04-05 Biochem review sheet answers ws
advertisement
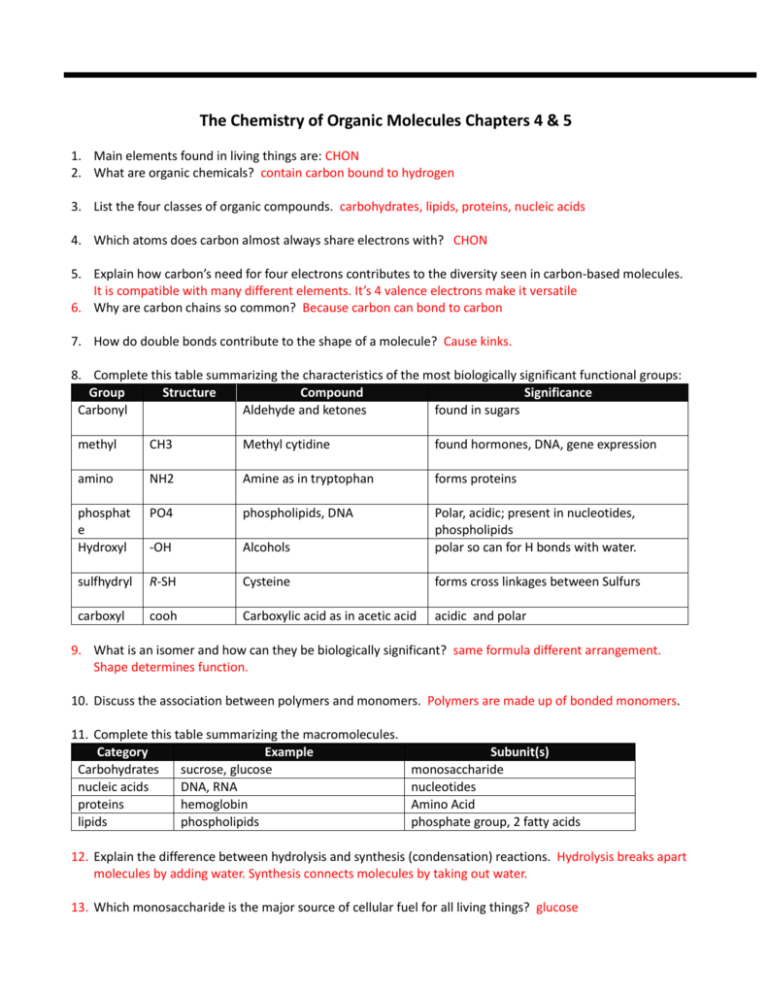
The Chemistry of Organic Molecules Chapters 4 & 5 1. Main elements found in living things are: CHON 2. What are organic chemicals? contain carbon bound to hydrogen 3. List the four classes of organic compounds. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 4. Which atoms does carbon almost always share electrons with? CHON 5. Explain how carbon’s need for four electrons contributes to the diversity seen in carbon-based molecules. It is compatible with many different elements. It’s 4 valence electrons make it versatile 6. Why are carbon chains so common? Because carbon can bond to carbon 7. How do double bonds contribute to the shape of a molecule? Cause kinks. 8. Complete this table summarizing the characteristics of the most biologically significant functional groups: Group Structure Compound Significance Carbonyl Aldehyde and ketones found in sugars methyl CH3 Methyl cytidine found hormones, DNA, gene expression amino NH2 Amine as in tryptophan forms proteins phosphat e Hydroxyl PO4 phospholipids, DNA -OH Alcohols Polar, acidic; present in nucleotides, phospholipids polar so can for H bonds with water. sulfhydryl R-SH Cysteine forms cross linkages between Sulfurs carboxyl cooh Carboxylic acid as in acetic acid acidic and polar 9. What is an isomer and how can they be biologically significant? same formula different arrangement. Shape determines function. 10. Discuss the association between polymers and monomers. Polymers are made up of bonded monomers. 11. Complete this table summarizing the macromolecules. Category Example Carbohydrates sucrose, glucose nucleic acids DNA, RNA proteins hemoglobin lipids phospholipids Subunit(s) monosaccharide nucleotides Amino Acid phosphate group, 2 fatty acids 12. Explain the difference between hydrolysis and synthesis (condensation) reactions. Hydrolysis breaks apart molecules by adding water. Synthesis connects molecules by taking out water. 13. Which monosaccharide is the major source of cellular fuel for all living things? glucose 14. Match the polysaccharide to it’s structure and then to it’s function: Cellulose Long chain with a few branches Forms the cell walls of bacteria. Chitin Long chain with many branches Forms the cell walls of fungi, and the exoskeletons of arthropods. Glycogen Long chain with no branches, forming long fibers Forms the cell walls of plant cells. Peptidoglycan Monomer has amino groups too. The form in which animals store glucose. Starch Monomer has amino acid chains. The form in which plants store glucose. 15. Why are lipids insoluble in water? Lipids have large hydrocarbon regions which are hydrophobic 16. Complete this table summarizing the types of lipids: Type Function(s) Organism use Steroids Hormones chemical signals Fats phospholipids Long-term energy storage and insulation in animals molecular component of cell membranes Waxes hydrophobic, antibiotic Energy storage, cushioning organs, insulation barrier between the inside of a cell and the outside environment ear wax Long term compact storage food for seedlings Oils 17. Explain the difference between a saturated and unsaturated fatty acid. Unsaturated have some double carbon bonds. 18. List some of the many functions of proteins. transport, hormones, receptors, defense, etc. 19. How do amino acids differ? R group 20. What is a peptide bond? covalent bond between two amino acids 21. Discuss the connection between the term peptide and polypeptide. peptide is the monomer of a protein which is also called a poly peptide. 22. Why is a protein’ shape so important? determines function. 23. Match the level of protein structure to it’s description and example: Primary Folding resulting in a three-dimensional Fibrous proteins, such as keratin. shape. Secondary Results when there are two or more polypeptides in a protein. Hemoglobin is an example. Tertiary The specific sequence of amino acids. Globular proteins, such as enzymes. Quaternary The coils and folds of a polypeptide. No example. 24. What happens when a protein denatures? unfolds 25. Explain the biological significance of chaperone proteins. assists protein folding 26. Discuss the effect of prions, both chemically and systematically. causes proteins to fold incorrectly. Causes diseases like Mad Cow. 27. Explain how DNA and RNA work together to build a protein. 28. What is ATP used for? Energy storage 29. Label this diagram showing the structure of a nucleotide: 30. Explain the difference between purines and pyrimidines. Purines – six membered ring fused to a five membered ring. Adenine and Guanine form a triple bond. Pyramidine – six membered fring. Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil – form double bond. 31. What is complementary base pairing? A bond to T, C to G 32. Why is ATP a high-energy molecule? Energy stored in chemical bonds between phosphates.











