Ch.17 marketing part 2
advertisement

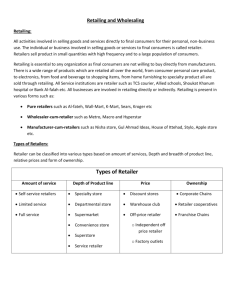
Chapter 17 Marketing Part 2 Marketing The process of finding out what customers want and then making a product/providing a service that will satisfy their needs and then persuading them to buy that product or use that service E.g. Meteor Christmas ads The Marketing Mix (4 P’s of marketing) Product, price, place, promotion Appear almost yearly on leaving cert paper (Q6, Q7, SAQ) PLACE This shows how the product reaches the consumer The channels of distribution shows us how a business can distribute its product so that consumers can easily get it E.g. Coca-cola aims to have its products at arms reach! Channels of Distribution 1. Traditional Manufacturer – Wholesaler – Retailer – Consumer Manufacturer makes product and sells to wholesaler in large amounts The wholesaler sells on the product to the retailer in smaller quantities The retailer sells individual products to the consumer E.g. Cadbury’s sell Boost bars to Musgrave’s, Musgrave’s sell to Clarkes, Clarkes sell to me! Yummy!! Ms. Sloan - Marketing Page 1 2. Alternative Manufacturer - Retailer – Consumer Manufacturer makes product and sells directly to the retailer. Usually done in big orders to big retailers Retailers will avail of big discounts and so can buy in bulk E.g. Tesco buys from Mars; Tesco sells to the consumer for profit 3. Direct Manufacturer - Consumer Manufacturer makes product and sells directly to the consumer. Usually done for specialised products E.g. Dell computers, fitted kitchens NOTE: The more stages in the channel of distribution, the more expensive the product become. 2012 Outline the factors a business should consider when choosing a suitable Channel of Distribution. Provide examples to illustrate your answer. Cost Cost is a factor in choice of channel of distribution. The more stages in the channel of distribution the more expensive the product will be for the consumer as each middleman will require a cut or mark-up. E.g. Ryanair was motivated by cost factors when it cut travel agents out of its ticket sales distribution network. Tesco and Dunnes Stores purchase directly from manufacturers. Type of good/durability Some goods are bulky, others fragile and more perishable. Perishable goods must be distributed quickly to the market e.g. fresh fish/flowers are delivered directly to the retailer. High quality products may be sold directly to consumer. Market size If the market is large then using a wholesaler to break bulk, store goods and transport products to the retailer may be the most economical distribution option. E.g. Cadburys distributes their products through wholesalers like Musgrave Group Ms. Sloan - Marketing Page 2 E-business Companies can advertise and sell their products on line using a company website. Consumers place orders and goods are delivered using the postal system or a courier delivery service. E.g. Dell computers Technological developments Have enabled direct contact between business and the consumers e.g. direct banking and insurance services. Customers can get quotations over the telephone, pay for services with a credit card, transfer funds etc. These services were originally carried out in a branch or by agent or broker. PROMOTION 4th P of the marketing mix which aims to show potential customers that the product exists How does a business promote its product? Through the promotional mix which consists of: a. Advertising b. Sales promotion c. Public relations d. Personal selling Advertising Take notes! Sales Promotion Incentives that a business offers to consumers to promote the sales of their products Free samples e.g. Nivea for men 2 for the price of 1 e.g. Muller rice yogurts Buy one get one free e.g. squeeze orange juice Competitions e.g. Kellogg’s Merchandising – displaying products in an eye-catching way to attract customers e.g. Apprentice airport duty free!!! Public Relations (PR) Part of the business responsible for portraying the business in a good light and developing a good relationship between the general public and itself e.g. O2 A public relations officer (PRO) is often hired to handle a business’s PR Ms. Sloan - Marketing Page 3 Techniques used in PR Sponsorship: a business can become involved in the community by sponsoring events e.g. O2 sponsors Irish rugby team Events: a business can organise a road show, a ball etc. to attract PR e.g. 'Pfizer No Butts 2008' Smoking Cessation Road show 2011LCQ Evaluate “Sales Promotion” and “Public Relations” as forms of Promotion. Sales Promotion is the use of short-term incentives/ “GIMMICKS” to attract customers to the product or services on offer. Activities other than direct advertising are included. It adds to the attractiveness of the product. It is useful for stimulating sales by offering customers price reductions, buy one get one free, coupons, samples, prizes, free draws, in-store displays etc. or any other incentives directly related to the product. It aims to attract new consumers for the product, rewarding loyal consumers and increasing buying frequency among occasional consumers. Sales promotion techniques involve some contact between the customer and the seller. It lasts for a short period of time and may be repeated at a later date. Evaluation Sales Promotion is popular in the large multiples such as Tesco, Dunnes, and Supervalu in the current climate in an effort to increase market share. It is a very effective method of selling goods and services Public Relations is taking steps to create a good image for the product/service. It aims to achieve favourable publicity and build a good corporate image of the business. Public Relations is about building a relationship with the public stakeholders. It is not directly concerned with increasing sales of products. The activities include: press releases; press conferences; TV Programmes; promotional films; sponsorship; publicity literature; donations to charity. Sometimes you will see that in certain businesses, when dealing with certain issues, they will have a spokesperson to come out and speak about the issue. This person is usually referred to as a Public Relations Officer. The activity may be carried out by the company’s own Public Relations Officer (PRO) or by a specialist PR agency. Ms. Sloan - Marketing Page 4 Public relations can pose challenges. Negative product publicity can be a nightmare for businesses e.g. Toyota recall of cars. It can lead to loss in the market share and customers losing trust in the quality of the product/service being offered. Public Relations: can take the form of press releases where the media are given information about the company. Sponsorship is another form where businesses pay money so that their product name will be displayed by individuals, organisations or at particular events. e.g. The Heineken Cup Ms. Sloan - Marketing Page 5