Chapter 1 Note Outline
advertisement

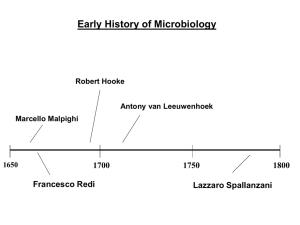
Chapter 1 – History of Microbiology Note Outline Early Years Antoni van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723) Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778) Eukaryotic1. Fungi 2. Protozoa movements: 1. Pseudopodia2. Cilia3. Flagella3. Algae Prokaryotes- 4. Bacteria 5. Archae Others 6. parasitic worms- why? 7. Viruses- Why was there a delay from Leeuwenhoek? Does Spontaneous Generation (abiogenesis) exist? 1. Francesco Redi (1626 – 1697) 2. John Turberville Needham (1713 – 1781) 3. Lazzaro Spallanzani (1729 – 1799) *reported results in 1799 Conclusions: 1. 2. 3. objections4. Pasteur (1822 – 1895) Biogenesis = How is this different from abiogenesis? Scientific Method 1. 2. 3. 4. control groupsWhat causes Fermentation? Pasteur Pasteurization* Father of Microbiology Biotechnology = Buchner (1860 – 1917) -fermentation doesn’t require living cells. Why? What causes Disease? 1857- Germ theory of Disease Robert Koch- etiology (study of causation of disease) Advances: (see p. 15) Koch's Postulates 1. 2. 3. 4. How can we prevent Infection and Disease? 1. Ignaz Semmelweis 2. Joseph Lister 3. Florence Nightingale 4. John Snow 5. Edward Jenner 6. Paul Ehrlich Today Molecular biology - Recombinant DNA – Gene therapy -