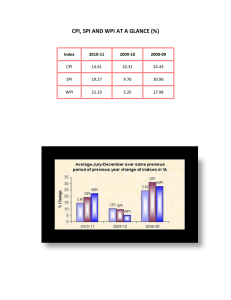
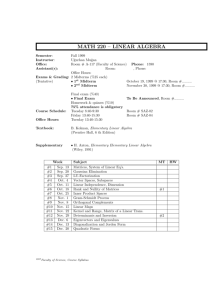
TQM 2 marks and 16 marks
advertisement

ANAND INSTITUTE OF HIGHER TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING GE2022 TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT UNIT –I PART –A 1. Define quality. It is to meet the customer‘s needs or satisfying the customer. Conformance to specifications, fitness for use 2. List the barriers of TQM One idea may be to look at new industry philosophies around continuous improvement. The adoption of 'way of working' philosophies and 'lean' philosophies and how they tie in with TQM. buzzwords such as 'empowerment', 'training' and 'knowledge-sharing' may be useful in researching seminars on such topics. look at how attitudes of employees are improved with 'growth involvement’. An interesting was the 'Fish Philosophy'. 3. What are the dimensions of quality? Performance—such as acceleration of a vehicle; Reliability—that the product will function as expected without failure; Features—the extras that are included beyond the basic characteristics; Durability—expected operational life of the product; and Serviceability—how readily a product can be repaired. 4. Name the criteria for manufacturing organization. Courtesy and friendliness of staff, promptness in resolving complaints, and atmosphere. Other definitions of quality in services include time—the amount of time a customer has to wait for the service. 5. Compare manufacturing and service organization Performance - Consistency Reliability - Responsiveness to customer needs Features - Courtesy/friendliness Durability - Timeliness/promptness Serviceability - Atmosphere 6. Define the concept of Deming philosophy Create and communicate to all employees a statement of the aims and purposes of the 1 company. Adapt to the new philosophy of the day; industries and economics are always changing. 7. Define TQM. TQM. - contributed to our knowledge and understanding of quality today 8. Factors that helps in improving the quality. Customer satisfaction, retention, empowerment 9. What is fitness of use? It focuses on how well the product performs its intended function or use. For example, a Mercedes Benz and a Jeep Cherokee both meet a fitness for use definition if one considers transportation as the intended function. 10. What is meant by support service? Support services provided are often how the quality of a product or service is judged. Quality does not apply only to the product or service itself; it also applies to the people, processes, and organizational environment associated with it. 11. Define quality assurance. Quality Assurance: TQM guarantees that all the products and even operations in the org. are of a certain quality standard. This promotes trust to the consumers and also maintains a healthy environment for employees. 12. Why do we need value for price paid? Value for price paid is a definition of quality that consumers often use for product or service usefulness. This is the only definition that combines economics with consumer criteria; it assumes that the definition of quality is price sensitive. 13. List the psychological criteria of the quality. Psychological criteria is a subjective definition that focuses on the judgmental evaluation of what constitutes product or service quality. Different factors contribute to the evaluation, such as the atmosphere of the environment or the perceived prestige of the product. For example, a hospital patient may receive average health care, but a very friendly staff may leave the impression of high quality. 14. Define the quality in manufacturing organization. Definitions of quality in manufacturing include performance—such as acceleration of a vehicle; reliability—that the product will function as expected without failure; features—the extras that are included beyond the basic characteristics; durability—expected operational life of the product; and serviceability—how readily a product can be repaired. 15. Differentiate manufacturing and service organization MANUFACTURING ORGANISATION Conformance to specifications 2 SERVICE ORGANIZATION Tangible factors Performance Consistency Reliability Responsiveness to customer needs Features Courtesy/friendliness Durability Timeliness/promptness Serviceability Atmosphere 16. What is meant by evolution of quality? Evolution of quality provides high degree of assurance that manufacturer will consistently produce medical devices that are safe Perform as intended Comply with customer requirements Comply with regulatory requirements Have the appropriate degree of quality 17. List first three quality gurus‘ in TQM. Walter A. Shewhart W. Edwards Deming Taylor 18. List the Pillars of TQM. Five Pillars of TQM are, · Product · Process · System · People · Leadership 19. Write the stages of industrial cycle applied by TQM. The TQM is applied to many stages of Industrial Cycle which are listed below: 1. Marketing 2. Engineering 3. Purchasing 4. Manufacturing 5. Mechanical 6. Shipping 7. Installation and product service. 20. Write the fundamental factors which affects quality. Fundamental factors affecting Quality: (9 M‘s) 1. Market 2. Money 3. Management 3 4. Men 5. Motivation 6. Materials 7. Machines and Mechanization 8. Modern Information Methods 9. Mounting Product Requirements PART-B 1. Discuss in detail about the basic concepts of quality. Definition of quality Example ` Fitness for use Value for price paid Benefits 2. Explain the dimensions of total quality management. performance—such as acceleration of a vehicle; reliability—that the product will function as expected without failure; features—the extras that are included beyond the basic characteristics; durability—expected operational life of the product; and serviceability—how readily a product can be repaired 3. What are terms that affect quality in manufacturing organization? a. Perform as intended b. Comply with customer requirements c. Comply with regulatory requirements d. Have the appropriate degree of quality 4. Explain in detail about the need for TQM Statistical sampling techniques were used to evaluate