Study Guide Chapter 7 - Atomic Structure and Periodicity 1. what is a
advertisement

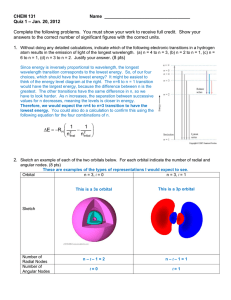
Study Guide Chapter 7 - Atomic Structure and Periodicity 1. what is a J of energy in units of kg, m, sec? 1. What is wavelength, frequency, constructive interference, destructive interference, valence electrons, core electrons,? 2. Convert between wavelength and frequency using c=8< 3. Convert between frequency and energy using )H=nh< 4. calculate de Broglie wavelength associated with matter using m=h/8v 5. Calculate energy associated with a transition in the Bohr model E=-2.178x10-18J(Z2/n2) a. calculate the energy associated with an energy changing levels of n b. calculate frequency and wavelength associated with this transition c. giving a wavelength, calculate the change in level number d. What is the significance of the sign in this calculation? e. What is the significance of using 4 instead of an n? 6. What is a “wave function” 7. Why does the probability function for an s orbital have a max at 0, while the radial probability has a value of 0 at radius of 0? 8. Give the names, symbols, possible values, and meaning of the 4 quantum numbers we use to describe atomic orbitals 9. What are the differences between a 1s and a 3s orbital? (Size, energy, # of nodes) 10. What is the Pauli exclusion principle? 11. Which has the lower energy a 3s or a 3d orbital? Why? 12. What is the Aufbau principle? 13. Give the orbital diagram for any element and the corresponding electron configuration? What are the tricky ones and why are they tricky 14. What is Hund’s rule 15. What is the same about elements in the same column of the periodic table? 16. What is an ionization energy, how does it go on the periodic table? 17. What is electron affinity, how does it go on the periodic table 18. what is atomic radius, how does it go on the periodic table 19. Review properties of Alkali metals