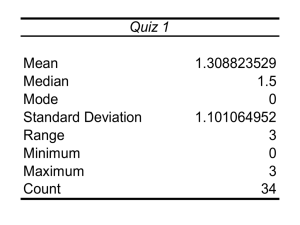
BIO 10 Lecture 1
advertisement
BIO 2 Lecture 1 WHAT IS SCIENCE? READING: (CONCEPT 1.5) “The word science is derived from a Latin verb meaning ‘to know.’ Science is a way of knowing.” - Biology, 7th ed., Campbell and Reese “Science is a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world, produced by a global community of researchers making use of scientific methods, which emphasize the observation, experimentation and explanation of real world phenomena.” - Wikipedia (2008) Science is: “1. The systematic observation of natural events and conditions in order to discover facts about them and to formulate laws and principles based on these facts. 2. The organized body of knowledge that is derived from such observations and that can be verified or tested by further investigation.” - Academic Press Dictionary of Science & Technology “Science … is the systematic and organized inquiry into the natural world and its phenomena. Science is about gaining a deeper and often useful understanding of the world.” - Multicultural History of Science page at Vanderbilt University. “As a practicing scientist, I share the credo of my colleagues: I believe that a factual reality exists and that science, though often in an obtuse and erratic manner, can learn about it. Galileo was not shown the instruments of torture in an abstract debate about lunar motion. He had threatened the Church's conventional argument for social and doctrinal stability: the static world order with planets circling about a central earth, priests subordinate to the Pope and serfs to their lord. But the Church soon made its peace with Galileo's cosmology. They had no choice; the earth really does revolve around the sun.” -Stephen J. Gould, The Mismeasure of Man “Science alone of all the subjects contains within itself the lesson of the danger of belief in the infallibility of the greatest teachers in the preceding generation . . .As a matter of fact, I can also define science another way: Science is the belief in the ignorance of experts.” -Richard Feynman, Nobel-prize-winning physicist in The Pleasure of Finding Things Out -Examples: Inquiry into Challenger disaster O-ring failure; Conspiracy theories about the assassination of President Kennedy What Do these Definitions of SCIENCE Have in Common? 1. The universe is real and its behavior has regular patterns (“laws”) that can be studied and modeled through science 2. Science is a method of learning about the universe and its behavior 3. Science is a collection of facts about the universe and how it behaves 4. Science is a collection of theories that have predictive power concerning how the universe will behave in the future 5. Science is progressive; it models the universe and its behavior more and more accurately over time What is the SCIENTIFIC METHOD? “In hypothesis-based science, deduction usually takes the form of predictions about what outcomes of experiments or observations we should expect if a particular hypothesis (premise) is correct. We then test the hypothesis by performing the experiment to see whether the results are as predicted. The deductive testing takes the form of “If ... then” logic.” - Biology, 7th ed., Campbell and Reese “Scientific method refers to a body of techniques for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, or correcting and integrating previous knowledge. To be termed scientific, a method of inquiry must be based on gathering observable, empirical and measurable evidence subject to specific principles of reasoning. A scientific method consists of the collection of data through observation and experimentation, and the formulation and testing of hypotheses.” - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scientific_method http://www.eas.slu.edu/People/RBHerrmann/Courses/EASA193F07/ Images/overview_scientific_method2.gif The scientific method is … “The stumbling way in which even the ablest of the scientists in every generation have had to fight through thickets of erroneous observations, misleading generalizations, inadequate formulations, and unconscious prejudice [that] is rarely appreciated by those who obtain their scientific knowledge from textbooks.” -James Bryant Conant (1893-1978), Science and Common Sense The scientific method is a way of learning about the universe that uncovers scientific facts and helps scientists build better theories. • • • • Begins with observations about the World and its behavior Develops testable hypotheses that might explain the observations Systematically eliminates hypotheses through careful experimentation Takes no prisoners -Dr. Ruth Ballard What are Scientific FACTS? Scientific facts are statements about the universe and its behavior that seem irrefutable at the time they are accepted as such. Scientific facts are discovered through a process of careful and reproducible observations and/or experiments that stand the test of time. Example: “The Earth is a sphere, not flat.” Although it certainly appears to the casual observer that the Earth is flat, and people believed for thousands of years that the Earth