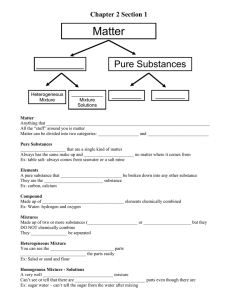
Matter – anything that has mass and occupies space, including all
advertisement

Matter – anything that has mass and occupies space, including all solids, liquids, and gases. Property – a characteristic used to descried matter. Mixture – matter that has two or more kinds of particles and thus may have different properties in different samples. Pure substance – a substance that has the same properties in any sample you choose. There are two kinds of pure substances: elements and compounds. Mechanical mixture - a mixture in any set of moving parts. Suspension Solution Element – a pure substance that can’t be broken down into any other pure substance. Compound – a pure substance that is made up of two or more elements that are chemically combined. Physical change Chemical change - a change in matter in which one or more new substances are produced. Chemical reaction –a change in matter in which one or more new substances are produced. Reactant – any substance that you start with in a chemical reaction. Product Word equation Corrosion – the eating always of metal as a result of a chemical reaction. Combustion – a chemical reaction in which oxygen is one of the reactants and in which heat is produced. Scientific law Law of conservation of mass