Name - Mr. Lesiuk
advertisement

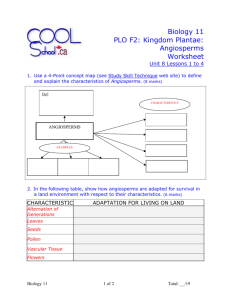
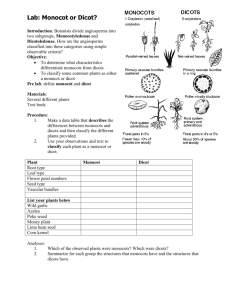
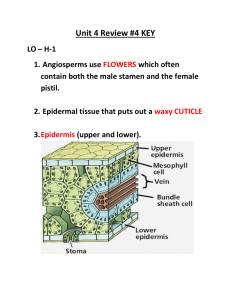
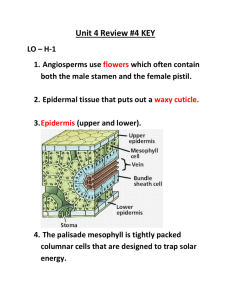
Name : ________________ Date: _______ Biology 11 Unit 4 - : Review # 4 UNIT # 4 : Kingdom Plantae (Learning Outcome G3- G4, H1-H3) – Make sure to read pp. 533-540 and 490-506 L.O. H – 1 Characteristics of Angiosperms ___ 1. What are the main reproductive organs/structures found on Angiosperms? ____2. Leaves and stems are covered with a waxy protective covering called a ….. ___ 3. What name is given to the layer of protective cells forming the outermost layer of a leaf? ___ 4. What is the function of the Palisade Mesophyll Layer? ____5. What cell organelles are very abundant/common in the cells that form the Palisade Layer? ___ 6. What is the function of the guard cells? ___ 7. What time of day are the stomata closed? ___ 8. Describe the mechanism by which guard cells open and close? ___ 9. Give at least two functions of the root cap. ___ 10. What happens in the Zone of Elongation in a root? ___ 11. What is the region called where cells take on their mature/adult characteristics? ___ 12. Describe the process of root action and how water and mineral absorption in roots occurs. ____13. What is the difference between H2O COHESION and H2O ADHESION? ____14 List some major uses of ANGIOSPERMS by humans. L.O H-2 Angiosperm Reproduction ___ 1. Pollen grains are developed inside what structure? ___ 2. List a couple of reasons why insects attracted to flowers? ___ 3. Describe what is meant by the term “pollination”. ___ 4 What migrates down the pollen tube after a pollen grain germinates? ___ 5. One sperm nucleus fertilizes the __________ to form a diploid structure called the _______________ ___ 6. The other haploid sperm nucleus unites with the other two nuclei (called the polar nuclei) in the female gametophyte to form the triploid ______________. ___ 7. What is the proper term for this process where two separate fertilizations take place? ___ 8. What are the three main parts of a seed? ___ 9. What female part of a flower goes on to become the fleshy part of a fruit? ___ 10. Describe the difference between complete and incomplete flowers? ___ 11. Try to think of an advantage a plant would have by possessing "Incomplete Flowers". ___ 12. What is the disadvantage to a plant that uses incomplete flowers? ____13. Typical plant ovaries contain dozens of small spherical structures that each bear the polar nuclei and the egg nucleus. What are these spherical structures called? OVER OVER _--> ____14 ***** Label all the parts of the complete flower found below****- L.O. H – 3 Angiosperms Vs Gymnosperms ___ 1. Describe some characteristics that separate Angiosperms from Gymnosperms? L.O. H – 4 Monocots Vs Dicots ___ 1. What is a cotyledon and what does it do? ____2. How many cotyledons do monocots have, how many do dicots have? ___ 3. What is distinctive about the veins in the leaves of a monocot? ____4. The tulip we dissected was either a dicot or a monocot. Which was it? And list at least three characteristics that help you know that it belonged to that class of angiosperms. ___ 5. How do the vascular bundles in the root of a monocot differ from the vascular bundles in the root of a dicot? ___ 6. Flower parts are found in multiples of ___________ in dicots? ___ 7. Why would remembering that a pirate and his bird (pair =di) would look for treasure marked by an "X" be helpful when it comes to Dicots? ___ 8 Dicots stems have vascular bundles arranged in what pattern, and how does this arrangement compare with the stem of a monocot? ___ 9. List at least four examples of monocots ___ 10. List at least four examples of dicots.