Kepler's Laws
Kepler’s Laws
September 21, 2009
Taking Care of Business (TCB)
Read textbook Unit 12
Take Moon observations
6 Observations due September 28
Test #1 – September 18 to September 21
Sept 16 class – last day of test material
Reserve your test date/time ASAP
InQsit instructions on Blackboard
Discussion Review
How were Tycho Brahe’s observations critical to the development of astronomy?
He brought up the idea of the planets positions again, and tried to improve them
Made a new model
Kepler’s First Law
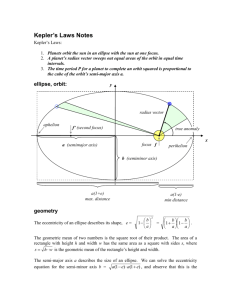
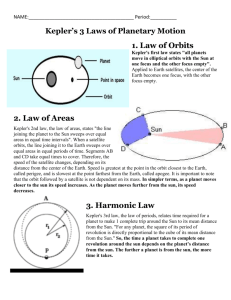
The orbit of each planet about the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus
Kepler’s Second Law
As a planet moves around its orbit, it sweeps out equal areas in equal times
To do this, a planet must move slower at aphelion than it does at perihelion
Kepler’s Third Law
More distant planets orbit the Sun at slower average speeds, obeying the mathematical relationship of p 2 =a 3
(p 2 =ka 3 ) where p is the planet’s orbital period in years and a is the average distance from the Sun in
AU
Example
What about comets? Assume a comet has a high eccentricity of 0.95
(e) with a semi-major axis of
40 (a) AU. How long will it take this comet to orbit the Sun? Where at in its orbit will it spend most of its time? Near the Sun at perihelion? Far from the
Sun at aphelion? Or maybe somewhere in between? p 2 = ka 3
P=253 years, at the aphelion when it is furthest away
If p is measured in years and a is measured in AU, then k = 1.
Post Tutorial Question
If a small weather satellite and the large
International Space Station are orbiting Earth at the same altitude above Earth’s surface, which object takes longer to orbit once around Earth?
a) the large space station
b) the small weather satellite
c) They would take the same amount of time.
Post Tutorial Question
Consider a planet orbiting the Sun. If the mass of the planet doubled but the planet stayed at the same orbital distance, then the planet would take a) more than twice as long to orbit the Sun.
b) exactly twice as long to orbit the Sun.
c) the same amount of time to orbit the Sun.
d) exactly half as long to orbit the Sun.
e) less than half as long to orbit the Sun.