quality, and quality control charts were used to monitor the production process. The meaning of quality for businesses changed dramatically in the late 1970s. Before then quality was still viewed as something that needed to be inspected and corrected. However, in the 1970s and 1980s many U.S. industries lost market share to foreign competition. In the auto industry, manufacturers such as Toyota and Honda became major players. In the consumer goods market, companies such as Toshiba and Sony led the way. These foreign competitors were producing lower-priced products with considerably higher quality. To survive, companies had to make major changes in their quality programs. Many hired consultants and instituted quality training programs for their employees 5. State the points for Evolution of quality. Definition – evolution of quality Quality gurus Contribution by gurus Comments 4 UNIT – II PART-A 1. What is quality planning? Quality planning is the pre-determined activities in order to achieve conformation to the requirements 2. Differentiate customer satisfaction and retention. Customers are important asset to the organization, satisfied customers will buy more, Retention, buy more frequently, and pay their bill promptly 3. Define Employee involvement. Employee involvement is one approach to improve quality and productivity. It is not an replacement for management nor is it the final word in quality improvement, it aims at better meeting of organizational goals at all levels. 4. What is meant by empowerment? The dictionary meaning of the term empowerment is to invest people with authority. Its purpose is to tap the enormous potential that lies within every worker. 5. List the Types of teams · Process improvement teams · cross-functional teams · natural work teams · self-directed/ self managed teams 6. Define 5s concept. It simplifies your work environment, reduces waste and non-value activity while improving quality efficiency and safety. 7. How will you measure the supplier rating? It depends on the characteristics used to measure the performance of a particular process Quantity Cost Time 5 Accuracy Function 8. How will you retain the customer? Customer retention represents the activities that produce the necessary customer satisfaction which in turn creates the customer loyalty. Advantages of continuous process. Reduce resources Reduce errors Meet or exceed expectations of downstream customers Make the process safer 9. What is meant by performance appraisal? Employees potential, confidence, experience. 10. How many steps for strategic planning? There are seven basic steps to strategic quality planning. a) Customer needs b) Customer positioning c) Predict the future d) Gap analysis e) Closing the gap f) Alignment g) Implementation 11. Name the categories of quality cost. a) Internal failure costs - The cost associated with defects that are found prior to transfer of the product to the customer. b) External failure costs - The cost associated with defects that are found after product is shipped to the customer. c) Appraisal costs - The cost incurred in determining the degree of conformance to quality requirement. d) Prevention costs - The cost incurred in keeping failure and appraisal costs to a minimum. 12. How the quality of costs are estimated in a firm. The companies estimate quality costs for the following reasons: a) To quantifying the size of the quality problem in the language of money improves communication between middle managers and upper managers. b) To identify major opportunities for cost reduction. 6 c) To identify the opportunities for reducing customer dissatisfaction and associated threats to product salability. 13. How many types of customers? There are two types of customers. Internal customers - each of them receives a product or service and in exchange, providers a product or service. External customers - one who uses the product or service, the one who purchase the product, or the who influences the sale of the product. 14. Name Three key elements to a partnering relationship. Three key elements to a partnering relationship i Long-term commitment ii. Trust iii. Shared vision 15. What are the types of sourcing? Three types of sourcing a) Sole sourcing b) Multiple sourcing c) Single sourcing 16. List the two conditions for the selection and evaluation of suppliers The two conditions for the selection and evaluation of suppliers The supplier understands and appreciates the management philosophy of the organization. The supplier has a stable management system. 17. How to motivate work force? Know thyself Know your employees Establish a positive attitude Share the goals Monitor progress Develop interesting work Communicate Celebrate success 18. What is meant by empowerment? Empowerment is an environment in which people have the ability, the confidence, and thecommitment to take the responsibility and ownership to improve the process and initiate the necessary steps to satisfy customer requirements within well defined boundaries in order to achieve organizational values and goals. 7 PART-B 1. What are the ten conditions for the selection and evaluation of suppliers? The supplier understands and appreciates the management philosophy of the organization. The supplier has a stable management system. The supplier maintains high technical standards and has the capability of dealing with future technological innovations. The supplier can supply precisely those raw materials and parts required by the purchaser, and those supplied meet the quality specifications. The supplier has the capability to produce the amount of production needed or can attain that capability. There is no danger of the supplier breaching corporate secrets. The price is right and the delivery dates can be met. In addition, the supplier is easily accessible in terms of transportation and communication. The supplier is sincere in implementing the contract provisions. The supplier has an effective quality system and improvement program such as ISO/QS 9000. The supplier has a track record of customer satisfaction and organization credibility. 