closet to the sun Describe the major motions withing the universe Describe the different motions of the earth in space Identify the effects of these motions on the physical geography of the planet Relate to rotation of the earth to the need for time zones Begin to appreciate the interrelationships between the various physical processes and systems operating on the earth Precession of the Equinoxes: means that the position of the equinoxes is changing slowly with respect to the background stars Eccentricity: the measure of the elliptical orbit of the earth Equinoxes: the two times each year when the sun shines equally on both northern and southern hemispheres (spring and autumn) Solstice: the time each year when the sun shines directly over the Tropic of Cancer or the Tropic of Capricorn (summer in the North, summer in the south) Short Answer (2 marks each) 1. Describe the Earth’s place in the Milky Way in terms of distance from the galactic center. How long would it take a person to travel to the center of the galaxy if they could travel at the speed of light, assuming the distance is 25,000 light years away? How many kilometers would that person have traveled?(one light-year is equal to 9,500,000,000,000 kilometers) - 25000 years to travel the distance - 9,500,000,000,000 * 25,000 = 237,500,000,000,000,000 kms 2. When is the earth at it’s aphelion? ___January 3 When is the earth at it’s perihelion?___July 4 3. Explain how the earth experiences eccentricity of its orbit around the sun and what effect it has on the solar heating of the earth. Over 100,000 years, the earth’s orbit changes from more circular to more elliptical and back again. When the orbit is more circular, the solar heating is more evenly spread over the earth (less contrast in temperature) 4. Briefly describe why we have more distinct seasons in Canada compared with lower latitude places such as Mexico. Due to the earth’s axis, we experience less sun(and less concentrated sunshine) in the winter than Mexico and therefore more distinct seasons. 5. What is the “wobble” and how does the “wobble” in the axis affect seasonal temperatures? The earth’s angle of tilt from the plane of the elliptic varies from 21.5 to 24.5 degrees over the course of about 40,000 years. When the tilt is greatest, the earth’s winters are coldest and summers are hottest. When the tilt is less, there is less difference between summer and winter. 6. (4 marks) a. Draw a simple sketch map to show the area of the northern hemisphere that can be called the “land of the midnight sun”. b. Explain why this area can boast of such a phenomenon. c. Why des this phenomenon help explain the great contrasts in temperature between winter and summer at such high latitudes? d. Copy and paste a promotion from the internet from a city, town or company that uses the “land of the midnight sun” to attract tourists or business.