B. Oral Religions - Las Positas College
advertisement

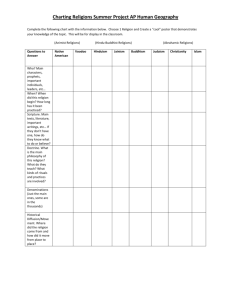
Las Positas College 3033 Collier Canyon Road Livermore, CA 94551-7650 (925) 373-5800 (925) 443-0742 (Fax) Course Outline for Religious Studies I RELIGIONS OF THE WORLD I. CATALOG DESCRIPTION: RELS 1 — RELIGIONS OF THE WORLD —3 units Introduction to religion by examining several religions; basic principles of each shown by fundamental scriptures and works in the visual and musical arts. 3 hours. II. NUMBER OF TIMES COURSE MAY BE TAKEN FOR CREDIT: One III. PREREQUISITE AND/OR ADVISORY SKILLS: None IV. EXPECTED OUTCOMES FOR STUDENTS: Upon completion of the course, the student is expected to be able to: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. V. formulate reasons for the existence of religion; compare and contrast the use of religious symbols; recognize patterns among religions; practice using a multidisciplinary approach to religious studies; identify the basic beliefs of several world religions; discover the place of religion in the local community; analyze the use of religious motifs in literature and art. CONTENT: A. Understanding Religion 1. Why is there religion? a. Speculations on the sources of religion b. Key characteristics of religion c. Meanings of the sacred d. Religious symbolism 2. Are there patterns among religions? a. Focus of beliefs and practices b. Religious views of the world and life c. Religious views of male and female d. Multidisciplinary approaches to study of religion B. Oral Religions 1. Discovering oral religions a. Past obstacles to appreciation of oral religions b. Modern recovery of oral religions c. Patterns in oral religions C. Hinduism 1. Origins of Hinduism 2. The Upanishads and the Axis Age 3. Living spiritually in the everyday world 4. Devotional Hinduism D. Buddhism 1. Life of the Buddha 2. Basic teachings of Buddhism Course Outline for Religious Studies 1 RELIGIONS OF THE WORLD E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. 3. Early development of Buddhism 4. Variations in Buddhism Jainism 1. Origins of Jainism 2. Jain ethics and practices 3. Jain scriptures 4. Jain art and architecture Sikhism 1. Nanak and the origins of Sikhism 2. Development of Sikhism 3. Sikh scriptures 4. Sikhism and the modern world Taoism 1. Origins of philosophical Taoism 2. Basic teachings of philosophical Taoism 3. Religious Taoism 4. Taoism and the modern world Confucianism 1. Living according to Confucian values 2. Confucian literature 3. Development of Confucianism 4. Confucianism and the arts Shinto 1. Origins and historical development of Shinto 2. Essentials of Shinto belief 3. Shinto religious practice 4. Shinto and the arts Judaism 1. Jewish and Biblical history 2. Jewish belief and religious practice 3. Development of rabbinical Judaism 4. Judaism in the modern world Christianity 1. Life and teachings of Jesus 2. Historical development of Christianity 3. Christian practice 4. Christianity and the arts Islam 1. Essentials of Islamic law and philosophy 2. Historical development of Islam 3. Islam and the modern world 4. Islam and the arts Religious Search in the Modern World 1. Modern influences on the future of religion 2. Recurring challenge of change 3. New religious phenomena 4. Eclectic spirituality VI. METHODS OF INSTRUCTION: A. Lecture B. Instructor-guided discussions of reading C. Small group discussions VII. TYPICAL ASSIGNMENTS: A. Reading: Page 2 Course Outline for Religious Studies 1 Page 3 RELIGIONS OF THE WORLD Read Chapter 1, “Understanding Religion,” and be prepared to discuss why religion is important to human existence. 2. Read Chapter II, “Discovering Oral Religions,” and be prepared to explain the place of shamanism, sacrifice, and magic in oral religions. Writing: 1. Visit a local museum and write a short essay about one work of art with a religious theme or subject. 2. Write an essay in which you compare and contrast four significant teachings of Jesus and the Buddha. Collaborative learning: 1. In your small group, choose one sacred text and perform a dramatic reading of it. 2. With several other students, do a series of interviews with local religious leaders and report your findings to the class. 1. B. C. VIII. EVALUATION: A. Methods of evaluation 1. Examinations – midterm and final a. Typical question: short answer 1) Briefly explain the four noble truths of Buddhism. b. Typical question: essay 1) Explain the differences in attitudes toward women in Islam, Protestant Christianity, and Hinduism. 2. Weekly post-discussion short writing assignments: a. Typical question 1) Can you identify any taboos in modern American culture that are similar to religious taboos? B. Frequency of evaluation: 1. Weekly journal 2. Weekly post-discussion short writing 3. One small group presentation of a dramatic reading of a sacred text 4. One joint presentation of roles of community religious leaders 5. Two written examinations (midterm and final) IX. TYPICAL TEXTS: A. Molloy, Michael. Experiencing the World’s Religions: Tradition, Challenge, and Change. Mountain View, CA: Mayfield, 1999. B. Smith, Huston. Forgotten Truth: The Common Vision of the World’s Religions. San Francisco: Harper San Francisco, 1992. C. Smith, Huston. The World’s Religions. San Francisco: Harper San Francisco, 1991. X. OTHER MATERIALS REQUIRED OF STUDENTS: None Creation Date: Revision Date: 10/20/99 rels1.doc