2. How to achieve the best quality through the customer? Definition of TQM Benefits Advantages Example – to show the best cost. 3. Explain the Traditional tools to improve the quality Traditional tools to improve the quality: Pareto diagram Affinity diagram Activity diagram 4. What is meant by QFD? explain. Quality Function Deployment (QFD) was developed to bring this personal interface to 8 modern manufacturing and business. In today's industrial society, where the growing distance between producers and users is a concern, QFD links the needs of the customer (end user) with design, development, engineering, manufacturing, and service functions. QFD is: Understanding Customer Requirements Quality Systems Thinking + Psychology + Knowledge/Epistemology Maximizing Positive Quality That Adds Value Comprehensive Quality System for Customer Satisfaction Strategy to Stay Ahead of The Game 5. Explain in detail about the cost of quality Example with cost of quality Draw a chart with the analysis 6. Write brief note theories of motivation. Herzberg‘s two factor theory Concept of work force. Empowerment Team work UNIT - III PART-A 1. List the seven traditional tools. i. Pareto Diagram ii. Process Flow Diagram iii. Cause and Effect Diagram iv. Check Sheets v. Histogram vi. Control Charts vii. Scatter Diagrams 2. What is meant by six sigma? It is a set of activities an organization uses to win and retain customers' satisfaction. it can be provided before, during, and after the sale of the product. 3. Define benchmark. It is systematic method by which organizations can measure themselves against the best industry practices. 4. Define Affinity diagram It is one of the tool to evaluate the quality of a product. 9 5. Draw Pareto diagram It is a diagrammatic tool to improve the quality. 6. Name the terms in benchmarking process. Planning Analysis Integration Action Maturity 7. What is meant by FMEA? FMEA is a systematic tool for identifying: effects or consequences of a potential product or process failure. methods to eliminate or reduce the chance of a failure occurring. 8. List the reasons to benchmark? The essence of benchmarking is the process of borrowing ideas and adapting them to gain competitive advantage. It is a tool for continuous improvement. 9. Two conditions for the selection and evaluation of suppliers The supplier understands and appreciates the management philosophy of the organization. The supplier has a stable management system. The supplier maintains high technical standards and has the capability of dealing with future technological innovations. 10. Name any 3 methods in six sigma concepts. Define : improvement opportunity with an emphasis on increasing customer satisfaction. Measure - determine process capability Analyze - identify the vital few process input variables that affect key product output variables (―Finding the knobs‖). 11. What is meant by kaizen? Kaizen is a Japanese word for the philosophy that defines management‘s role in continuously encouraging and implementing small improvements involving everyone. It is the process of continuous improvement in small increments that make the process more efficient, effective, under control and adaptable. 12. List the characteristics used to measure the performance of a process. i. ii. iii. iv. v. Quantity Cost Time Accuracy Function 13. What are the elements of customer services ? identify each market segment write down the requirements communicate the requirements organise processes organize the physical spaces 10 14. What is FMEA? It is a Failure Mode and Effective Analysis(FMEA) is a systematic tool for identifying: effects or consequences of a potential product or process failure. Methods to eliminate or reduce the chance of a failure occurring. FMEA generates a living document that can be used to anticipate and prevent failures from occurring. 15. Define loss function for one piece of product. Loss function for one piece of product: Where: L = Loss in Dollars y = Quality Characteristic (diameter, concentration, etc) m = Target Value for y k = Constant (defined below) 16. What is Taguchi‘s key argument? Taguchi's key argument was that the cost of poor quality goes beyond direct costs to the manufacturer such as reworking or waste costs. Traditionally manufacturers have considered only the costs of quality up to the point of shipping out the product. 17. What are the points focused by quality improvement? Increased Employee Value 18. List the qualities of QIT member. ♦commitment to quality, customer satisfaction, and the success of the organization ♦ ♦a big picture view of the organization and of the industry ♦ ♦ 19. List the steps in Benchmarking process Planning Analysis Integration Action 11 Maturity 20. What is meant by QFD? Quality Function Deployment is a planning tool used to fulfill customer expectations. It is a disciplined approach to product design, engineering, and production and provides in-depth evaluation of a product . PART-B 1. Explain the various methods of six sigma with example. Six Sigma Define - improvement opportunity with an emphasis on increasing customer satisfaction. Measure - determine process capability Analyze - identify the vital few process input variables that affect key product output variables (―Finding the knobs). Improve - Make changes to process settings, redesign processes, etc. to reduce the number of defects of key output variables. Control - Implement process control plans, install real-time process monitoring tools, and standardize processes to maintain levels. 