1st GP
advertisement

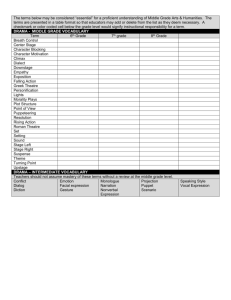
Technical Theatre Level I – High School Week 1 Unit of Study: Theatre Terminology and Theatre Safety TEKS High School Theatre Arts Level I (Content) I.5.A. analyze and apply appropriate behavior at various types of live performances I.5.B. develop appropriate theatre vocabulary to apply the concepts of evaluation (intent, structure, effectiveness, value) to live theatre, film, television, and electronic media in written and oral form with precise and specific observations Vocabulary Word Wall acting The Stage and the School Resource Binder Theatre Safety Page 49 College Prep TEKS HIGH School Theatre Arts Level I (Skills and Processes) I.5.A. analyze and apply appropriate behavior at various types of live performances I.5.B. develop appropriate theatre vocabulary to apply the concepts of evaluation (intent, structure, effectiveness, value) to live theatre, film, television, and electronic media in written and oral form with precise and specific observations Resources The Stage and The School Glossary R32 - R50 Theatre Safety Pages 440-441 The Acting Areas Page 360 Basic Drama Projects Theatre Information Packet (TIPack) Part D: Basic Theatre Terminology Internet Resources: Reading/Writing and Theatre Arts: Research and Correlations First Grading Period Instructional Guidelines The teacher will: review theatre safety policies and procedures present the “word wall” vocabulary and definitions describe and illustrate proper audience etiquette Key Questions 1. Rigor 2. C Relev ance 3. What are the divisions of a theatre and a stage? Where do many of the theatre terms derive from? How would you describe proper audience etiquette? Student Behaviors Getting the Big Ideas Utilize the terminology and language of the theatre Identify and label parts of the stage demonstrate and discuss theatre safety policies and procedures Strategies Lecture Explicit Teaching Group Discussions Guided Practice Teacher Questions Primary Resources Assessment Students will take a vocabulary quiz to test their knowledge of theatre terminology. Students will be able to correctly label a stage diagram. Students will work in groups to create theatre safety posters depicting policies and procedures. Before: Engage Have students walk through and discover the theatre facilities. During: Explore Have students explain and describe the vocabulary associated with the theatre facilities. After: Summarize The student will be able to orally present a tour of the theatre facilities using appropriate theatre terminology. Technology Connection Theatre Safety SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) Page 1 of 18 Special Education Instructional Modifications/ Accommodations Determined by ARD/IEP SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) During: Check for Understanding Have students label a printed stage diagram. Page 2 of 18 Technical Theatre Level I – High School Week 2 Unit of Study: Producing the Play: The Artistic Staff TEKS Grades 9-12 (Content) I. 3. C. define the director’s role as a unifying force, problem-solver, interpreter of script, and collaborator Vocabulary Word Wall Producer Director Assistant Director Critiques Scenic Designer Technical Director Bilingual Word Wall Resources The Stage and the School Chapter 8 – Producing the Play Pages 333 - 339 Pages 343 - 373 Instructional Guidelines The teacher will: guide students in examining how a play is produced, including the responsibilities of each staff member present “word wall” vocabulary and definitions 1. Rigor B Relev ance 2. 3. College Prep Student Behaviors Getting the Big Ideas Key Questions The Stage and the School Resource Binder Production Staff Page 40 Internet Resources: Reading/Writing and Theatre Arts: Research and Correlations First Grading Period TEKS Grades 9-12 (Skills and Processes) I. 3. D. define the director’s responsibility to the author’s intent, script, actors, designers, technicians, and the audience Who are the key members of the artistic staff, and what are their responsibilities? Who serves as the “producer” in an high school production/ How important is the job of the director to the overall success of a show? Compare the roles and responsibilities of the various members of the artistic staff. Examine the differences between the role of producer in high school and professional theatre. Discover the importance of the director to all aspects of a show. Strategies Guided practice Role-playing Discussions Collaborating learning activities Review and re-teach Teacher Questions Graphic Organizer Primary Resources Assessment Students will make a chart the different positions on the artistic staff and their responsibilities. Students must analyze each position and determine which responsibilities will overlap. Students will dramatize a job interview