was flat, the FACT is that the Earth is a sphere. • Early sailors observed that the tops of mountains and buildings come into view above the horizon before objects nearer to the ground • Mariners sailed all the way around the globe, always going in one direction • Newton’s Law of Gravity provided a mechanism for how a spherical Earth could “work” We’ve photographed it from space We’ve orbited around it in space ships What are Scientific THEORIES? “A scientific theory is much broader in scope than a hypothesis ... is general enough to spin off many new specific hypotheses that can be tested ... [and], compared to any one hypothesis, is generally supported by a much more massive body of evidence.” - Biology, 7th ed., Campbell and Reese “Example: “Evolutionary adaptations evolve by natural selection.” • All theories are NOT equally valid! Good theories explain all (or most) of the facts and make testable predictions that are borne out by experimentation • A better theory is one that explains more facts and has more predictive power than the former theory • Thus, scientific theories can (and do) change or get replaced over time, but in a directed manner Fact or Theory? • • • • The Earth revolves around the Sun Humans reproduce sexually All crows are black The DNA sequence of humans and chimps is approximately 98% identical • Humans and chimps evolved from a common ancestor Can a THEORY become a FACT? YOU BET! Theories become facts when the evidence supporting them becomes do overwhelming that to refute them is basically absurd … Examples: “The Earth is a sphere” used to be a theory. “The Earth revolves around the Sun” used to be a theory. “Whales are mammals, not fish”, used to be a theory ... The Scientific Method at Work: Disproving Abiogenesis • Aristotle (384-322 BC) proposed the idea of spontaneous generation or abiogenesis • Abiogenesis postulates that living things arise from nonliving matter • The idea persisted for over 2,000 years • In ancient times, the scientific method was unknown and not systematically practiced • People based their beliefs on what they saw around them but did not carefully and reproducibly test their beliefs • (Unfortunately, this is still true is some segments of society today – e.g. dowsing, flower whispering, astrology, coffee ground readings, DNA activation healing, etc., etc.) • Example: In Egypt, the Nile flooded every spring, leaving behind nutrientrich mud. Frogs were plentiful at this time – much more so than in the dry season. • Therefore, people concluded that muddy soil must give rise to frogs. • Example: In parts of Europe, medieval farmers stored grain in barns with thatched roofs. As these roofs aged, they would leak, causing the grain inside to get moldy. Moldy grain, in turn, attracted mice. • Therefore, people concluded that moldy grain must give rise to mice. Actual Abiogenesis Recipes • Recipe for bees: – Kill a young bull, and bury it in an upright position so that its horns protrude from the ground. After a month, a swarm of bees will fly out of the corpse. • Recipe for mice: – Place a dirty shirt or some rags in an open pot or barrel containing a few grains of wheat or some wheat bran, and in 21 days, mice will appear. There will be adult males and females present, and they will be capable of mating and reproducing more mice. Testing Abiogenesis through the Scientific Method • Redi’s (1626-1697) Experiments: Evidence against spontaneous generation: 1. Unsealed – maggots on meat (FLIES) 2. Sealed – no maggots on meat 3. Gauze – few maggots on gauze (NO FLIES) • The results of Redi’s experiment disproved the idea of spontaneous generation for larger organisms, but people still thought microscopic organisms like algae or bacteria could arise that way … • Lazzaro Spallanzani’s Experiments (1765) • Critics said sealed vials did not allow enough air for organisms to survive and that prolonged heating destroyed “life force” • Therefore, abiogenesis remained the theory of the time • By 1860, the debate had become so heated that the Paris Academy of Sciences offered a prize for any experiments that would help resolve this conflict • The prize was claimed in 1864 by Louis Pasteur, as he published the results of an experiment that disproved the hypothesis that abiogenesis occurs in microscopic organisms • Hypothesis: Microbes come from cells of organisms on dust particles in the air; not the air itself. • Experiment: – Pasteur put broth into several special Sshaped flasks – Each flask was boiled and placed at various locations – S-shaped Flask – Filled with broth – The special shape was intended to trap any dust particles containing bacteria • Pasteur’s S-shaped flask kept microbes out but let air in, proving that the lack of bacterial growth was NOT the result of a lack of sufficient air • Disproved the abiogenesis of microbes and supported the theory of biogenesis (life only arises from other life forms) • Since that time, all experiments that have attempted to disprove biogenesis have failed, which is why it is now so widely an accepted scientific theory that it is accepted by most scientists as FACT.