Frog Systems - Frost Science
advertisement
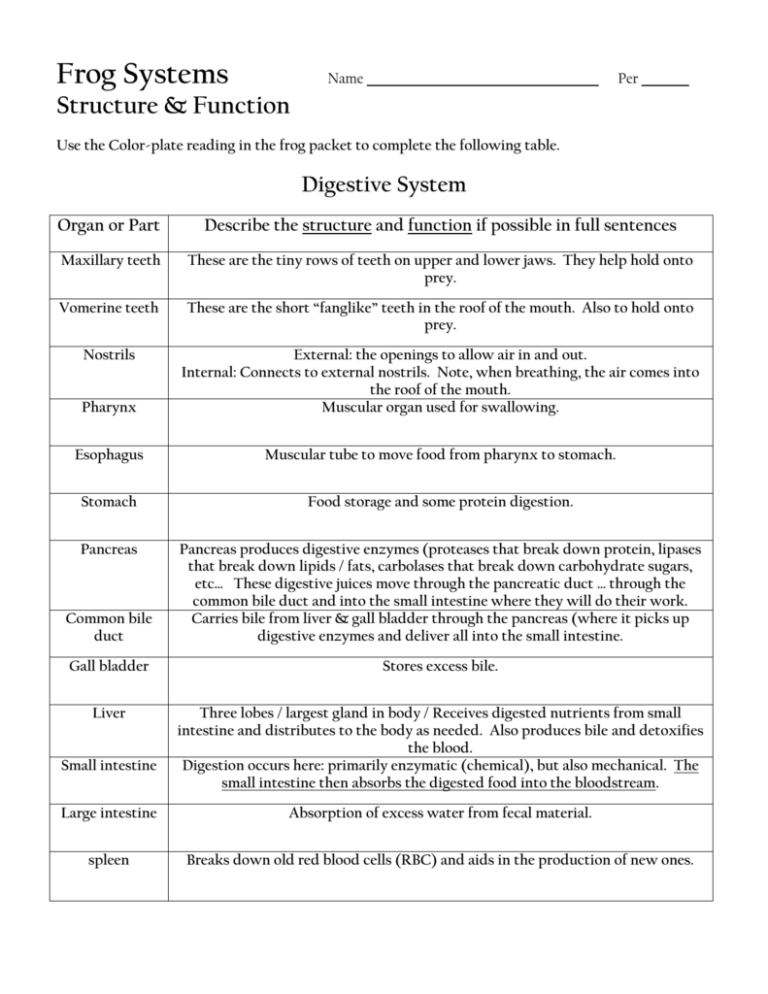
Frog Systems Name Per Structure & Function Use the Color-plate reading in the frog packet to complete the following table. Digestive System Organ or Part Describe the structure and function if possible in full sentences Maxillary teeth These are the tiny rows of teeth on upper and lower jaws. They help hold onto prey. Vomerine teeth These are the short “fanglike” teeth in the roof of the mouth. Also to hold onto prey. Nostrils Pharynx External: the openings to allow air in and out. Internal: Connects to external nostrils. Note, when breathing, the air comes into the roof of the mouth. Muscular organ used for swallowing. Esophagus Muscular tube to move food from pharynx to stomach. Stomach Food storage and some protein digestion. Pancreas Common bile duct Pancreas produces digestive enzymes (proteases that break down protein, lipases that break down lipids / fats, carbolases that break down carbohydrate sugars, etc… These digestive juices move through the pancreatic duct … through the common bile duct and into the small intestine where they will do their work. Carries bile from liver & gall bladder through the pancreas (where it picks up digestive enzymes and deliver all into the small intestine. Gall bladder Stores excess bile. Liver Three lobes / largest gland in body / Receives digested nutrients from small intestine and distributes to the body as needed. Also produces bile and detoxifies the blood. Digestion occurs here: primarily enzymatic (chemical), but also mechanical. The small intestine then absorbs the digested food into the bloodstream. Small intestine Large intestine Absorption of excess water from fecal material. spleen Breaks down old red blood cells (RBC) and aids in the production of new ones. Respiratory System Organ or Part Describe the structure and function if possible in full sentences Internal & External Nares Nostrils: Openings in the upper jaw (mandible) that lead to the inside of the mouth. Allows frog to breath when mouth is closed. Oral Cavity Properly called the buccal cavity. This is the inside of the mouth. Glottis Small slit-like opening at the back of the buccal cavity that opens to allow air to enter and leave the lungs. Closes to hold breath when swimming and when swallowing to keep water and food out. Larynx Connected to the Glottis, this is the chamber that contains vocal chords and leads to the lungs. Used to conduct air to the lungs and as a voice box so the frog can communicate. Bronchi 2 Bronchi lead away from the larynx carrying air to each lung. Each bronchus leads into a lung and then divides into smaller and smaller ducts, ending with alveoli which are grape like structures where gases are exchanged between the air and the bloodstream. Lungs: Contain alveoli. Function is to exchange gasses between the air inside the alveoli and the tiny blood vessels (called capillaries) that are embedded within the alveoli tissue. Lungs Alveoli Capillaries Abdominal muscles The tiny airsacs in the lungs. They fill with air when the frog inhales. Oxygen then diffuses through their thin lining into the capillaries / blood. Carbon Dioxide (waste gas) diffuses in the opposite direction from the blood to the air. This CO2 rich blood is then exhaled and the process repeated. Tiny blood vessels that are embedded within tissues. This is how the tissues (cells) actually exchange gasses, water, sugar, and other materials with the blood. They are found in all parts of the body, but we discussed how they surround and are part of the alveoli. Stomach muscles. Used for movement.