scenario based on the different jobs. Before: Engage Have students set up a graphic organizer (Venn diagram). During: Explore Determine how the different jobs relate by completing the graphic organizer. After: Summarize Have students role play a scenario where each group member is interviewing for a different job. Technology Connection For more information, go to Job Descriptions SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) Page 3 of 18 Special Education Instructional Modifications/ Accommodations Determined by ARD/IEP SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) Before: Engage Have students use a preprinted graphic organizer. Page 4 of 18 Technical Theatre Level I – High School Week 3 Unit of Study: Producing the Play: The Behind-The-Scenes Staff TEKS Grades 9-12 (Content) I. 3. C. define the director’s role as a unifying force, problem-solver, interpreter of script, and collaborator Vocabulary Word Wall Stage Manager Grips Properties Chief Business Manager Publicity Manager House Manager Instructional Guidelines The teacher will: examine how a play is produced, including the responsibilities of each staff member present “word wall” vocabulary and definitions Student Behaviors Getting the Big Ideas Key Questions 4. Internet Resources: Reading/Writing and Theatre Arts: Research and Correlations College Prep Bilingual Word Wall Resources The Stage and the School Chapter 8 – Producing the Play pp. 339-373 First Grading Period TEKS Grades 9-12 (Skills and Processes) I. 3. D. define the director’s responsibility to the author’s intent, script, actors, designers, technicians, and the audience Rigor D Relev ance 5. 6. Who are the key members of a production staff, and what are their responsibilities? What items are included in a master production schedule checklist? How important is promoting a show? Learn how to stage a play by dividing tasks into manageable parts, preparing a schedule, and delegating responsibilities Learn how to make a promptbook. Discover the importance of promoting a play. Strategies Guided practice Role-playing Discussions Collaborating learning activities Review and re-teach Teacher Questions Primary Resources Assessment Students will analyze the different production jobs and their responsibilities. Students will create a prompt book page for a short scene from a play. Students will design and create a publicity poster for a play or a musical. Before: Engage How important is the production staff to the overall success of a production? During: Explore Create a page from a promptbook. Create a publicity poster for a play or musical After: Evaluate Have students present their posters to the class and discuss their design choices. Technology Connection For more information, go to Job Descriptions SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) Page 5 of 18 Special Education Instructional Modifications/ Accommodations Determined by ARD/IEP SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) Before: Engage Have students work in pairs to create the promptbook page and the poster design. Page 6 of 18 Technical Theatre Level I – High School Week 4 Unit of Study: Theatre and Other Art Forms TEKS Grades 9-12 (Content) I.1.F. analyze and describe the interdependence of all theatrical elements. Vocabulary Word Wall Theatre Composer Choreographer Ballet Modern Dance Tap dance Synthesis Performance Art College Prep Bilingual Word Wall Resources The Stage and the School Chapter 15 – Theatre and Other Art Forms pp. 563-583 Instructional Guidelines The teacher will: guide students as they examine the difference between Theatre Arts and other art forms present “word wall” vocabulary and definitions Student Behaviors Getting the Big Ideas Key Questions The Stage and the School Resource Binder Theatre and Other Art Forms: Study Guide Page 65-65 1 Rigor A Relev ance 2 3 Internet Resources: Reading/Writing and Theatre Arts: Research and Correlations First Grading Period TEKS Grades 9-12 (Skills and Processes) I.5.A. analyze and apply appropriate behavior at various types of live performances How would you distinguish the difference between theatre and the other fine arts? What has been the importance of music and dance throughout history? How important are other art forms in contemporary productions? distinguish theatre from the other fine arts explain how music and dance have evolved throughout history evaluate the importance of music, dance choreography, and set design to other art forms and media. Strategies Lecture Collaborating learning activities Discussions Guided Practice Review and Re-teaching Teacher Questions Graphic Organizer Primary Resources Assessment Students will demonstrate an understanding or characteristics that define theatre and distinguish it from the other fine arts through classroom discussions. Students will complete a