2. Describe the seven traditional tools of TQM. i. Pareto Diagram ii. Process Flow Diagram iii. Cause and Effect Diagram iv. Check Sheets v. Histogram vi. Control Charts vii. Scatter Diagrams 3. What is meant by benchmark process? Explain. Benchmarking is a systematic method by which organizations can measure themselves against the best industry practices. The essence of benchmarking is the process of borrowing ideas and adapting them to gain competitive advantage. It is a tool for continuous improvement. BENCHMARKING PROCESS 1. Planning 2. Analysis 3. Integration 4. Action 5. Maturity 4. Discuss the various types of diagrams that are used to improve the quality? i. Affinity Diagram ii. Interrelationship Digraph iii. Tree Diagram iv. Matrix Diagram v. Prioritization Matrices 12 vi. Process Decision Program Chart vii. Activity Network diagram viii. 5. What are the objectives of Performance measures? Establish baseline measures and reveal trends. Determine which processes need to be improved. Indicate process gains and losses. Compare goals with actual performance. Provide information for individual and team evaluation. Provide information to make informed decisions. Determine the overall performance of the organization. 6. List the uses of six sigma. SERVICE QUALITY Customer service is the set of activities anorgaqnization uses to win and retain customers' satisfaction. it can be provided before, during, and after the sale fo the product. Elements of customer service are: Organization 1. Identify each market segment 2. Write down the requirements 3. Communicate the requirements 4. Organise processes 5. Organize the physical spaces Customer care 6. meet the customer's expectations 7. get the customer point of view 8. deliver what is promised 9. make the customer feel valued 10. respond to all complaints 11. over respond to the customer. 12. provide a clean and comfortable UNIT - IV PART-A 1. List the seven steps in quality planning Customer needs b) Customer positioning c) Predict the future d) Gap analysis e) Closing the gap 13 f) Alignment g) Implementation 2. What is meant by QFD? QFD links the needs of the customer (end user) with design, development, engineering, manufacturing, and service functions. 3. Define cost of quality. Quality cost is the extra cost incurred due to poor or bad quality of the product or service. 4. List the performance measures. Relevance to customer Improvement Cost Visible Timely 5. What is meant by Taguchi Quality loss function? The costs of quality would vary with the products deviation on either side of the mean. The squared-error loss function has been in use but Taguchi modified the function to represent total losses. 6. List the points for improvement needs. Customer retention Customer satisfaction Multiple sourcing 7. What is TPM? Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a maintenance program which involves a newly defined concept for maintaining plants and equipment. The goal of the TPM program is to markedly increase production while, at the same time, increasing employee morale and job satisfaction 8. Give three characteristics used to define the quality loss function. Nominal–the-Best Characteristic Smaller-the-Better Characteristic Larger-the-Better Characteristic 9. What are the requirements of improvement needs? Increased Employee Value Informed Employees Technical Training Quality Training 10. Use of Taguchi quality loss function. a. To improve the quality b. To get the market retention 14 11. What are the benefits of QFD? i. Customer driven ii. Reduces implementation time iii. Promotes teamwork iv. Provides documentation 12. What are the steps required to construct an affinity diagram? i. Phrase the objective ii. Record all responses iii. Group the responses iv. Organize groups in an affinity diagram 13. What are the parts of house of quality? i. Customer requirements ii. Prioritized customer requirements iii. Technical descriptors iv. Prioritized technical descriptors v. Relationship between requirements and descriptors vi. Interrelationship between technical descriptors 14. How will you build a house of quality? List customer requirements List technical descriptors Develop a relationship matrix between WHATs and HOWs\ Develop an interrelationship matrix between HOWs Competitive assessments Develop prioritized customer requirements Develop prioritized technical descriptors 15. Define FMEA? Failure Mode Effect Analysis is an analytical technique that combines the technology and experience of people in identifying foreseeable failure modes of a product or process and planning for its elimination. 16. What is meant by larger-the better? The Larger–the-Better characteristic is just the opposite of the Smaller-the-Better characteristc. For this characteristic type, it is preferred to maximize the result, and the ideal target value is infinity. 17. What is meant by Smaller-the- Better? Smaller-the-Better characteristic, the ideal target value is defined as zero. An example of this characteristic is minimization of heat losses in a heat exchanger. Minimizing this characteristic as much as possible would produce a more desirable product. 18.Define nominal upper and lower boundaries For a nominal characteristic, there is a defined target value for the product which 15 has to be achieved. There is a specified upper and lower limit, with the target specification being the middle point. Quality is in this case is defined in terms of deviation from the target value. An example of this characteristic is the thickness of a windshield in a car. 19. The objectives of Performance measures i. Establish baseline measures and reveal trends. ii. Determine which processes need to be improved. iii. Indicate process gains and losses. iv. Compare goals with actual performance PART – B 1. Explain Quality Loss Function for Various Quality Characteristics with example. The costs of quality would vary with the products deviation on either side of the mean. Now if you were to plot the costs versus the diameter of a nut, for example, you would have a quadratic function, with a minimum of zero at the target diameter. We expect therefore that the loss (L) will be a quadratic function of the variance (σ, or standard deviation) from the target (m). The squared-error loss function has been in use since the 1930's, but Taguchi modified the function to represent total losses. 