Plant Diversity Web Activity
advertisement

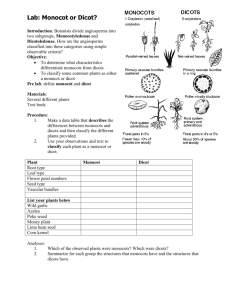
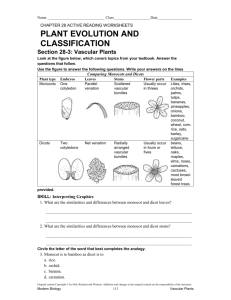
Date ______ Plant Diversity Web Activity Name __________________ Plant Evolution: https://www.learner.org/courses/essential/life/session4/closer2.html 1. What was the environment of the ancestors of modern land plants? 2. What are the four groups of land plants that exist today? 3. Explain why organisms that live in water do not need strong support systems? 4. List two adaptations that allowed land plants to grow tall. 5. Explain why organisms that live in water do not need well developed transport systems. 6. What type of tissue allows land plants to transport materials throughout the organism (this answer is not a the webpage) 7. How does the sperm cell reach the egg cell for an organism that lives in water? 8. What process did land plants evolve so that fertilization could occur on dry land? 9. Why did land plants evolve seeds? 10. What two groups of plant do not produce seeds? NonVascular Plants (Moss) http://www.nhptv.org/natureworks/nwep14c.htm 1. Why are mosses usually restricted to moist habitats? 2. What is produced by the moss gametophyte? 3. What is produced and released by the moss sporophyte? Date ______ Plant Diversity Web Activity Name __________________ Seedless Vascular Plants (Ferns) http://www.nhptv.org/natureworks/nwep14ferns.htm 1. Where do ferns grow best? 2. What are fern leaves called? 3. What are the horizontal stems of ferns called? 4. In the diagram of the fern label the roots, fronds and rhizomes. 5. What is produced on the underside of the fronds? 6. What is produced by the gametophyte stage (prothallus) of a fern? 7. What is produced when a fern egg cell is fertilized by a sperm cell? Date ______ Plant Diversity Web Activity Name __________________ Division Coniferophyta: Gymnosperms http://www.nhptv.org/natureworks/nwep14e.htm 1. Spruce, cedar, and pine trees are all examples of _______________. 2. About how many species of conifers are there? ________________________________________ 3. What is the cup of a yew tree called? ____________________________________ 4. Why do birds sometimes eat only the cup and leave the seeds of yew trees? 5. What type of gymnosperm resembles a palm, but is not really a palm? _________________ 6. What group of gymnosperms has only one surviving species? _____________________________ 7. Where are Ginkgo biloba trees originally from? ________________________________________ Date ______ Plant Diversity Web Activity Name __________________ Procedure: Visit the indicated websites and answer the following questions about plants Division Anthophyta: Angiosperms http://www.nhptv.org/natureworks/nwep14f.htm 1. Angiosperms are _________________ plants. 2. Where are angiosperm seeds found? _____________________________________________ 3. What process must angiosperms go through before they can reproduce? ________________ 4. What are the male sex organs of angiosperms? ____________________________________ 5. Where is the pollen made in angiosperms? ________________________________________ 6. What are the female sex organs of angiosperms? ___________________________________ 7. Where is the pollen left on angiosperms? _________________________________________ 8. What does cross-pollinate mean? _______________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 9. How many seed leaves do monocots start with? ________ 10. How many seed leaves do dicots start with? ________ 11. About how many species of monocots are there? ________________ 12. About how many species of dicots are there? ___________________ Evolution of Angiosperms http://biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio303/coevolution.htm 13.What is co-evolution? __________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 14. How are plants such as, pines, grasses and ragweed pollinated? __________________________________________ 15. Why must these plants produce so much pollen? _______________________________________________ _____________________________________ Date ______ Plant Diversity Web Activity Name __________________ 16. Today, over ______ of Angiosperms are insect-pollinated and _______ of insects, at least at some stage, depend on flowers for their food. 17. What are the three things that a plant must supply in order to be pollinated by insects. ____________________________________ ______________________________________ A. B. ____________________________________ ______________________________________ ____________________________________ ______________________________________ C. Monocots and Dicots http://www.sciencemonster.com/life-science/monocots-dicots/monocots-dicots-01.html 18. What are some examples of plants that are monocots? ___________________________ 19. What are some examples of plants that are dicots? _______________________ 20. What are the five signs that determine whether a plant is a monocot or dicot? ___________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ ________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 21. What are cotyledons? 22. Looking at a flower how could you tell if the plant is a monocot or dicot? ___________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ 23. Describe the arrangement of the xylem and phloem in a monocot and dicot stem. ___________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ Date ______ Plant Diversity Web Activity Name __________________ 24. In the space below sketch a cross section of a monocot stem and dicot stem. Label the xylem and phloem. Monocot Dicot 25. Explain the vein pattern in both the monocot and dicot leaves. ___________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ 26. Identify each of the following pictures as monocots or dicots. ____________ ____________ ___________ ____________