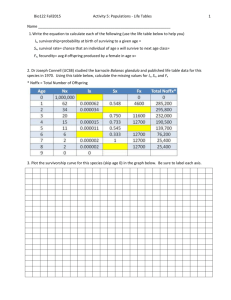
Populations: Survivorship Curves
advertisement

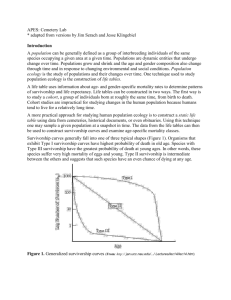
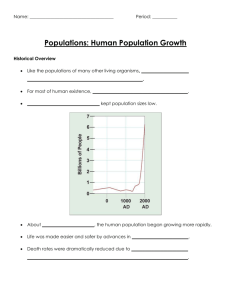
Populations: Survivorship Curves “The Ghost of Populations Past” Objectives: Students will: • Investigate survivorship • Develop survivorship curves from data collected in the field • Analyze a human survivorship curve developed from the collected data • Describe the various types of survivorship curves as they relate to ecological life history strategies Objectives: What will you need What will you be to know? able to do? • Collect human • Survivorship survivorship data • Ecological life history • Develop survivorship strategies curves using a computer spreadsheet • Survivorship curves • Analyze survivorship (Types I – III) curves of humans and other organisms Introduction • Populations grow, shrink, succeed, or fail • Survivorship refers to a way that populations shrink • Genetics and the environment play a role in how species survive • How different species live or die can be described by means of a Survivorship curve. Introduction • Survivorship Curves: Mathematical models Show how many members of a species are likely to survive Follows a group of individuals from birth to ultimate death of all members Protocol/Procedure • Part 1 Details: A Trip to a Cemetery Choose a 25-year birth year range. Ex. 1800-1824, 1825-1849, 1850-1874, etc… Choose a cemetery, record the location on the data sheet (be sure to record all information requested on the data sheet). In the cemetery, locate 75 males and 75 females who were born in the year range you chose, record year of birth and year of death on the data sheets Protocol/Procedure No dates on headstone? Birth date within range? Can’t use! Birth date MUST be in the range you select! Introduction Introduction Protocol/Procedure • Part 2 Details – Data Analysis and Questions For all 150 individuals, calculate “Age at Death” by subtracting the birth year from the death year (record on the same data sheets) Using 5 year increments and the second set of data tables, tally how many males died every 5 years. Repeat using the females. (See example next slide.) Introduction Protocol/Procedure Introduction • Part 2 Calculation Example: Male Gender Birth year Death year Age at death male 1876 1900 24 male 1899 1901 2 male 1879 1904 25 male 1881 1981 100 male 1887 1986 99 Age at death # total from population 0-5 1 21-25 2 96-100 2 Bring your data to school on the first day of class! The Standards • Explain how variations in structure, behavior or physiology allow some organisms to enhance their reproductive success and survival in a particular environment. • Explain that the variation of organisms within a species increases the likelihood that at least some members of a species will survive under gradually changing environmental conditions. • Relate how distribution and abundance of organisms and populations in ecosystems are limited by the ability of the ecosystem to recycle materials and the availability of matter, space and energy. • Relate how birth rates, fertility rates and death rates are affected by various environmental factors • Examine the contributing factors of human population growth that impact natural systems such as levels of education, children in the labor force, education and employment of women, infant mortality rates, costs of raising children, birth control methods, and cultural norms.