AP World History
advertisement

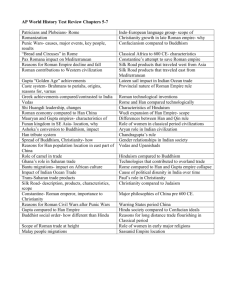
AP World History – Periods 2 and 6 Study Guide for 1st Unit Test (Chapters 1-7) Test: October 31st (Multiple choice part) and November 4th (DBQ in class) Study Tips: Follow the study guide below Don’t wait until a few days before to start studying & reviewing! Study your notes and the quizzes for Chapters 1-5. You may want to consider making index cards or typing up an outline as a way to review. The test format will consist of 70 multiple choice questions and one DBQ essay. Chapter 1 Culture Stone tool making Transition to plant & animal domestication Role of women in the transition to agriculture-based lifestyle Creation of agricultural communities Attributes of Civilization River Valley Civilizations – importance, reasons for them Agriculture in Mesopotamia Sumerians Ancient Egyptian Unification & Religion Indus Valley Civilization –characteristics and reasons for collapse Ancient civilizations and their famous accomplishments in architecture/infrastructure Chapter 2 Geographic features of the Chinese civilization (location and natural barriers) Mandate of Heaven Warring States Period Confucianism, Daoism, Legalism – major characteristics Chinese Dynasties – chronological order up to Han Technological accomplishments of the Chinese civilization (Shang and Zhou) Religious practices during Shang and Zhou dynasties (see power point on Ancient China) Cultural similarities of Olmec and Chavin civilizations Celtic culture (linguistic family, political composition, role of women) Nubia (location and interactions with Egypt) Chapter 3 Mycenaeans and Minoans – accomplishments and geographic location Hyksos Akhenaten Assyrian society, conquests, and methods of control Geographic extent of the Assyrian Empire (core region and conquered territories) Israelites Diaspora Tenets of Jewish faith & practice Phoenician economy Carthage and its army Chapter 4 The Medes King Cyrus – methods of controlling the empire (+ treatment of conquered peoples) King Darius – unified Persia (Iran) Major beliefs of Zoroastrianism Polis Acropolis Agora Hoplites Oligarchy Greek concept of democracy Staples of Greek farming Results of population explosion in Greece Humanism and Principles of Greek philosophical thought Famous Greek philosophers (Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle) and their main ideas/accomplishments Result of the Persian Wars Results of the Peloponnesian War Persia’s involvement in the Peloponnesian War The Hellenistic Age and its “cosmopolitan” features Chapter 5 Results of the Punic Wars ( Major reasons for the collapse of the Roman republic Paterfamilias Patron/Client relationship Transition from the Roman Republic to the Principate Christian beliefs and early conflict with the Roman authorities Stages in treatment of Christians by the Roman government Roman technological innovations Confucian view of family, state, and female behavior (“the three submissions”) China’s resources Standardizations and their purpose under Qin Dynasty Persecutions under Shi Huangdi Daoism and its appeal in the Chinese society Chinese exports during Han dynasty Silk Decline of the Han Dynasty Major similarities between Rome and Han China (politics, economy, society, religion, etc). Chapter 6 Vedic Age Caste (Varna) System in India Importance of Brahmins Rig Veda Nirvana Major elements/concepts of Hinduism Major elements/concepts of Buddhism Jainism “Four Noble Truths” Mauryan government & trade King Ashoka Gupta Empire “Theater state” Ancient Indian exports Scientific accomplishments of the Gupta Empire Collapse of the Gupta Empire Strategic regional importance of Southeast Asia Chapter 7 Silk Road (connections, geography, goods exchanged) Military technologies of the Silk Road Role of pastoralists in facilitating trade/exchange along the Silk Road Monsoon The Indian Ocean Maritime system (geography) Spread of religions along the trade networks The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea (pp.208-209) The Bantu Migration Linguistic legacy of the Bantu Migration “Great traditions and “small traditions” World Religions Monotheistic and polytheistic religions Geographic places of origin of Hinduism, Buddhism, Judaism, Christianity, and Islam Major tenets of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam Similarities and differences between Hinduism and Buddhism Role of women in Eastern Religious traditions The Caste system and other systems of social inequalities around the world Spread of Buddhism ALSO REVIEW/STUDY: Regions of the world Geographic locations of empires and their capital cities Primary Sources on Hinduism, Jainism, and Buddhism Primary and secondary sources in Chapter 7 DOCUMENT – BASED QUESTION for the test will be about factors that contributed to the spread of Buddhism and Christianity. So, review handouts and notes on Christianity from Chapter 5 and on Buddhism from Chapter 6. Content from Chapter 7 as well as Video Guides: Connections Across Land / Connections Across Water will also help you prepare for the writing part of the test!