2. Describe the concepts of QFD. Quality Function Deployment is a planning tool used to fulfill customer expectations. It is a disciplined approach to product design, engineering, and production and provides in-depth evaluation of a product. Quality Function Deployment (QFD) was developed to bring this personal interface to modern manufacturing and business. In today's industrial society, where the growing distance between producers and users is a concern, QFD links the needs of the customer (end user) with design, development, engineering, manufacturing, and service functions. QFD is: 1. Understanding Customer Requirements 2. Quality Systems Thinking + Psychology + Knowledge/Epistemology 3. Maximizing Positive Quality That Adds Value 4. Comprehensive Quality System for Customer Satisfaction 5. Strategy to Stay Ahead of The Game 3. What are the stages of FMEA? 1. Specifying possibilities a. b. c. d. e. Functions Possible failure modes Root causes Effects Detection/Prevention 16 2. Quantifying risk a. Probability of cause b. Severity of effect c. Effectiveness of control to prevent cause d. Risk priority number 4. Correcting high risk causes a. Prioritizing work b. Detailed action c. Assigning action responsibility d. Check points on completion 4. Revaluation of risk a. Recalculation of risk priority number 4.What are the goals of TPM? List the basic steps to get an organization started toward TPM. The overall goals of Total Productive Maintenance, which is an extension of TQM are i. ii. iii. iv. v. Maintaining and improving equipment capacity Maintaining equipment for life Using support from all areas of the operation Encouraging input from all employees Using teams for continuous improvement Give the seven basic steps to get an organization started toward TPM a) b) c) d) e) f) g) Management learns the new philosophy Management promotes the new philosophy Training is funded and developed for everyone in the organization Areas of needed improvement are identified Performance goals are formulated An implementation plan is developed The several types of FMEA Design FMEA Process FMEA Equipment FMEA Maintenance FMEA Concept FMEA Service FMEA System FMEA Environment FMEA 5. Derive the Taguchi‘s Loss function. Loss function for one piece of product: 17 Where: L = Loss in Dollars y = Quality Characteristic (diameter, concentration, etc) m = Target Value for y k = Constant (defined below) The cost of the counter measure, or action taken by the customer to account for a defective product at either end of the specification range, Ao, is found by substituting y = m + 0 into the loss function: 6. Describe the Categories of Quality Cost. Many companies summarize quality costs into four broad categories. They are, a) Internal failure costs - The cost associated with defects that are found prior to transfer of the product to the customer. b) External failure costs - The cost associated with defects that are found after product is shipped to the customer. c) Appraisal costs - The cost incurred in determining the degree of conformance to quality requirement. d) Prevention costs - The cost incurred in keeping failure and appraisal costs to a minimum. UNIT-V Part A 1. Why ISO 9000 is needed? ISO 9000 is needed to unify the quality terms and definitions used by industrialized nations and use terms to demonstrate a supplier‘s capability of controlling its processes. 2. Define ISO9000-2000. ISO 9000 is a series of quality management systems standards created by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), a federation of 132 national standards bodies. 3. What is ISO 14000? It is series of environmental management systems (EMS) standards, providing a framework for organizations to demonstrate their commitment to environmental responsibility. 4. List 4 benefits of ISO 9000. Fewer on-site audit by customers. Increased market share 18 5. Advantages of ISO14000. Improved quality, both internally and externally. Improve product and service quality levels from suppliers. Greater awareness of quality by employees. 6. List some organization which has ISO standards. Neda Telecommunications, district passport office-Delhi, Computer Maintenance corporation, Infosys. 7. What are the requirements for ISO? General requirements Environmental policy Planning Implementation and operation Checking and corrective action 8. What is meant by auditing? Determine the actual performance conforms to the documented quality systems 9. Define hazard analysis. Hazard Analysis of Critical Control Points (HACCP), enforced by such agencies as the US Department of Agriculture's Food and Safety Inspection Service (FSIS) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), is a scientific process control system for eliminating contaminants at critical areas in the food production and distribution process. 10. What is meant by Malcolm Baldrige Criteria? Malcolm Baldrige Criteria is a set of guidelines written and used as a yardstick to assess if an organization is able to meet a business excellence level 11. Give some other quality systems? QS-9000 TE-9000 AS9000 12. Give the objectives of the internal audit? a) Determine the actual performance conforms to the documented quality systems. b) Initiate corrective action activities in response to deficiencies. c) Follow up on noncompliance items of previous audits. d) Provide continued improvement in the system through feedback to management. 13. What are the requirements of ISO 14001? General requirements Environmental Planning Implementation and operation Checking and corrective action Management review policy 14.What are the four elements for the checking & corrective action of ISO 14001? a) Monitoring and measuring 19 b) Nonconformance and corrective and preventative action c) Records d) EMS audit 15.Give the types of Organizational Evaluation Standards? Environmental Management System Environmental Auditing Environmental Performance Evaluation 16. Give the types of Product Evaluation Standards? Environmental Aspects in Product Standards Environmental Labeling Life-Cycle Assessment 17.What are the four elements for the planning of ISO 14001? a) Environmental aspects b) Legal and other requirements c) Objectives and targets d) Environmental Management Programs 18.What are the benefits of ISO? Fewer on-site audit by customers. Increased market share. Improved quality, both internally and externally. Improve product and service quality levels from suppliers. Greater awareness of quality by employees. A documented formal systems. Reduced operating costs. 