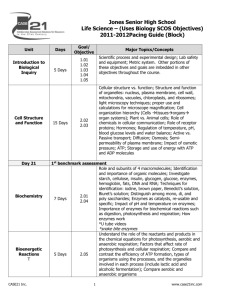
Recent Years' Paper 2B Questions, IB Biology Exam, HL
advertisement
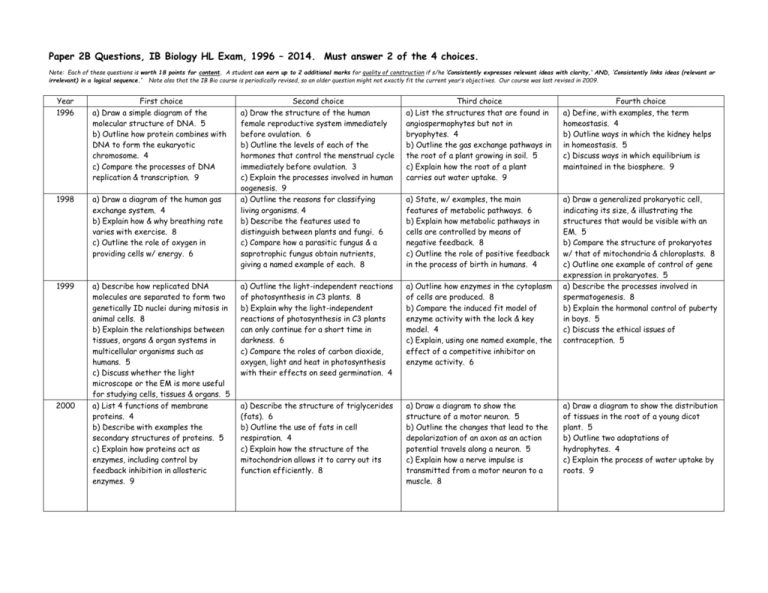
Paper 2B Questions, IB Biology HL Exam, 1996 – 2014. Must answer 2 of the 4 choices. Note: Each of these questions is worth 18 points for content. A student can earn up to 2 additional marks for quality of construction if s/he ‘Consistently expresses relevant ideas with clarity,’ AND, ‘Consistently links ideas (relevant or irrelevant) in a logical sequence.’ Note also that the IB Bio course is periodically revised, so an older question might not exactly fit the current year’s objectives. Our course was last revised in 2009. Year 1996 First choice a) Draw a simple diagram of the molecular structure of DNA. 5 b) Outline how protein combines with DNA to form the eukaryotic chromosome. 4 c) Compare the processes of DNA replication & transcription. 9 1998 a) Draw a diagram of the human gas exchange system. 4 b) Explain how & why breathing rate varies with exercise. 8 c) Outline the role of oxygen in providing cells w/ energy. 6 1999 a) Describe how replicated DNA molecules are separated to form two genetically ID nuclei during mitosis in animal cells. 8 b) Explain the relationships between tissues, organs & organ systems in multicellular organisms such as humans. 5 c) Discuss whether the light microscope or the EM is more useful for studying cells, tissues & organs. 5 a) List 4 functions of membrane proteins. 4 b) Describe with examples the secondary structures of proteins. 5 c) Explain how proteins act as enzymes, including control by feedback inhibition in allosteric enzymes. 9 2000 Second choice a) Draw the structure of the human female reproductive system immediately before ovulation. 6 b) Outline the levels of each of the hormones that control the menstrual cycle immediately before ovulation. 3 c) Explain the processes involved in human oogenesis. 9 a) Outline the reasons for classifying living organisms. 4 b) Describe the features used to distinguish between plants and fungi. 6 c) Compare how a parasitic fungus & a saprotrophic fungus obtain nutrients, giving a named example of each. 8 Third choice a) List the structures that are found in angiospermophytes but not in bryophytes. 4 b) Outline the gas exchange pathways in the root of a plant growing in soil. 5 c) Explain how the root of a plant carries out water uptake. 9 Fourth choice a) Define, with examples, the term homeostasis. 4 b) Outline ways in which the kidney helps in homeostasis. 5 c) Discuss ways in which equilibrium is maintained in the biosphere. 9 a) State, w/ examples, the main features of metabolic pathways. 6 b) Explain how metabolic pathways in cells are controlled by means of negative feedback. 8 c) Outline the role of positive feedback in the process of birth in humans. 4 a) Outline the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis in C3 plants. 8 b) Explain why the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis in C3 plants can only continue for a short time in darkness. 6 c) Compare the roles of carbon dioxide, oxygen, light and heat in photosynthesis with their effects on seed germination. 4 a) Outline how enzymes in the cytoplasm of cells are produced. 8 b) Compare the induced fit model of enzyme activity with the lock & key model. 4 c) Explain, using one named example, the effect of a competitive inhibitor on enzyme activity. 6 a) Draw a generalized prokaryotic cell, indicating its size, & illustrating the structures that would be visible with an EM. 5 b) Compare the structure of prokaryotes w/ that of mitochondria & chloroplasts. 8 c) Outline one example of control of gene expression in prokaryotes. 5 a) Describe the processes involved in spermatogenesis. 8 b) Explain the hormonal control of puberty in boys. 5 c) Discuss the ethical issues of contraception. 5 a) Describe the structure of triglycerides (fats). 6 b) Outline the use of fats in cell respiration. 4 c) Explain how the structure of the mitochondrion allows it to carry out its function efficiently. 8 a) Draw a diagram to show the structure of a motor neuron. 5 b) Outline the changes that lead to the depolarization of an axon as an action potential travels along a neuron. 