Population Ecology: Chapter Objectives & Key Terms
advertisement

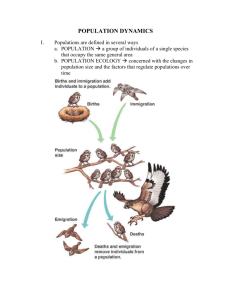
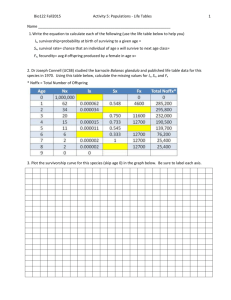
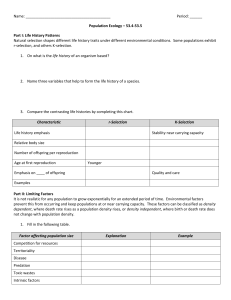
Chapter 36: Population Ecology Chapter Objectives Opening Essay Explain how the introduction of Nile perch into Lake Victoria changed the ecology of the lake and surrounding region. Population Structure and Dynamics 36.1 36.2 36.3 36.4 36.5 36.6 36.7 36.8 Define a population. Describe the general type of work performed by population ecologists. Define population density and describe different types of dispersion patterns. Explain how life tables are used to track mortality and survivorship in populations. Compare Type I, Type II, and Type III survivorship curves. Describe and compare the exponential and logistic population growth models, illustrating both with examples. Explain the concept of carrying capacity. Describe the factors that regulate growth in natural populations. Define boom-and-bust cycles, explain why they occur, and provide examples. Explain how life-history traits vary with environmental conditions and with population density. Compare r-selection and K-selection and indicate examples of each. Describe the major challenges inherent in managing populations. The Human Population 36.9 36.10 36.11 Explain how the structure of the world’s human population has changed and continues to change. Describe the key factors that affect human population growth. Explain how the age structure of a population can be used to predict changes inpopulation size and social conditions. Explain the concept of an ecological footprint. Describe the uneven use of natural resources in the world. Key Terms age structure carrying capacity clumped demographic transition density-dependent dispersion pattern ecological footprint exponential growth model K-selection life history life table limiting factors logistic growth model maximum sustained yield per capita rate of increase population population density population ecology population momentum random r-selection survivorship curve sustainable resource management uniform Word Roots demo- 5 people; -graphy 5 writing (demography: the study of human populations; demographic transition: the shift from zero population growth characterized by high birth and death rates to zero population growth characterized by low birth and death rates) capit- 5 head (per capita rate of increase: the average contribution of each individual [literally, each “head”] in a population to population growth) Student Media Population Structure and Dynamics Activity: Techniques for Estimating Population Density and Size (36.2) Activity: Investigating Survivorship Curves (36.3) BLAST Animation: Population Dynamics (36.6) The Human Population Activity: Human Population Growth (36.9) Activity: Analyzing Age-Structure Diagrams (36.9) GraphIt!: Age Pyramids and Population Growth (36.9)