Earth Science
advertisement

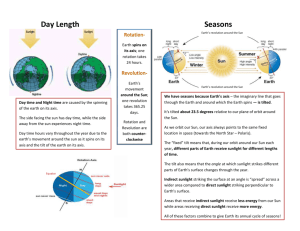
Earth Science Chapter 19 Section 1 A. Days and Years: The study of the moon, stars and other objects in space is called Astronomy. Motions of the Earth: Earth - Sun Relationships: - The Earth intercepts only a minute percentage of the suns energy - less than 1/2000000000 ( one two-billionth ) - Solar radiation represents 99.9% of the energy that heats the Earth - Solar energy is not distributed equally over the Earth's land and sea surfaces - This unequal heating drives the ocean's currents and creates winds that transport heat from the tropics to the poles in an attempt to reach an energy balance Motions of the Earth: The Earth travels around the sun in a path called an orbit. The Earth has two principle motions in it’s orbit: 1. Rotation = The spinning of the earth about its axis, (an imaginary line running through the poles) Our planet rotates once every 24 hours producing the daily cycle of daylight and darkness. (one day) 2. Revolution = The movement of the earth in its orbit around the sun once every 365 1/4 days. (one year) The earth travels at a speed of 113,000 Km/hour in it’s orbit. - The distance between the sun and earth is about 150 million Km (93 million miles) - Because the earth's orbit is not perfectly circular, the distance between the earth and the sun varies during the course of the year. - Each year on about January 3rd, our planet is about 147 million Km from the sun, closer than any other time of the year. This position is called Perihelion. - 6 months later, on July 4th, our planet is about 152 million Km from the sun, farther away than any other time of the year. This position is called Aphelion. - Calendars based on a 365 ¼ day Earth orbit with a leap year of 366 days every 4th year or orbit. B. The Seasons on Earth: -We have seasons because the sun strikes the earth's surface at different angles and distances at different times of the year. The earth is tilted at 23 1/2 degrees on its axis from the perpendicular elliptical plane of the axis. This is termed "Inclination of the Axis" - On June 21 or 22 the earth is in a position where the axis in the northern hemisphere is tilted at 23 1/2 degrees toward the sun. At this time the vertical rays of the sun are striking at 23 1/2 degrees North latitude at a point known as the Tropic of Cancer. For people living in the northern hemisphere June 21 or 22 is known as the Summer Solstice. - On December 21 or 22 the earth is in an opposite position, where the sun's vertical ray's are striking at 23 1/2 degrees South latitude at a point known as the Tropic of Capricorn. For people living in the northern hemisphere December 21 or 22 is known as the Winter Solstice. - The Equinoxes occur midway between the solstices. September 22 or 23 is the date of the Autumnal (Fall) Equinox in the northern hemisphere and March 21 or 22 is the date of the Vernal (spring) Equinox. On these dates the vertical rays of the sun are striking the equator ( 0 degrees latitude ) , because the earth is tilted neither toward or away from the sun.