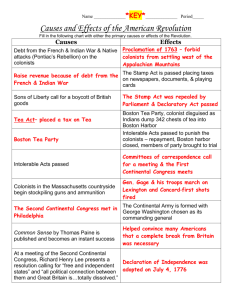
Act Provisions Colonists Reaction Result

Name_________________ Date _______________ Period ____ Mrs. Napolitano
Colonists Reaction Result
Stamp Act
Townshend
Act
Put a tax on legal documents such as wills, diplomas, marriage papers, newspapers almanacs, playing cards and dice.
The Townshend Act taxed glass, paper, paint, lead, and tea and other goods. It established new ways to collect taxes. Customs officials were sent to the colonies and were allowed to use
writs of assistance to enforce the law.
Quartering
Act
Under the Quartering
Act colonists had to provide housing, candles, bedding, and beverages to British soldiers stationed in the colonies.
Riots broke out. Mobs burned down houses and tarred and feathered tax collectors.
They boycotted British goods.
Colonists once again protested that this was “taxation without representation” and writs of assistance violated their rights as
British citizens.
Colonists boycotted (non-importation agreements) British goods. Colonists also burned British officials in effigy, paraded, and petitioned the
British government.
Many colonists believed the
Quartering Act was a clear violation of the English Bill of Rights of 1689.
The New York Assembly refused to
Obey the Quartering Act.
British merchants suffered. Trade fell
by 14%. In 1766
Parliament repealed the Stamp Act.
British merchants hurt by the non-importation agreements pressured Parliament to repeal the taxes.
The Townshend Act was repealed by Parliament in
1770.
King George III dismissed the
NY assembly. The
Quartering Act was eventually
repealed by Parliament in 1770.
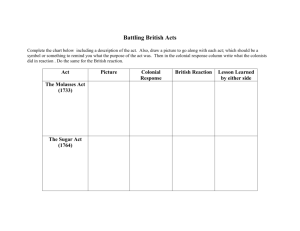
Sugar Act
Tea Act
Colonists Reaction
The Sugar Act replaced
an earlier tax on molasses.
The new law made it easier
to bring smugglers to trial.
The British East India
Company (BEIC) was in financial trouble because colonists were refusing to buy British tea to protest the tax on it.
The Tea Act allowed the
BEIC to bypass the local colonist merchants and sell directly to the colonists.
Colonists continued to do what they had already been doing before the Sugar
Act to avoid paying the tax – they smuggled molasses into the colonies and bribed tax collectors to look the other way.
American tea merchants were angry because they thought the Tea Act violated their right to “free enterprise.”
Daughters of Liberty brewed “liberty tea” from raspberry leaves. Members of the Sons of Liberty threw 342 chests of tea into Boston Harbor on the night of
December 16, 1773 to protest the Tea
Act.
Result
Writs of assistance were
used to try and catch smugglers
( legal documents which allowed British customs officials to inspect a ship’s cargo without giving any reason to the ship’s owner or crew).
Britain punished Boston with the Intolerable Acts that were not to be lifted until they
paid for the tea.
Intolerable Acts
Acts the Port of Boston until all of the property damages caused by the Boston Tea Party were paid for. Citizens of Boston were only allowed to hold only one town meeting per year. All juries were to be chosen by
British officials and any customs officials charged with a crime would stand trial in
Britain. A new Quartering Act stated colonists would have to house British soldiers when no other housing was available.
Committees of Correspondence spread word to the other colonies that sent shipments of food overland to Boston. In September of 1774 delegates from 12 colonies met in Philadelphia –
First Continental Congress (FCC). The FCC agreed to boycott British goods and not to export goods to Britain. They urged the colonists to set up militias. In Massachusetts, they began collecting weapons and gunpowder and storing it in Concord.
The opening shots of the
American Revolution.