19. Give the ISO 9001 requirements? Scope Normative Reference Terms and Definitions Quality Management System Management Responsibility Resource Management Product Realization PART-B 1. Describe in detail about ISO9000 and ISO 14000. ISO 9000 is a series of quality management systems standards created by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), a federation of 132 national standards bodies. The ISO 9000 quality management systems (QMS) standards are not specific to products or services, but apply to the processes that create them. The standards are generic in nature so that they can be used by manufacturing and service industries anywhere in the world. First released ISO 14000, released in 1996, is a global series of environmental management systems (EMS) standards, providing a framework for organizations to 20 demonstrate their commitment to environmental responsibility. An EMS enables an organization to control the environmental aspects and impacts of its activities, products and services by establishing targets and objectives related to identified environmental management goals. 2. Why auditing is required to improve the quality? Explain. The environmental management systems (EMS) standards, providing a framework for organizations to demonstrate their commitment to environmental responsibility. a) Initiate corrective action activities in response to deficiencies. b) Follow up on noncompliance items of previous audits. c) Provide continued improvement in the system through feedback to management. The above are the primary objectives of audit. The environmental aspects and impacts of its activities, products and services by establishing targets and objectives related to identified environmental management goals. Once implemented, an EMS will improve compliance with legislative and regulatory requirements, reduce exposure to liability, prevent pollution, reduce waste and create a more positive public image. 3. Explain the concept of Malcome Bridge criteria. The Malcolm Baldrige Criteria is a set of guidelines written and used as a yardstick to assess if an organization is able to meet a business excellence level. The Baldrige Criteria has seven categories which of its own clearly states its objectives and guidelines. The seven categories are listed below:1. Leadership 2. Strategic Planning 3. Customer and Market Focus 4. Information and Data Analysis 5. Human Resource Management and Development 6. Process Management 7. Business Results Take a closer look and you may notice that the Baldrige Criteria are build upon a set of values and concepts as opposed to how TQM Principles are used in Total Quality Management. There are eleven values and concepts in the Baldrige Criteria listed below:1. Visionary Leadership 2. Customer-Driven Excellence 3. Organizational and Personal Learning 4. Valuing Employees and Partners 5. Agility 6. Focus on the Future 7. Managing for Innovation 8. Management by Fact 9. Public Responsibility and Citizenship 10. Focus on Results and Creating Value To ensure the application of these values and concepts, they are embodied in the detail Baldrige Criteria categories mentioned above. Each category has set up its own criteria to the highest standard of Business Excellence. While the values and concepts remain quite unchanged 21 over the years, the detail criterion for each category has changed every year. The objective for yearly changes to the criteria is to ensure it is reviewed and kept current to the business and environment changes and needs. 4. Describe in detail about the concept of hazard analysis? Hazard Analysis of Critical Control Points (HACCP), enforced by such agencies as the US Department of Agriculture's Food and Safety Inspection Service (FSIS) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), is a scientific process control system for eliminating contaminants at critical areas in the food production and distribution process. HACCP helps to prevent, as close to 100 percent as possible, harmful contamination in the food supply. To ensure safer food, HACCP requires the following seven principles to be followed: Conduct a hazard analysis Identify critical control points (CCPs) Establish critical limits for CCPs Establish monitoring procedures Establish corrective actions and verification procedures 5. What are the seven elements for the implementation & operations of ISO 14001? Structure and responsibility Training, awareness and competency Communication EMS documentation Documentation control Operational control Emergency preparedness and response 6. Give the ISO 9000 Series of Standards? ISO 9000, ―Quality Management and Quality Assurance Standards Guidelines for Selection and Use ISO 9001, ―Quality Systems – Model for Quality Assurance in Design, Development, Production, Installation & Servicing ISO 9002 - Quality Systems – ―Model for Quality Assurance in Production ,installation & servicing ISO 9003, ―Quality Systems – ―Model for Quality Assurance in Final Inspection and Test‖. ISO 9004-1, ―Quality Management and Quality System Elements – Guidelines 22 ANAND INSTITUTE OF HIGHER TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING GE2022 TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT UNIVERSITY QUESTIONS (2 Marks) UNIT-1 1. List down any two of the analysis techniques for quality cost. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 2. Define quality as per crosby (APRIL/MAY 2008) 3. What are the seven faces of Quality? (APRIL/MAY 2009) 4. Define Strategic planning. (APRIL/MAY 2009) 5. How can quality be quantified? (NOV/DEC 2011) 6. What are the benefits of TQM? (NOV/DEC 2011) 7. List the various factors which constitute the frame work of TQM. (APRIL/MAY 2012) 8. Define the tools required to implement kaizen in a manufacturing system. (APRIL/MAY 2012) 9. List out the six basic concepts of Total Quality Management. (NOV/DEC 2012) 10. What are four absolutes of quality observed by Crosby? (NOV/DEC 2012) 11. What are the elements of TQM? (MAY/JUNE 2013) 12.What do you mean by service quality? (MAY/JUNE 2013) UNIT-II 1. Explain service quality. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 2. Explain kaizen. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 3. Why do the business people measure customer satisfaction? (APRIL/MAY 2009) 4. What are the strategic goals of performance measure? (APRIL/MAY 2009) 5. What are the important habits of quality leader? (NOV/DEC 2011) 6. Name a few barriers to Team’s progress. (NOV/DEC 2011) 7. How are the customer needs and requirements documented? (APRIL/MAY 2012) 8. What are the benefits of 5’s? (APRIL/MAY 2012) 9. State the importance of customer retention. (NOV/DEC 2012) 10. What is Kaizen? (NOV/DEC 2012) 11. List the characteristics of successful quality leaders. (MAY/JUNE 2013) 12. List out any four benefits of Employee involvement. (MAY/JUNE 2013) UNIT-III 1. Mention the various measurements of dispersion. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 2. List down the seven tools of quality. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 3. Mention the ways to reduce variability. (APRIL/MAY 2009) 4. Mention the uses of Control chart. (APRIL/MAY 2009) 5 What are the benefits of Benchmarking? (NOV/DEC 2011) (NOV/DEC 2012) 6. Name some new management tools. (NOV/DEC 2011) 7. What are the benefits of TPM? (APRIL/MAY 2012) 23 8. What are the problems involved in benchmarking a direct competitor. (APRIL/MAY 2012) 9. Describe the evolution of six sigma in Motorola Company. (NOV/DEC 2012) 10. What are the types of check sheets commonly used? (MAY/JUNE 2013) 11. What is bench marking? Give an example. (MAY/JUNE 2013) UNIT-IV 1. List down the types of FMEA. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 2. Explain benchmarking process. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 3. What are the goals of TPM? (APRIL/MAY 2009) 4. List out various techniques adopted for JIT. (APRIL/MAY 2009) 5. How can QFD be deployed? (NOV/DEC 2011) 6. What is the formula for measuring equipment effectiveness? (NOV/DEC 2011) 7. What does “DMAIC” convey in six sigma? (APRIL/MAY 2012) 8. What is meant by “House of Quality”? (APRIL/MAY 2012) 9. What is Taguchi quality loss function? (NOV/DEC 2012) 10. Draw the general structure of house of quality. (NOV/DEC 2012) 11. What are the functions of quality circles? (MAY/JUNE 2013) 12. List the objectives of TPM programme. (MAY/JUNE 2013) UNIT-V 1. What do you understand by NCR. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 2. Explain the need for ISO 14000 QUALITY SYSTEMS. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 3. Define environmental policy. (APRIL/MAY 2009) 4. What are the elements of a Quality Systems? (APRIL/MAY 2009) 5. What are the general requirements of quality management system? (NOV/DEC 2011) 6. Draw the documentation pyramid. (NOV/DEC 2011) 7. Define the term “quality loss function”. (APRIL/MAY 2012) 8. List down the main elements of ISO-14000. (APRIL/MAY 2012) 9. List out the global benefits of adopting ISO 9000 quality system. (NOV/DEC 2012) 10. Differentiate between ISO 9000 and Qs 9000. (NOV/DEC 2012) 11. What are organization standards and product standards? (MAY/JUNE 2013) 12. What is the concept of environmental management system? (MAY/JUNE 2013) 24 ANAND INSTITUTE OF HIGHER TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING GE2022 TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT UNIVERSITY QUESTIONS (16 Marks) UNIT-1 1 i. Explain about quality council and quality planning ii. Explain about Deming’s philosophy (APRIL/MAY 2008) 2 i. Explain the contribution of juran to the quality movement. ii. Discuss about the implementation steps of TQM and mention the importance of the management commitment. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 3. What are the different definitions given for quality? Explain how it got evolved and what are its prime concerns.(16) (APRIL/MAY 2009) 4.i Discuss the management techniques for establishing quality costs.(8) ii Describe the various Quality Statements. Give examples.(8) (APRIL/MAY 2009) 5 i Describe the six basic concepts of TQM. (8) ii Explain the various dimensions of quality. (8) (NOV/DEC 2011) 6 i Discuss the Deming’s philosophy for TQM. (8) ii Explain the barriers to TQM implementation and solution. (8) (NOV/DEC 2011) 7. Discuss Juran’s principles of quality improvement.(16) (APRIL/MAY 2012) 8. Explain Deming’s fourteen point philosophy for quality improvement. (16) (APRIL/MAY 2012) 9. i Elaborate the Deming’s philosophy over the quality and productivity improvement.(10) ii Describe the barriers in the implementation of TQM. (6) (NOV/DEC 2012) 10.Consider any one service organization of your choice and explain the various dimensions of quality of service.(16) (NOV/DEC 2012) 11.i.Explain the characteristics of TQM derived from its definitions.(8) ii.Explain the Juran’s views of TQM.(8) (MAY/JUNE 2013) 12. i."Various difficulties can be anticipated in the implementation of TQM programme “.Validate the statement. (8) ii.Discuss in detail the dimensions of Quality in the context of ‘Service’.(8) (MAY/JUNE 2013) UNIT-II 1. Explain the following i. Juran triology ii. PDSA cycle iii. Maslow’s theory of need hierarchy. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 2. Discuss about the supplier partnership procedures. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 3 i Explain the key elements of partnering.(8) ii Explain the conditions for selection and evaluation of suppliers.(8) (APRIL/MAY 2009) 25 4 i Compare Deming and Juran approaches.(8) ii Explain the importance of customer satisfaction.(8) (APRIL/MAY 2009) 5 i Write about the system of recognition and reward followed in an organization. (12) ii What are the suggestions to improve the appraisal system? (4) (NOV/DEC 2011) 6 Explain the different approaches towards Continuous Process Improvement.(16) (NOV/DEC 2011) 7. i Give an example for “win/win” and “win/lose” strategy in day to day life.(6) ii Design a customer satisfaction questionnaire to evaluate the level of customer satisfaction in the following industries.(10) (APRIL/MAY 2012) 1.A mobile service provider. 2. A sport shoe manufacturer. 8.i Discuss how quality council is structured in 1. University Academic Department 2. Manufacturing facility (12) ii Distinguish between internal and external customers.(4) (APRIL/MAY 2012) 9. i Explain the PDCA improvement cycle in detail. (10 ii Brief on employee empowerment. (6) (NOV/DEC 2012) 10. What is a team? Explain the functions and characteristics of a successful team. (16)(NOV/DEC 2012) 11.i.What is meant by strategic planning? Narrate the seven steps procedure of strategic planning cycle.(8) (MAY/JUNE 2013) ii.Explain the characteristics of successful team?(8) (MAY/JUNE 2013) 12..i.Explain the phases of PDSA cycle with suitable illustration.(8) ii.Write about quality statement and customer orientation.(8). (MAY/JUNE 2013) UNIT-III 1. Explain about the new seven tools of quality and its applications in detail. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 2. Discuss about the need, types, construction, and applications of control charts. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 3. Explain the different types of control charts available for problem solving. Enumerate on the different patterns commonly noticed in control charts.(16) (APRIL/MAY 2009) 4.With a specific application compare the affinity diagram and relationship diagram in terms of getting highly creative solutions for managerial problems.(16) (APRIL/MAY 2009) 5 i Explain the relevance of 6-sigma concept in achieving quality output in a process. (12) ii Give an example of a company practicing six-sigma concept. (4) (NOV/DEC 2011) 6 i What is Benchmarking and why do the organizations adopt this technique? (2+4) ii Explain the Benchmarking process. (10) (NOV/DEC 2011) 7 i Perform an FMEA to anticipate various problem faced and method to eliminate the process of “getting up from bed in the morning and going to school”. (10) ii. Describe how simultaneous or concurrent design is better over sequential design in guarantying to the end users. (6) (APRIL/MAY 2012) 8. i With an example illustrate how benchmarking can help a system to improve both efficiency and effectiveness of a system.(8) 26 ii. With examples explain the concept of six sigma.(8) (APRIL/MAY 2012) 9. Discuss the new seven tools in detail with their typical application. (16) (NOV/DEC 2012) 10. Discuss the reasons for benchmarking and state the advantages and limitations.(16) (NOV/DEC 2012) 11..i.Explain how benchmarking improves product/process quality. (8) ii.Describe the various stages in FMEA.(8) (MAY/JUNE 2013) 12.i.Listout the new seven management tools and explain any two in detail.(8) ii.What is Six sigma concept?How can it be effective in a service organization.(8). (MAY/JUNE 2013) UNIT-IV 1. Discuss about the objectives, process, outcome and benefits of quality functional deployment (QFD). (APRIL/MAY 2008) 2. Explain briefly about the following i. Taguchi quality loss function. ii. Pillars of TPM. (APRIL/MAY 2008) 3. Describe the different benchmarking metrics that can be used in educational institutions.(16) (APRIL/MAY 2009) 4. Explain the different steps involved in Failure Mode Effect Analysis with an example.(16) (APRIL/MAY 2009) 5 Explain the seven step plan to establish the TPM in an organization in detail. (NOV/DEC 2011) 6 Explain the concept of Taguchi's quality loss function in detail. Give an example (NOV/DEC 2011) 7. Devise a QFD methodology for design and development of cups used in vending machine for dispersing hot and cold beverages. (16) (APRIL/MAY 2012) 8. i. Discuss the benefits of QFD.(6) ii. For an out of round condition (smaller the better) of a steel shaft, the true indicator readings for eight shafts are 0.05,0.04,0.04,0.03,0.04,0.02,0.04 and 0.03 mm, (10) (APRIL/MAY 2012) 1. If the average loss at 0.03 is Rs.15, what is the loss function? 2. What is the loss at 0.05? 3. What is the average loss? 9 i What are the goals of TPM and explain the six losses in TPM?(10) ii Expalin the componenets of Quality costs.(6) (NOV/DEC 2012) 10 Write notes on : i. QFD (8) iiQuality circles (4) iii Typical performance measures of TQM.(4) (NOV/DEC 2012) 11..With suitable example explain various stages of building a house of quality matrix.(16) (MAY/JUNE 2013) 12.i Explain the different types of cost contributing to the cost of quality.(8) ii Explain the Taguchi’s quadratic quality loss function. How it differs from traditional approach of quality loss cost?(8) (MAY/JUNE 2013) 27 UNIT-V 1. Explain about the philosophy and the requirements of ISO 9000:2000 (APRIL/MAY 2008) 2. i. Discuss about the documentation process in ISO 9000:2000 system. ii. Explain about the auditing process and role of external agencies (APRIL/MAY 2008) 3. List the different types of quality audits available in practice and explain when each has to be carried out? (APRIL/MAY 2009) 4. i Explain the requirements of Environmental Management Systems.(8) ii Discuss the benefits of environmental management systems.(8) (APRIL/MAY 2009) 5 i Explain the benefits of EMS. (8) ii Discuss quality auditing in detail. (8) (NOV/DEC 2011) 6 Discuss the implementation of TQM with a case study from the manufacturing industry. (NOV/DEC 2011) 7. i Discuss the need for standardization procedures for quality assurance. Explain the requirements of ISO system of documentation.(10) ii. Expalin the term quality cost(6) (APRIL/MAY 2012) 8.i Differentiate between external and internal audits on quality.(6) ii. Differentiate between ISO 9000 and QS 14000.List the benefits that a firm would enjoy by implementing these series of quality documentation procedures.(10) (APRIL/MAY 2012) 9 i Discuss the elements of ISO 9000:2000 qulaity system (10) ii What are the gains realized by a company with the TQM implementation.(6) (NOV/DEC 2012) 10. What methodology would you suggest to implement TQM in an automobile manufacturing company? (16). (NOV/DEC 2012) 11..i Explain the major clauses of QS 9000 standards.(8) ii.Discuss the benefits of ISO 9000 certification.(8) (MAY/JUNE 2013) 12.List and explain the elements of ISO 9000 quality system.(16) (MAY/JUNE 2013) 28