5 c) Explain how a nerve impulse is transmitted from a motor neuron to a muscle. 8 a) Draw a diagram to show the distribution of tissues in the root of a young dicot plant. 5 b) Outline two adaptations of hydrophytes. 4 c) Explain the process of water uptake by roots. 9 2001 a) Describe the process of fertilization in humans. 6 b) Outline the way in which a pregnancy can be detected at a very early stage. 4 c) Explain the factors that cause a population to follow the sigmoid (Sshaped) growth curve. 8 a) Draw a diagram of a prokaryotic cell. 6 b) Outline the structure of the nucleosomes in eukaryotic chromosomes. 4 c) Explain how DNA replication is carried out by eukaryotes. 8 a) Draw a diagram to show the structure of a cell membrane. 5 b) Outline the ways in which substances move passively across membranes. 5 c) Explain how ATP is produced by photophosphorylation in chloroplasts. 8 a) Compare the way in which autotrophic, heterotrophic, and saprotrophic organisms obtain energy. 6 b) Outline the international system used for naming species of living things. 4 c) Discuss the definition of the term species. 8 2002 a) Outline the general features used to classify organisms into the kingdoms Prokaryotae, Protoctista, Fungi, Plantae & Animalia. 5 b) Outline a technique for transferring genes between species. 5 c) Discuss the need to maintain the biodiversity of organisms as a reservoir of alleles. 8 a) Draw a diagram to show the distribution of tissues in a cross-section of a root in a dicot plant. 5 b) Describe the process of mineral ion uptake into roots. 5 c) Explain the functions of the different tissues in a leaf. 8 a) Draw the structure of a mitochondrion as seen in an electron micrograph. 5 b) Describe the central role of acetyl CoA in carbohydrate and fat metabolism. 5 c) Discuss the importance of a balanced diet for people with varying energy needs. 8 a) Discuss the ways in which proteins within the cell are transported to the cell surf. 4 b) Describe the roles of mRNA, tRNA, and ribosomes in translation. 6 c) Discuss the theory that species evolve by natural selection using two named examples. 8 2003 a) Draw a diagram of the ultrastructure of an animal cell as seen in an EM. 6 b) Describe the process of active transport. 4 c) Explain the process of aerobic respiration including oxidative phosphorylation. 8 a) Draw the structure of a dicot animalpollinated flower. 6 b) Compare the adaptations of xerophytes & hydrophytes. 8 c) Describe how water is transported in a plant. 4 a) Define the terms active, passive, natural and artificial immunity. 4 b) Explain the role of antibody production with regard to vaccinations. 8 c) Describe the roles of nerves, muscles, and bones in producing movement. 6 a) Outline the process of fertilization in humans. 6 b) Describe how sexual reproduction promotes genetic variation within a species. 4 c) Explain how energy and nutrients enter, move through, and exit a food chain in an ecosystem. 8 2004 a) Outline enzyme-substrate specificity. 5 b) Explain how allosteric control of metabolic pathways by end-product inhibition includes negative feedback and non-competitive inhibition. 8 c) Distinguish between fibrous and globular proteins, giving one example of each. 5 a) State a role for each of four different named enzymes in DNA replication. 6 b) Outline the differentiation of cells in a multicellular organism. 4 c) Explain how meiosis results in great genetic variety among gametes. 8 a) Outline locomotion in each of the following: swimming in a bony fish; flying in a bird. 5 b) Draw a labeled diagram of the human elbow joint. 4 c) Explain how skeletal muscle contracts. 9 a) Explain how the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis rely on lightdependent reactions. 8 b) Outline the effect of temperature, light intensity, and CO2 concentration on the rate of photosynthesis. 6 c) Distinguish between xerophytes and hydrophytes, giving one structural adaptation for each type of plant. 4 2005 a) The process of translation involves the use of transfer RNA (tRNA) and amino acids. 5 Outline the structure of tRNA. b) Draw the basic structure of an amino acid, and label the groups that are used in peptide bond formation. 