AP Statistics: Describing Relationships - Chapter 3 Syllabus
advertisement

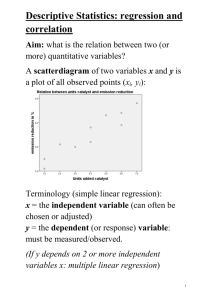
Name ___________________________ Chapter 3 Syllabus - AP Statistics - A Describing Relationships Chapter Objective: Students will study the importance of relationships between quantitative variables, use scatterplots to display the relationship, and describe the relationship using correlation, linear association, and a leastsquares regression model. Day 1 9/27 TOPICS: ▪Explanatory and response variables ▪Scatterplots ▪Correlation Day 2 10/1 TOPICS: ▪Scatterplots ▪Correlation ▪Interpret a regression line ▪Making Predictions ▪Extrapolation Introduction – Chapter 3 Project 3.1 – Scatterplots and Correlation Concepts and Skills to Master: ►Identify explanatory and response variables in situations where one variable helps explain or influences the other ►Construct a scatterplot to display the relationship between two quantitative variables ►Describe the direction, form, and strength of the overall pattern of a scatterplot ►Recognize outliers in a scatterplot ►Know the basic properties of correlation ►Calculate and interpret correlation ►Explain how the correlation r is influenced by extreme observations II. Assignments A. Warm Up B. Chapter 3 Project; due ___OCT. 8th ___ C. CYU p.144, 149, 154 D. Technology Lab: Scatterplots and Correlation III. Homework A. Reading Guide 3.1 B. Pages 158-159 #2, #6, #7, #11, #14 I. 3.1 – Scatterplots and Correlation 3.2 – Least Squares Regression I. Concepts and Skills to Master: ►Know the basic properties of correlation ►Calculate and interpret correlation ►Explain how the correlation r is influenced by extreme observations ►Interpret the slope and y intercept of a leastsquares regression line in context. ►Use the least-squares regression line to predict y for a given x ►Explain the dangers of extrapolation II. Assignments A. Warm Up B. Homework Q & A C. Chapter 3 Project D. Classwork – 3.1 Quiz handout I. Homework A. Textbook: pages 160-162 #14 – 18, #21, #26 B. Reading Guide 3.2 C. Chapter 3 Project Syllabus continued on back… Essential Questions To Answer 1. 2. 3. 4. What is a relationship between two or more variables? How can we examine it? What type of variables impact association studies? How are they displayed? Where are the individuals in a graphical representation of bivariate data? What is the difference between independent and dependent variables and explanatory and response variables? 5. What are confounding (‘lurking’) and other variables? 6. If the overall pattern of a bivariate observation is regular, how can we describe it by a smooth curve that is a mathematical model? 7. Why are residual plots used to determine linearity in the association of bivariate data? 8. What is the distinction between association and causation? 9. What is the distinction between association and independence? Day 3 10/3 TOPICS: ▪Residuals and the LeastSquares Regression Line ▪Calculating the Equation of the LeastSquares Regression Line ▪Computer Regression Output ▪Residual Plots Day 4 10/5 QUIZ 3.2 – Least-Squares Regression I. Concepts and Skills to Master: ►Calculate the equation for the least squares regression line ►Calculate and interpret residuals in context ►Explain the concept of least squares ►Find the slope and intercept of the least squares regression line from the means and standard deviations of x and y and their correlation ►Construct and interpret residual plots to assess if a linear model is appropriate II. Assignments A. Warm Up B. Homework Q & A C. Technology Lab D. Classwork – pages 162-163 #27-32 III. Homework A. Chapter 3 Project B. Textbook: pages 191-192 #36, 38, 40, 43, 45, 47, 53 C. Chapter 3 Take Home Quiz - Study for Quiz 3.2 Least Squares Regression I. Concepts and Skills to Master: ►Use the standard deviation of the residuals to assess how well the line fits the data ►Use r2 to assess how well the line fits the data ►Interpret the standard deviation of the residuals and r2 in context ►Identify the equation of a least squares regression line from computer output ►Explain why association doesn’t imply causation Recognize how the slope, y intercept, standard deviation of the residuals, and r2 are influenced by extreme observations I. Assignments A. HW Q & A B. Class Discussion – Concepts and Skills To Master C. Guided Notes D. Quiz II. Homework A. Textbook: pages 192-197 #49, 54, 58-61, 71-78 B. Complete Chapter 3 Project TEST Chapters 1- 4 Test PROJECT : Due Tuesday, Oct. 9th Monday – 10.15.2012 Chapter 3 Vocabulary Coefficient of Determination Correlation r (correlation coefficient) Influential Observations Least Squares Regression Line Residual plot Direction Extrapolation Linear Regression Line Response Variable Explanatory Variable Form and Strength Negative and Positive Association Residual Scatterplots