note taking guide
advertisement

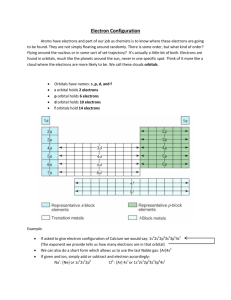
Name: __________________________________________ Date: ___________________ Period: ___________ Electron Configuration & Orbital Diagram PPT note taking guide 1. Electron Configuration Shows the arrangement of _____________________ in an atom. 2. Orbital Diagram Another way of writing the ___________________ _____________________. An _________________ is a ____________________ space for an ____________________. Atoms can have ________________ potential _____________________. ________________________ are represented by ____________________ grouped by sublevel with small _______________________ indicating the _______________________. 3. Pauli Exclusion Principle An atomic orbital can hold a ____________________ of _____ electrons and those 2 electrons must have _________________ spins. An ________________ is represented by an ________________. ________________ is represented by the _____________ facing _____ or ______________. 4. Hydrogen H has an atomic number of _____, so it has _____ electron available to place in the orbital diagram. Configuration: _________________________ Orbital Diagram: 5. Helium He has an atomic number of _____, so it has ____ electron available to place in the orbital diagram. Configuration: _________________________ Orbital Diagram: 6. Aufbau Principle Electrons are placed in the _________________ energy level ______________________. Write the order of energy levels from lowest energy to highest energy. 7. Lithium Li has an atomic number of _____, so it has ____ electron available to place in the orbital diagram. Configuration: _________________________ Orbital Diagram: 8. Beryllium Be has an atomic number of _____, so it has ____ electron available to place in the orbital diagram. Configuration: _________________________ Orbital Diagram: 9. Boron B has an atomic number of _____, so it has ____ electron available to place in the orbital diagram. Configuration: _________________________ Orbital Diagram: 10. Hund’s Rule When filling _______________ other than _____, __________________ are placed in individual orbitals ______________, before they are __________________ up. 11. Carbon C has an atomic number of _____, so it has ____ electron available to place in the orbital diagram. Configuration: _________________________ Orbital Diagram: 12. Nitrogen N has an atomic number of _____, so it has ____ electron available to place in the orbital diagram. Configuration: _________________________ Orbital Diagram: 13. Oxygen has an atomic number of _____, so it has ____ electron available to place in the orbital diagram. Configuration: _________________________ Orbital Diagram: 14. Organization of Orbitals The periodic table has _________________ the _____________________. The “_____” orbitals The “_____” orbitals The “_____” orbitals The “_____” orbitals The first _______ is Principal Energy Level _____. The second ________ is Principal Energy Level _____. Principal Energy Level _______ begins in the _____ row. Principal Energy Level _______ begins in the _____ row. 15. and so the pattern continues… 16. Sublevels The “_____” sublevel can hold _____ electrons. The “_____” sublevel can hold _____ electrons. 2 electrons in each of the _____ orbitals (_____, _____, _____) The “_____” sublevel can hold _____ electrons. 2 electrons in each of the _____ orbitals. The “_____” sublevel can hold _____ electrons. 2 electrons in each of the _____ orbitals. 17. Practice Problems Fluorine: Configuration: _________________________ Orbital Diagram: Magnesium: Configuration: _________________________ Orbital Diagram: Sulfur: Configuration: _________________________ Orbital Diagram: Potassium: Configuration: _________________________ Orbital Diagram: 18. Noble Gas Configuration Is an ___________________ version of ____________________ ____________________________. Uses the _______________ __________ that _______________ (comes before) the element, then the __________________ ______________________ that comes after the noble gas. Used for elements with larger atomic numbers. Example: Nitrogen: Noble Gas Configuration: _______________ Orbital Diagram: 19. Valence Electrons Is important because it shows the ___________________ _________________ present in an atom. Nitrogen has an atomic number of _____. It has 7 total ____________________. If you look at the electron configuration, you can count _____ electrons. But if you look at the _________________ ____________ Configuration, you can count 5 electrons. These _____ electrons are the ________________ ___________________, the electrons found in the __________________ energy level. The periodic table organizes valence electrons. The number of ______________ electrons are written above each ______________ in the diagram. 20. Practice Problems Iron: Noble Gas Configuration: _______________ Orbital Diagram: Tin: Noble Gas Configuration: _______________ Orbital Diagram: