Name: _____________________________________
Period: ___________
Populations: Human Population Growth
Historical Overview
Like the populations of many other living organisms, _____________________
___________________________________________________.
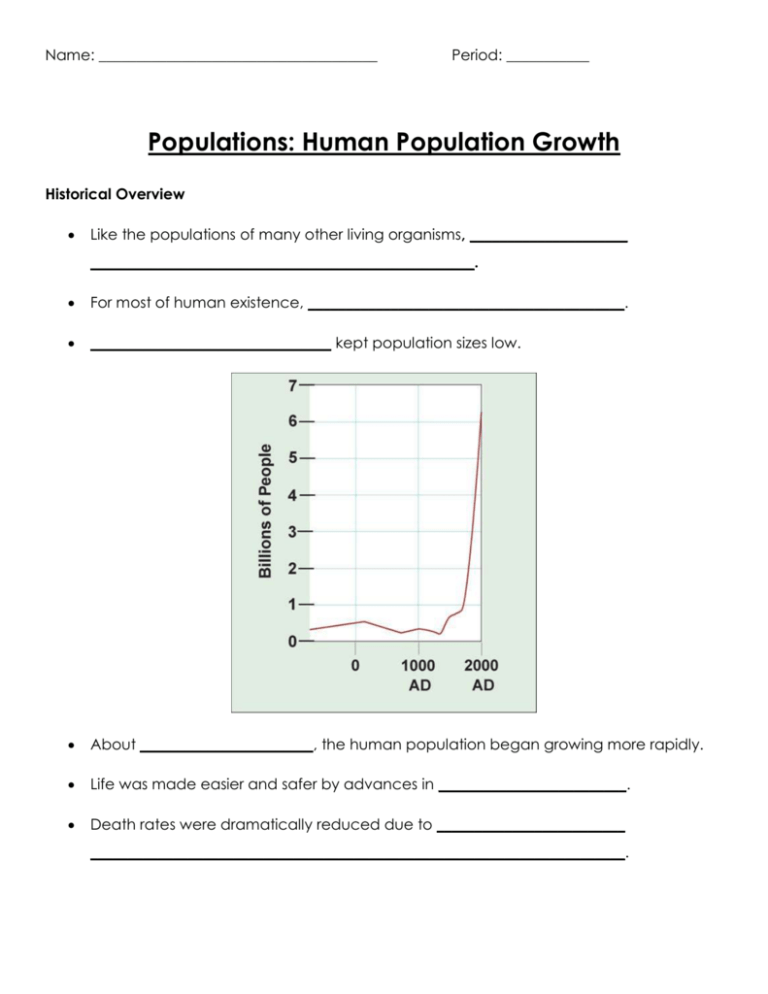
For most of human existence, __________________________________________.
________________________________ kept population sizes low.
About _______________________, the human population began growing more rapidly.
Life was made easier and safer by advances in _________________________.
Death rates were dramatically reduced due to _________________________
_______________________________________________________________________.
With these advances, the human population experienced
exponential growth.
Human Population Growth
Patterns of Population Growth
The scientific study of human populations is called ______________________.
Prentice Hall
Demography examinesCopyright
thePearson
characteristics
of human populations and attempts to
___________________________________________________________.
_______________________________________________________________________ help predict
why some countries have high growth rates while other countries grow more slowly.
The Demographic Transition
Over the past century, population growth in the United States, Japan, and much of
Europe has __________________________.
According to demographers, these countries have completed
the_______________________________, a dramatic change in birth and death rates.
The demographic transition has _______________________.
o In stage 1, ______________________________________________________.
o In stage 2, ______________________________________________________.
_______________________________________.
o In stage 3, _______________________________________________________
_______________________.
Patterns of Population Growth
The
demographic
transition is
complete when
the birthrate
falls to meet the
death rate, and
population
Age
Structure
growth
stops.
Population growth depends, in part, ________________________________
_________________________________________.
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Demographers can predict future growth using models called _________
_____________________.
Age-structure diagrams show the population of a country broken down by
________________________________________.
U.S. Population
In the United
States, there are
nearly equal
numbers of people
in each age group.
This age structure
diagram predicts a
slow but steady
growth rate for the
80+
60–64
Age (years)
40–44
20–24
0–4
Rwandan Population
In Rwanda, there
are many more
young children
than teenagers,
and many more
teenagers than
adults.
80+
Males
Females
60–64
Age (years)
40–44
20–24
This age structure
diagram predicts a
0–4
population that will
Future Population Growth
Percentage of Population
double in about 30
years.
To predict human population growth, demographers must consider the
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
_______________________________________________________________________
double in about 30
______________________________________.
years.
If growing countries move toward the demographic transition, ___________
___________________________________.
Ecologists suggest that if growth does not slow down, there could be
___________________________________________________________________.
Economists assert that ______________________________________________ may control the
Copyright
Pearson Prentice Hall growth.
negative impact of
population
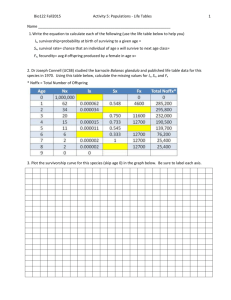
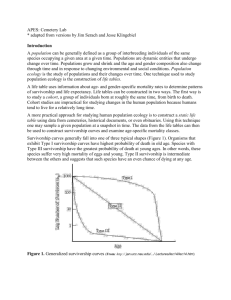
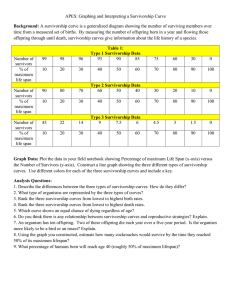
Survivorship
A survivorship curve is a graph showing _______________________________
_________________________________________________ (e.g. males/females).
Survivorship curves can be constructed for a given ______________(a group of
individuals of roughly the same age) based on a life table
Survivorship curves tell us something about ______________________________
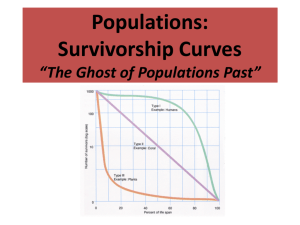
___________________. There are basically three types of survivorship curves:
Type I survivorship curves are for species that have a high survival rate of the young, live out
most of their expected life span and die in old age.
Examples: _____________________
Type II survivorship curves are for species that have a __________________________
______________________________________________. Death could be due to hunting or diseases.
Examples : coral, squirrels, honey bees, birds, and many reptiles.
Type III survivorship curves are found in species that ___________________________
______________________________________________.
Examples: Plants, oysters and sea urchins