Population - cashmerebiology
advertisement

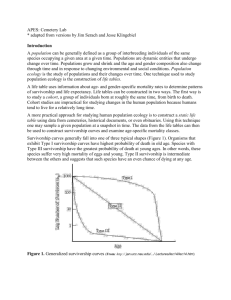
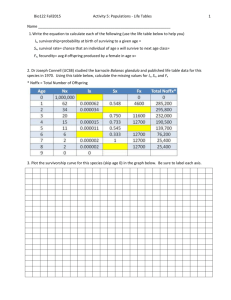
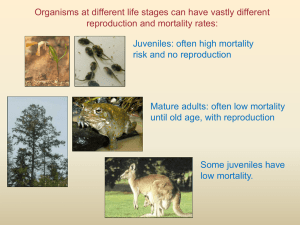
Learning outcomes for today • Define a population and describe the attributes that make up that population • Describe the 3 types of population distribution • Work in a pair to learn about survivorship curves and age structure Definition • A group of interbreeding individuals of the same species that live in a particular area at a defined time. Natality • Number of births per 1000 people per year crude birth rate = births per year total population X 1000 Mortality • Number of deaths per 1000 people per year Crude death rate = deaths per year total population X 1000 Density • Number of individuals of a population per unit area of habitat at a specific time. – E.g. Pine trees per hectare of the Urewera forest in 2007 – E.g. Diatoms per cubic metre of sea water taken of Raglan beach in 2006 Low Density • Only a few animals per unit area • Highly territorial, solitary animals High Density • Individuals crowded together • Colonial organisms Distribution • How individuals are spaced in an area • 3 types of distribution 1. Random 2. Clumped 3. Uniform Distribution - Random • Presence of one individual does not directly affect the location of another individual. • Uncommon in animals • Often seen in plants Distribution - Clumped • Individuals are grouped in patches, sometimes around a resource • The presence of one individual increases the probability of finding another • E.g. Herding or highly social species (buffalo) Distribution - Uniform • Individuals are evenly spaced • Presence of one individual decreases the probability of finding another close by Pair Share Class 1. Describe why some organisms may exhibit a clumped distribution because of a. Resources in the environment b. A group social behaviour Pair Share Class 2.Describe a social behaviour found in some animals that may encourage a uniform distribution Pair Share Class 3. Describe the type of environment that would encourage uniform distribution Pair Share Class 4. Give an example of each of the following types of distribution patterns a. Clumped b. Random c. Uniform Survivorship • There are three types of survivorship curves – Type I • Mortality is very low in the infant and juvenile years, and throughout most of adult life. Mortality increases rapidly in old age. – Type II • Mortality is relatively constant through all life stages (no one age is more susceptible than another) – Type III • Mortality is very high during early life stages, followed by a very low death rate for the few individuals reaching adulthood. Survivorship Your Task: Biozone exercise Survivorship curves 286 Population Age Structure • The age structure of a population refers to the relative proportion of individuals in each age group in the population. • The population is usually divided into three groups – Pre-reproductive – Reproductive – Post-reproductive Population Age Structure • This is usually shown as a age pyramid. The shape of the pyramid show different things – True pyramid – an expanding population – Bell shaped – a stable population – Urn shaped – a diminishing population An Expanding Population A Stable Population A Diminishing Population