graphic organizer that shows the evolution of music and dance throughout history. Students will evaluate the usage of music, choreography, and set design to represent theme, mood, character, and action in a videotaped production or movie. Before: Engage How important are other art forms in all types of productions? During: Explore Discover the evolution of music and dance by completing the graphic organizer. After: Summarize Explain how other art forms are used in contemporary productions to convey theme, mood, character, and action.. SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) Page 7 of 18 Special Education Technology Connection Instructional Modifications/ Accommodations Determined by ARD/IEP SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) Before: Engage Have students use a preprinted organizer. Page 8 of 18 Technical Theatre Level I – High School Week 5 Unit of Study: Stage Settings: Time and Setting TEKS Grades 9-12 (Content) I. 3. A. develop and practice stagecraft skills Vocabulary Word Wall Time Setting Conventions Mood Atmosphere Bilingual Word Wall Resources The Stage and the School Chapter 10 – Stage Settings pp. 397 – 402 Instructional Guidelines The teacher will: show students how sets define time, setting, style, mood, and atmosphere guide students on the basic principles of set design present “word wall” vocabulary and definitions Key Questions Internet Resources: Reading/Writing and Theatre Arts: Research and Correlations 1. Rigor B 2. Relev ance 3. What are the purposes of scenery in a play? What are the effects of scenery in a play? How does scenery define time and setting? Student Behaviors Getting the Big Ideas describe a set for one of the College Prep First Grading Period TEKS Grades 9-12 (Skills and Processes) I. 3. B. safely apply technical knowledge and skills to create ad/or operate functional scenery, properties, lighting, sound, costumes, makeup, and publicity scenes from a previously studied play discuss how the set helped establish the time, setting, and style of the play list a few of the “staging conventions” used in the theatre Strategies Guided practice Role-playing Discussions Collaborating learning activities Review and re-teach Teacher Questions Primary Resources Assessment Students will identify the use of scenery to convey the style of a particular play; Students will determine which scenic elements helped establish the time, setting, and style of a previously studied play. Students will identify the use of “staging conventions” in pictures and diagrams of sets from various plays. Before: Engage Have students discuss the different types of sets used in previously studied plays. During: Check for Understanding Have students list the effectiveness of the setting to convey: time, setting, style, mood, and atmosphere.. After: Evaluate Have students present pictures of sets and discuss the usage of “staging conventions” in each. Technology Connection For more information, go to Set Design SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) Page 9 of 18 Special Education Instructional Modifications/ Accommodations Determined by ARD/IEP SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) During: Check for Understanding Have students work in groups or pairs on their “staging conventions” presentations. Page 10 of 18 Technical Theatre Level I – High School Week 6 Unit of Study: Stage Settings: Development of Scenic Design TEKS Grades 9-12 (Content) I. 3. A. develop and practice stagecraft skills Vocabulary Word Wall Periaktoi Shutters Plastics Cut-outs Ground Row Box Set Unit Set Screen Set Curtain Set Skeleton Set Resources The Stage and the School Chapter 10 – Stage Settings pp. 403- 412 The Stage and the School Resource Binder Transparencies and Overlays Page 15 – Perspective Page 16 – Floor Plan College Prep Bilingual Word Wall Internet Resources: Reading/Writing and Theatre Arts: Research and Correlations First Grading Period TEKS Grades 9-12 (Skills and Processes) I. 3. B. safely apply technical knowledge and skills to create ad/or operate functional scenery, properties, lighting, sound, costumes, makeup, and publicity Instructional Guidelines The teacher will: guide students in discovering the changes in the development of scenic design throughout history show students the different types of sets show students how to convert measurements from different measurement scales Key Questions 1. Rigor B 2. Relev ance 3. How has scenic design developed from the Renaissance through modern times? What are some types of sets? What are some of the basic principles and considerations of set design? Student Behaviors Getting the Big Ideas Compare and contrast scenic design elements from Renaissance to today. Draw an overhead floor plan of a box set Draw a perspective of a box set Strategies Guided practice Role-playing Discussions