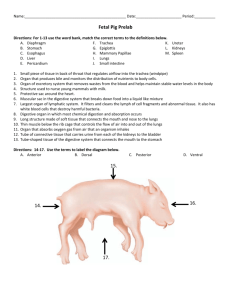
Organ System - group of organs working together Organ
advertisement

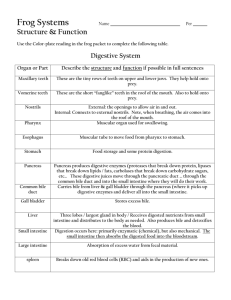
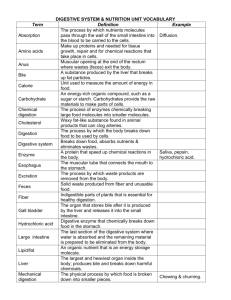
ORGAN SYSTEM ORGAN TISSUE CELLS Organ System - group of organs working together Organ - Tissue form organs Tissue - cells with similar structure and function form tissue Cells – Basic unit of life Body Systems • Digestive System – Living organisms require energy to survive. Humans obtain energy from: 1. Carbohydrates (sugar and starch) 2. Lipids (fats and oils) 3. Protein (meat and legumes) This food energy must be processed by the digestive system in order for the body to use it. Types of Digestion 1. Mechanical digestion – involves the physical breakdown of food into very small pieces. 2. Chemical digestion – involves the breakdown of large particles into smaller particles by substances called Enzymes. Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system is a long tube that starts at your mouth and ends at the rectum. Mouth and Esophagus 1. Mechanical – teeth 2. Chemical – saliva (contains water and enzymes called Salivary Amylase. The enzyme digests large starch molecules into smaller molecules. Swallow food – Epiglottis covers the trachea (wind pipe), food moves down the Esophagus in a wave like movement called Peristalsis. Peristalsis is caused by contraction of smooth muscle tissue. 2) Stomach 1. Mechanical – muscles churn food. 2. Chemical – Gastric juices, mucus, hydrochloric acid, water, and digestive enzymes break down proteins into smaller particles. The food (now a liquid) is released into the small intestine. 3) Small Intestine – chemical digestion continues. Pancreas sends digestive enzymes to the small intestine and along with enzymes released by the small intestine, the breakdown of the food is complete. Gall bladder – stores bile, which breaks up lipids (fat) into smaller droplets. The bile is sent to the small intestine. Bile is produced in the Liver. The small intestine now absorbs the nutrients into the Epithelial Tissue, and then into the blood stream. The inner surface of the small intestine is covered by Villi – small, finger-like projections, that increase the small intestines surface area. Villi – small intestine 4)Large Intestine – mechanical and chemical digestion is complete. Water is absorbed, along with some vitamins and minerals. Anything not absorbed collects in the rectum. http://kitses.com/animation/swfs/digestion.swf Respiratory System Responsible for supplying your blood with oxygen and removing Carbon dioxide from your blood. Breathing Occurs because of your ribs and diaphragm muscles. Inhale – muscles contract, pulling ribs up and diaphragm down. This increases the size of the chest and lungs, decreasing the pressure and pulling air into the lungs. Exhale – muscles relax, pulling ribs down and diaphragm up. This decreases the size of the chest and lungs, increasing the pressure and forcing air out of the lungs. Breathing Your cells need oxygen to release energy. Carbon dioxide is produced when energy is released and it must be removed from the body. Respiratory System Oxygen – rich air enters the Trachea via the mouth and nose. Air travels down the trachea through the Bronchi. The bronchi narrow to form Bronchioles, which end in air – filled sacs called Alveoli. Alveoli air hollow sacs (one cell thick) surrounded by capillaries. Gas exchange happens in the alveoli. Oxygen into the blood, carbon dioxide into the lungs. Alveoli