File - Mr.Fletcher Biology 11
advertisement

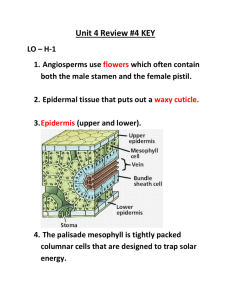
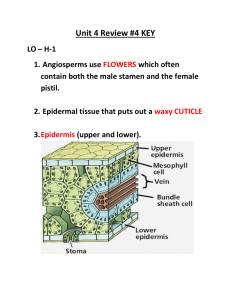
Angiosperms: The Flowering Plants Mrs. Mangat Biology 11 Discuss after this video: Is the Venus Fly trap a plant or animal? • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_DZiTACpr hE http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uJpgMDOZI nA&feature=endscreen&NR=1 General Characteristics • Produce flowers and fruit to attract pollinators • Seeds are not naked but enclosed by protective fruit which is formed by the flower • Deciduous (drop their leaves every year) (a) Wings enable maple fruits to be easily carried by the wind. (b) Seeds within berries and other edible fruits are often dispersed in animal feces. (c) The barbs of cockleburs facilitate seed dispersal by allowing the fruits to “hitchhike” on animals. Divided Into 2 Groups • 1. Monocotyledons • 2. Dicotyledons A Cotyledon is a seed leaf found in the protected seeds of angiosperms that stores food for the young sporophyte and becomes the first leaf to appear as the seed germinates Monocot vs. Dicot Characteristics of Monocots • • • • • One cotyledon in the seed Single seed leaf Vascular bundles are scattered throughout the stem Parallel veins on the leaves Floral parts in threes or multiple of three. Characteristics of Dicots • 2 cotyledons in the seed • 2 seed leaves • Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring near the outside of the stem • Branching network of veins on the leaves • Floral parts in 4 or 5 or multiples of 4 or 5 Both have same basic structure of nodes and internodes. petiole blade leaf Monocot or Dicot? Flowers-Basic Structure • The flower is the defining reproductive adaptation of angiosperms • Flowers are made up of four types of modified leaves sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels. • 1. SEPALS-small, green-leaf structures that surround the carpel and stamen • 2. PETALS-brightly colored and fragrant to attract polinators to the flower Four parts continued…………. • 3. STAMENS-are the male reproductive organs that produce microspores. Consist of lon, slender FILAMENT with an ANTHER at its tip that produces pollen. • 4. CARPEL/PISTIL-are female reproductive organs that produce megaspores and are found in the centre of the flower. Consist of a sticky STIGMA for catching pollen attached to a long STYLE that connects to the OVARY. Inside the ovary are OVULES in which the EGG (gametophyte) develops. The ovule becomes the SEED and the ovary becomes a protective FRUIT. Angiosperm Life Cycle • Mature plant is the sporophyte. • Some plants easily self-pollinate, but most have mechanisms to ensure cross-pollination. • Male gametophytes reach female gametophytes by producing a pollen tube. Haploid, Diploid, or Triploid? Fertilization Summary • http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/cont ent/angiosperm.html • http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/content/cat_010/ 2904002.html • When pollen tube reaches female gametophyte, sperm nuclei enter • One sperm nucleus fuses with egg=zygote • Other with 2 polar nuclei already present in embryo sac=3N (form triploid ENDOSPERM) • Called DOUBLE FERTILIZATION • Endosperm provides food for embryo Joke of the day • What did the male stamen say to the female pistil? I like your style!!! Ha ha!!!!! Homework • • • • Chapter 25 Section Reviews: Page 540 #1-4 Page 542 #1-4 Angiosperm worksheet