Collaborating learning activities Review and re-teach Teacher Questions Primary Resources Assessment Students will use a graphic organizer to compare and contrast scenic elements from various periods in history. Students will compute the measurements needed to construct a floor plan in ½” scale. Students will draw both an overhead and perspective design of a box set to scale. Before: Engage Have students discuss changes in scenery throughout history. During: Check for Understanding Have students draw a floor plan and perspective of a set for a selected play. After: Evaluate Have students present their drawings to the class and discuss the scenic elements incorporated in their designs. Technology Connection For more information, go to Set Design SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) Page 11 of 18 Special Education Instructional Modifications/ Accommodations Determined by ARD/IEP SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) During: Check for Understanding Have students work in pairs on their overhead floor plans and perspective drawings. Page 12 of 18 Technical Theatre Level I – High School Week 7 Unit of Study: Stage Settings: Procedures in Scenic Design TEKS Grades 9-12 (Content) I. 3. A. develop and practice stagecraft skills Vocabulary College Prep Word Wall Rendering Unity Emphasis Proportion Balance Central Axis Color Coding Hue Value Shades Intensity Saturation Bilingual Word Wall Resources The Stage and the School Chapter 10 – Stage Settings pp. 412- 422 First Grading Period TEKS Grades 9-12 (Skills and Processes) I. 3. B. safely apply technical knowledge and skills to create ad/or operate functional scenery, properties, lighting, sound, costumes, makeup, and publicity Instructional Guidelines The teacher will: The Stage and the School Resource Binder Color Activity Page 50 guide students in discovering the “pre-design” and “artistic’ considerations to designing scenery present “word wall” vocabulary and definitions Key Questions 4. Rigor 5. C Relev ance Internet Resources: Reading/Writing and Theatre Arts: Research and Correlations 6. Why is it important to have a pre-design checklist? What artistic principles should a scenic designer consider? Why is color one of the most important elements of staging? Student Behaviors Getting the Big Ideas Design a chart for a “pre-design checklist”. Survey our auditorium based on the pre-design checklist. Draw both a pigment and light color wheel. Strategies Guided practice Role-playing Discussions Collaborating learning activities Review and re-teach Teacher Questions Primary Resources Assessment Students will create a pre-design checklist. Students will utilize their pre-design checklist to make a survey of our theatre. Students will explain the differences between primary and secondary colors, and their effects on creating mood and atmosphere. Before: Engage Why are available resources and artistic considerations important to set design? During: Check for Understanding Have students survey the school’s theatre for available resources based on a predesign checklist. After: Evaluate Have students demonstrate the effects of colors and hues on establishing mood and atmosphere. Technology Connection For more information, go to Set Design SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) Page 13 of 18 Special Education Instructional Modifications/ Accommodations Determined by ARD/IEP During: Check for Understanding Have students work in pairs on their checklists and color wheels. SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) Page 14 of 18 Technical Theatre Level I – High School Week 8 Unit of Study: Stage Settings: Constructing The Set TEKS Grades 9-12 (Content) I. 3. A. develop and practice stagecraft skills College Prep Vocabulary Word Wall Butt Joint Miter Joint Toggle Rails Sizing Floor Block Edging Walking Floating Running Scumable Spattering Rag Rolling Stippling Feather Dusting Dry Brushing Gridding Bilingual Word Wall Resources The Stage and the School Chapter 10 – Stage Settings pp. 423 - 445 First Grading Period TEKS Grades 9-12 (Skills and Processes) I. 3. B. safely apply technical knowledge and skills to create ad/or operate functional scenery, properties, lighting, sound, costumes, makeup, and publicity Instructional Guidelines The teacher will: The Stage and the School Resource Binder The Flat: Activity Page 44 Transferring A Backdrop Using a Grid Page 46 guide students in the design and construction of stage flats guide students in learning the various methods of texturing when painting flats present “word wall” vocabulary and definitions Student Behaviors Getting the Big Ideas Key Questions 7. Rigor 8. C Relev ance 9. How are flats constructed for the stage? How are flats safely assembled, moved, and stored in the theatre? Why is texturing important in making scenery