Excel 2002 Handout
advertisement

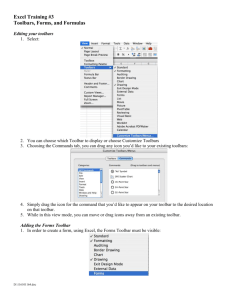
Excel 2002 An Excel file is a workbook that contains several worksheets that are identified by tabs at the bottom of the window. A worksheet is divided into rows and columns—the intersection of a row and a column is called a cell. Information is entered into cells. Standard and Formatting Toolbars Cell Formula Bar Column Headings (A-IV) and Row Headings (1-65,536) Task Pane & close button for task pane Status Bar Sheet Tabs Highlighted row and column heading Drawing Toolbar Scroll Bars Widen Column: Double click or click and drag Mouse Pointer Move. Click and drag to move Standard and Formatting Toolbars on separate rows To view all the icons on the Standard and Formatting Toolbars, we want the toolbars on separate rows: 1. Select the Tools Menu 2. Choose Customize 3. Click Show Standard and Formatting toolbars on two rows. 4. Click Close to return to the worksheet Entering Text To enter text or numbers, position the mouse on the cell (big white plus sign) and click to select the cell. Begin entering the information. Press ENTER, TAB, or the ENTER Icon on the Formula Toolbar. Position mouse on the cell and click Type the information in the cell. Press ENTER, TAB, or click ENTER icon. ENTER icon Merge and Center Cells Enter the information in the cell and press ENTER. Position the mouse on the cell with the text (you will get the white plus sign) and click and drag to select the cells to merge and center. Click the Merge and Center icon on the Formatting Toolbar. When completed, the cells will be merged as one. Note: If you accidentally select too many or too few cells, select the merged cell and click the Merge and Center icon ONCE. This will undo the merge/center. Click to select the cell, type the information in the cell, and press ENTER. Position mouse on cell A1 and click and drag to select A1:C1. Click the Merge and Center icon. Cells that have been merged and centered. Formatting Text You can quickly format text using icons on the Formatting Toolbar. For more extensive formatting, use the Format Menu. Change font style or size Bold, Italicize, Underline Borders Merge and Center Alignment Indent Background and Font Color Convert a Number to Text Position the mouse pointer on the cell and DOUBLE click (or you can click ONCE and position your mouse in front of the number in the Formula Bar). Move mouse pointer to the beginning of the number and type the apostrophe ONCE and press ENTER. A Smart Tag Indicator (green triangle) will be displayed in the upper left hand corner of the cell. If you click on the cell, a Smart Tag Action icon will be displayed. If clicked, it will inform you that the number has been stored as text. Smart Tag Indicator Double click the cell and type ‘ in front of the year and press ENTER. Click on the cell. The Smart Tag Actions icon will be displayed. If you click the Smart Tag Actions icon, it will tell you that the number has been stored as text, as well as other actions that can be taken. Formulas A formula is a mathematical statement that calculates a result. In Excel, ALL formulas begin with an equal sign (=). A formula can have a cell reference, functions (avg, max, or min), arithmetic operators, and constants (a value that does not change). Arithmetic Operators Operator Meaning + Addition Subtraction * Multiplication / Division ^ Exponentiation Formula =A1 + A2 =A1 – A2 =A1 * A2 =A1/A2 =A1 ^ A2 Results (if A1= 10 and A2 = 4) 14 6 40 2.5 10,000 Once a formula has been entered, it can be copied to other worksheet cells using the Fill Handle or using the Copy and Paste Commands. The cell references will automatically change when the formula has been copied. Commonly Used Functions Functions are predefined formulas that perform calculations by using specific values, called arguments, in a particular order, or structure. The structure of the function begins with the function name, an open parenthesis, the argument, and a closing parenthesis. If the function begins a formula, start with an equal sign. Commonly Used Functions Function Purpose Sum Max Min Average Count Function CountA Example Addition Highest Number Lowest Number Average Counts the number Purpose =sum(A1:A3) =max(A1:A3) =min(A1:A3) =average(A1:A3) =count(A1:A3) Example Counts text =counta(A1:A3) Results (A1= 10, A2 = 4, and A3 = 6) 20 10 4 6.67 3 Results (A1= Red, A2 = Blue, and A3 = Green) 3 SUM Function Position your cursor on the cell where you want the formula and click ONCE. Click the AutoSum button on the Standard Toolbar and press ENTER (if you did not want to use the icon, create the formula as follows: =sum( click and drag to select the cells, and press ENTER). Select the cell with the SUM Function, use the Fill Handle, and copy the formula down (or across, depends on the information in the worksheet). Select the cell, position the mouse on the AutoSum icon on the Standard Toolbar, click ONCE to display the cells in the formula and click ONCE more to display the answer. Fill Handle Position the mouse on the fill handle, click and drag to select cells, and release to display. Fill Handle Position mouse on fill handle— changes to +. Click and keep clicked. Drag to select cells and release. Functions The AutoSum drop-down arrow on the Formatting Toolbar lists the Average, Count, Max, and Min functions. Click More Functions… to get an alphabetical list of all the functions. Format Numbers There are several icons on the Formatting Toolbar that can be used to format numbers. Currency, Percentage, and Comma Font and Font Size Font Style Increase/ Decrease Decimal Borders However, the Format Cells Dialog Box can be used to format numbers. Select the Format Menu and choose Cells. Applying Borders to Cells Click and drag to select the cells. Click the Borders drop-down arrow on the Formatting Toolbar. There are several choices. Position your mouse on the one you want and click ONCE. There are more border choices by selecting the Format Menu, selecting Cells, and choosing the Border tab. The styles and border direction can be changed. Applying Shading (Fill) to Cells Select the cells to shade, click the Fill Color drop-down arrow on the Formatting Toolbar, and select a color. Sheet Tab—Name and Color To name the sheet tab, double click, type in name, and press ENTER. To change the color of the tab, right mouse click the sheet tab, select Tab Color, select a color, and press OK. Page Setup Each worksheet that is printed must be set up—print either in portrait or landscape, add a custom footer, and print the gridlines and row/column headings. Select the File Menu and choose Page Setup. The Page Setup dialog box is displayed. Save Workbook When a workbook is saved, all the worksheets will be saved. If it is the first time the workbook is saved, click the Save icon on the Formatting Toolbar or select the File Menu and choose Save As. Change the Save In directory to the 3 ½ floppy (A:). Type the file name and click Save. After the workbook has been saved, click the Save Icon to update the workbook. Cell Formulas Cell formulas display formulas created. On the keyboard, press CTRL ~ to display the cell formulas. It may be necessary to widen the columns to view the formulas. Press CTRL ~ to return to the worksheet. It may be necessary to widen the columns to view the formulas. Printing Press the print icon on the Standard Toolbar or select the File Menu, select Print, and choose OK. Adding a Graphic You may want to add a graphic when creating a worksheet. You can insert a Microsoft graphic or you may select a graphic from a CD, diskette, or from a folder on the server. Select the Insert Menu, select Picture, and choose From File. Select the Look In drop-down arrow and select the location where the graphic is. Select the graphic and insert. You may have to resize the graphic.