4 c) Explain the process of translation. 9 a) Plants are classified together in a kingdom. Other organisms are classified in other kingdoms. Outline the value of classifying organisms. 4 b) Draw a labeled diagram to show the external parts of a named dicotyledonous plant. 5 c) Explain how roots absorb water and then transport it to the xylem, noting any special adaptations that help these processes occur. 9 a) Outline the structure of DNA. 5 b) Describe the effects of polygenic inheritance using two specific examples. 5 c) Explain the process of transcription in eukaryotes. 8 a) Define the terms gene and allele and explain how they differ. 4 b) Outline one example of inheritance involving multiple alleles. 5 c) Using an example you have studied, explain a cross between two linked genes, including the way in which recombinants are produced. 9 2006 a) Using a table, compare the structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5 b) Identify one specific disease in humans caused by a prokaryotic pathogen, name the pathogen and outline its mode of transmission and its possible effects. 5 c) Explain the production of antibodies against a pathogen. 8 2007 a) The plasma membrane controls the movement of substances into and out of cells. Draw a labeled diagram to show the structure of a biological membrane such as the plasma membrane. 5 b) Explain how ion movements cause a nerve impulse to pass along a neuron. 8 c) Outline the process of water uptake by root epidermal cells. 5 a) The activity of enzymes determines the rate at which chemical reactions occur in living organisms. Outline the effects of two factors that can both increase and decrease enzyme activity. 6 b) Explain how end product inhibition is used to control the rate of chemical reactions in cells. Include an example in your answer with the names of both the enzyme and the inhibitor. 8 c) Outline the process of blood clotting. 4 a) The carbon cycle involves both the production and the fixation of carbon dioxide. Draw a labeled diagram to show the processes involved in the carbon cycle. 5 b) Explain the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis. 8 c) Outline the consequences of rising carbon dioxide concentrations in the Earth's atmosphere. 5 2008 a) Draw and label a diagram of a dicot animal-pollinated flower as seen with the naked eye and a hand lens. 5 b) Describe how meiosis results in an enormous genetic variety in the production of pollen. 5 c) Using the theory of natural selection, explain how new species of dicotyledonous plants develop. 8 a) Outline the various means of transfer of different types of molecules through the plasma membrane. 4 b) Describe the transport of water through an angiosperm root system. 6 c) Explain the homeostatic control of water balance in the human body. 8 a) Outline the first three levels of protein structure, including the types of bonding within each and the significance of each level. 5 b) Using a table, compare competitive and noncompetitive inhibition and give one named example of each. 5 c) Explain the production of antibodies. 8 a) Outline the formation of carbohydrate molecules in photosynthesis starting from the absorption of light energy. 6 b) Describe the metabolic events during germination of an angiosperm seed that is rich in starch. 4 c) Explain the formation of ATP by chemiosmosis in cellular respiration. 8 a) Blood vessels carry blood to and from the kidney. Draw a labeled diagram to show the internal structure of the kidney, including the vessels that are connected to it. 5 b) Compare the composition of blood arriving at the kidney with the composition of blood carried away from it. 4 c) Explain the relationship between the structure and functions of arteries, capillaries, and veins. 9 a) Outline the regulation of pregnancy by two named hormones. 4 b) Describe the principles of synaptic transmission in the nervous system. 6 c) Explain homeostasis giving two specific examples that show the role of the endocrine or the nervous system. 8 a) The male reproductive system produces huge numbers of sperm, each of which is genetically different. Draw a labeled diagram of the male reproductive system. 