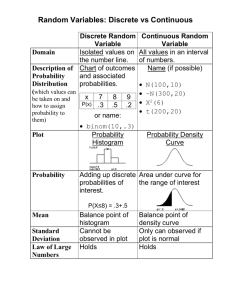
Quantile-Quantile Plots
advertisement

Quantile-Quantile Plots Also called QQ plots Normal probability plots Uses Check whether data came from normal distribution Suggest how data is different from normal distribution See if two datasets are from the same distribution General idea Using x and s from data, plot sorted data against what you would expect if it were from a normal distribution. Points should follow straight line if normal. Advantages of QQ-plot over histogram Can see if data’s tails are thicker or thinner than a normal distribution. Skewness can be more apparent Disadvantages of QQ-plot Not intuitive Takes practice Styles of QQ-plots differ between software packages, books, etc. 1 Practice Data: n=25, x 108.52, s 19.15 Obtained from Normal 100, 20 data standardized values for data percentiles Z Quantiles for percentiles 66 75 83 84 91 94 99 102 103 103 104 107 112 114 115 117 118 118 122 124 125 127 131 133 146 -2.22076 -1.75070 -1.33287 -1.28064 -0.91504 -0.75836 -0.49722 -0.34053 -0.28830 -0.28830 -0.23607 -0.07939 0.18176 0.28621 0.33844 0.44290 0.49513 0.49513 0.70404 0.80850 0.86073 0.96518 1.17410 1.27855 1.95752 0.02 0.06 0.10 0.14 0.18 0.22 0.26 0.30 0.34 0.38 0.42 0.46 0.50 0.54 0.58 0.62 0.66 0.70 0.74 0.78 0.82 0.86 0.90 0.94 0.98 -2.05375 -1.55477 -1.28155 -1.08032 -0.91537 -0.77219 -0.64335 -0.52440 -0.41246 -0.30548 -0.20189 -0.10043 0.00000 0.10043 0.20189 0.30548 0.41246 0.52440 0.64335 0.77219 0.91537 1.08032 1.28155 1.55477 2.05375 Expected data values using Z quantiles from percentiles 69.198 78.751 83.983 87.836 90.994 93.735 96.202 98.480 100.623 102.671 104.654 106.597 108.520 110.443 112.386 114.369 116.417 118.561 120.838 123.305 126.046 129.204 133.057 138.289 147.842 Different software packages use different algorithms for how to divide 0-to-1 up into equally spaced n points. Idea: The 10th percentile of the data should match up to what you would expect from a normal x, s distribution’s 10th percentile, same with 50th percentile, etc. xi x for each s data point should match up with the p th percentile for the standard normal distribution. Equivalent idea: The p th percentile for the standardized value xi, standardized 2 Probability Plot of data Normal 99 95 90 Mean StDev N AD P-Value 108.5 19.15 25 0.214 0.831 Mean StDev N AD P-Value 108.5 19.15 25 0.214 0.831 Percent 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 5 1 60 70 80 90 100 110 data 120 130 140 150 Probability Plot of data Normal - 95% CI 99 95 90 Percent 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 5 1 50 75 100 125 150 175 data The first graph is from Stat>Basic Statistics>Normality test. The second graph is from from Graph > Probability Plot. The 2nd graph includes a 95% pointwise confidence interval for what you would expect if the data came from a normal distribution. The pvalues are from the Anderson Darling test for normality. There are a number of tests for normality. 3 120 80 Sample Quantiles Normal Q-Q Plot -2 -1 0 1 2 Theoretical Quantiles 2 1 0 -1 -2 Theoretical Quantiles Normal Q-Q Plot 80 100 120 140 2 1 0 -1 -2 Standard Normal Quantiles Sample Quantiles -2 -1 0 1 2 127 146 Percents Data Z-scores 0.98 0.94 0.78 0.62 0.5 0.38 0.18 0.06 0.02 66 75 83 91 99 107 117 Data values 4 Note how Minitab Probability Plot’s y-axis has unequal spacing for the percents Some standard normal quantiles 1.96 1.282 0.842 0.524 0.253 0 -0.253 -0.524 -0.842 -1.282 -1.96 percents 0.975 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.025 quanitles The above 4 plots were programmed in R. Probability Plot of data Normal 99 Mean StDev N AD P-Value 95 90 108.5 19.15 25 0.214 0.831 Percent 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 5 1 60 70 80 90 100 110 data 120 130 140 150 5 Histogram of Chi-sq df=4 Normal 90 Mean StDev N 80 4.011 3.009 500 70 Frequency 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 -3 0 3 6 9 12 Chi-sq df=4 15 18 Probability Plot of Chi-sq df=4 Normal - 95% CI 99.9 Mean StDev N AD P-Value 99 95 Percent 90 4.011 3.009 500 13.472 <0.005 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 5 1 0.1 -5 0 5 10 Chi-sq df=4 15 20 Histogram of Left Skewed Normal 90 Mean StDev N 80 35.99 3.009 500 70 Frequency 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 21 24 27 30 33 Left Skewed 36 39 42 Probability Plot of Left Skewed Normal - 95% CI 99.9 Mean StDev N AD P-Value 99 95 Percent 90 35.99 3.009 500 13.472 <0.005 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 5 1 0.1 20 25 30 35 Left Skewed 40 45 6 Histogram of t-distn, df=4 Normal 200 Mean StDev N 0.06165 1.356 500 Mean StDev N AD P-Value 0.06165 1.356 500 4.404 <0.005 Mean StDev N -0.1607 1.399 20 Frequency 150 100 50 0 -3 0 3 6 t-distn, df=4 9 12 Probability Plot of t-distn, df=4 Normal - 95% CI 99.9 99 95 90 Percent 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 5 1 0.1 -5 0 5 t-distn, df=4 10 15 Histogram of t, df=4, n=20 Normal 9 8 Frequency 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 t, df=4, n=20 1 2 3 Probability Plot of t, df=4, n=20 Normal - 95% CI 99 Mean StDev N AD P-Value 95 90 -0.1607 1.399 20 0.733 0.047 Percent 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 5 1 -5.0 -2.5 0.0 t, df=4, n=20 2.5 5.0 7 Histogram of Beta(2,2) Normal 40 Mean StDev N 0.5039 0.2308 500 Mean StDev N AD P-Value 0.5039 0.2308 500 2.741 <0.005 Frequency 30 20 10 0 -0.00 0.15 0.30 0.45 0.60 Beta(2,2) 0.75 0.90 1.05 Probability Plot of Beta(2,2) Normal - 95% CI 99.9 99 95 90 Percent 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 5 1 0.1 -0.4 -0.2 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 Beta(2,2) 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 Can be used to plot random values against random values to if distributions are the same. 0 -1 -2 Znorm 1 2 30 random values from two distributions -2 -1 0 1 2 tDistnDF4 8