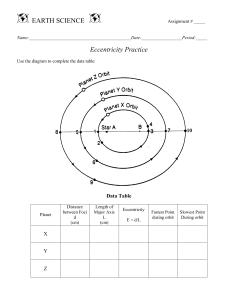
Name: Orbital Variations Notes Milutin Milankovich, a geophysicist and astronomer, determined that Earths orbit experiences 3 orbital variation cycles: Eccentricity Obliquity (axial tilt) Precession The three orbital variations result in a cyclical variation in the amount of solar radiation that reaches Earth particularly at a latitude of 65°N where the albedo of sea ice has a great effect on Earths average temperature Eccentricity: The eccentricity of an orbit is a measure of how far an ellipse is from being circular Earths average eccentricity is 0.017 which is basically circular The actual Eccentricity range is 0.005 (min) - 0.057 (max) Name: Changes in eccentricity results in a smaller or greater difference in distance to the aphelion and perihelion of Earths orbit, thus resulting in changes to the amount of solar radiation Earth receives at these points. Perihelion is when Earth is closest to the sun Aphelion is when the Earth is farthest from the sun Less eccentric orbit= less climate variation throughout the year More eccentric orbit= more climate variation throughout the year The eccentricity cycle lasts 100,000 year cycle because of gravitational pull by other planets as they orbit Obliquity Obliquity: The tilt of the axis relative to the plane of orbit. Insolation: the amount of solar radiation reaching a given area. Angle of Insolation: angle at which sunlight hits Earths surface- from 0° (indirect) to 90° (direct) Name: Earth’s current tilt is at 23.5° Causes more direct sunlight in summer (higher angle of insolation) and less direct sunlight in winter (lower angle of insolation) Least tilt (21.5°) results in Less extreme seasonal differences Most tilt (24.5°) results in More extreme seasonal differences The Obliquity Cycle lasts about 40,000 years Prcession ( aka Wobble) Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. Each processional change happens on a 25,920 year cycle. Name: Natural Climate Changes Earth’s climate cycles through glacial and interglacial periods approximately every 100,000 years because of the combined changes in eccentricity, obliquity, and precession and the resulting effect on insolation Glacial period= ice age Interglacial period= warm period We are currently in an interglacial period Along with milankovich cycles, climate is also further complicated by Changes in precipitation, rate of melting/evaporation, cloud cover, variations in greenhouse gases, vegetation, and sea level.