appear convincing and alive? Label the various components of a stage flat Describe how you would paint various types of textures Construct a model of a flat to scale and apply a textured finish Strategies Guided practice Role-playing Discussions Collaborating learning activities Review and re-teach Teacher Questions Primary Resources Assessment Internet Resources: Reading/Writing and Theatre Arts: Research and Correlations Students will identify the different parts of a stage flat. Students will compute the measurements needed to construct a flat in ½” scale. Students will build a flat model. Before: Engage Why are flats considered the basic unit of construction for scenery in the theatre? During: Check for Understanding Build and texture a scale model flat (a life sized flat may be constructed.) After: Evaluate Have students demonstrate the effects of texturing on their model or life sized flats. Technology Connection For more information, go to Faux Texture Finishing SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) Page 15 of 18 Special Education Instructional Modifications/ Accommodations Determined by ARD/IEP During: Check for Understanding Provide students with a pre-labeled flat design. SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) Page 16 of 18 Technical Theatre Level I – High School Week 9 Unit of Study: Performance and Evaluation TEKS High School Theatre Arts Level I (Content) I.3.E. perform the roles of actor, ensemble member, and director in production decision-making and collaborate with others to producer theatre with a unified production for public performance I.3.F. concentrate in one or more areas of theatre production (acting, technical theatre, theatre management), demonstrating responsibility, artistic discipline, and creative problem solving Vocabulary The Stage and the School Bilingual Word Wall CH. 4 Acting Pages 97-157 Audience Etiquette Page 160 Assessing the Success of a Production Pages 555-559 Instructional Guidelines The teacher will: guide students as they examine all concepts presented to date. present an evaluation/critique sheet based on the concepts and elements to be demonstrated. facilitate the performance and critiques of monologues or scenes. Key Questions 1. Rigor D Relev ance College Prep TEKS High School Theatre Level I (Skills and Processes) I.3.E. perform the roles of actor, ensemble member, and director in production decision-making and collaborate with others to producer theatre with a unified production for public performance I.3.F. concentrate in one or more areas of theatre production (acting, technical theatre, theatre management), demonstrating responsibility, artistic discipline, and creative problem solving I.5.B. develop appropriate theatre vocabulary to apply the concepts of evaluation (intent, structure, effectiveness, value) to live theatre in written or oral from with precise and specific observations Resources Word Wall Basic Drama Projects Chapter 29– Critique a Performance Pages 384 – 395 How to Practice Critical Ethics Page 386 Basic Drama Projects Resource Binder Critique Sheet: Write a Critique and Discuss a Production Page 120 Internet Resources: Reading/Writing and Theatre Arts: Research and Correlations SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) First Grading Period 2. How can you best demonstrate skills and concepts learned to date through production? How important is objective and fair criticism in the review of a production?. Student Behaviors Getting the Big Ideas Demonstrate mastery of the skills and concepts learned by participating as a member of a stage crew for a production.. Understand and explore the elements of objective criticism. Strategies Guided practice Role-playing Discussions Collaborating learning activities Review and re-teach Teacher Questions Assessment Students will demonstrate the concepts and skills acquired to date through active participation as a technical crew member or assistant in a staged production Students will present a written and oral critique of performances as a member of a team. Before: What criteria do we use to critique performances? Have students list criteria for evaluating effective performances demonstrating acting concepts and skills.. During: Check for Understanding Have students work in small groups to prepare performances demonstrating acting concepts and skills. After: Evaluate Have students review the performancse through a written and oral critique based on the criteria agreed upon. Page 17 of 18 Special Education Instructional Modifications/ Accommodations Determined by ARD/IEP SAISD © 2007-08 High School Tech Theatre I (First Grading Period – Week 1) Technology Connection American Theatre Critics Association During: Check for Understanding Have students work in small groups to prepare performances and critiques. Page 18 of 18