5 b) Explain the events in meiosis that lead to the genetic diversity of sperm. 8 c) Outline the events after meiosis in the male reproductive system that result in the production of semen. 5 a) Describe a pyramid of energy and the reasons for its shape. 4 b) Outline the conversion of light energy to chemical energy in photosynthesis. 6 c) Explain the conversion of the chemical energy of organic compounds into ATP in aerobic cell respiration. 8 2009 MOST RECENT curriculum revision 2010 2011 2012 a) a) Draw a labeled diagram of the structure of a chloroplast as seen with an electron microscope. 4 b) Describe how water is carried by the transpiration stream. 7 c) Explain how flowering is controlled in long-day and short-day plants. 7 a) Outline a possible cause of Down syndrome. 4 b) Outline the processes involved in oogenesis within the human ovary. 8 c) Discuss the ethical issues surrounding in vitro fertilization. 6 a) Distinguish between RNA and DNA. 3 b) Explain the process of DNA replication. 8 c) Outline how enzymes catalyze reactions. 7 a) Outline how antibiotic resistance in bacteria can arise in response to environmental change. 5 b) Outline the principle of immunity. 6 c) Discuss the benefits and dangers of vaccination. 7 a) Blood is a liquid tissue containing glucose, urea, plasma proteins and other components. List the other components of blood. 5 b) Outline how the human body prevents blood glucose concentration from rising excessively. 5 c) Blood plasma, glomerular filtrate, and urine have different concentrations of solutes, such as glucose, protein and urea. Explain the processes occurring in the kidney that cause differences in the concentrations of these solutes between blood plasma, glomerular filtrate, and urine. a) The main parts of growing plants are roots, stems and leaves. Draw a plan diagram to show the arrangement of tissues in the stem of a dicot plant. 5 b) Outline the adaptations of plant roots for absorption of mineral ions from the soil. 5 c) Photosynthesis and transpiration occur in leaves. Explain how temperature affects those processes. 8 a) Eukaryotic cells have intracellular and extracellular components. State the functions of one named extracellular component. 4 b) Outline, with an example, the process of exocytosis. 5 c) Translation occurs in living cells. Explain how translation is carried out, from the initiation stage onwards. 9 a) Most of the DNA of a human cell is contained in the nucleus. Distinguish between unique and highly repetitive sequences in nuclear DNA. 5 b) Draw a labeled diagram to show four DNA nucleotides, each with a different base, linked together in two strands. 5 c) Explain the methods and aims of DNA profiling. 8 a) Membrane proteins vary in their positions within the membrane and in their functions. Outline the positions and functions of proteins in membranes. 8 b) Explain how polar and non-polar amino acids help channel proteins and enzymes carry out their functions. 5 c) Compare competitive and noncompetitive inhibition of enzymes. 5 a) During a period of physical exercise, the rate of urine production falls, but the ventilation rate and the body temperature rise. Explain the mechanisms that are used to cool the body when it is overheated. 5 b) Explain how the collecting ducts can alter the volume of urine produced by the kidney. 5 c) Describe the structure of the ventilation system, including the alveoli. 8 a) Describe the characteristics of stem cells that make them potentially useful in medicine. 5 b) Outline a technique of gene transfer resulting in genetically modified organisms. 5 c) Explain the use of karyotyping in human genetics. 8 a) Gametes are produced in humans by spermatogenesis and oogenesis. Compare spermatogenesis and oogenesis. 5 b) Explain the processes that result in genetic variation in the sperm produced by an adult male. 5 c) Outline the process of in vitro fertilization. 8 a) All organisms in an ecosystem are involved in the carbon cycle. Outline the roles of living organisms in the carbon cycle. 8 b) Explain how triose phosphate is produced and used in the chloroplasts of a plant. 5 c) Explain the conditions that are needed to allow a seed to germinate. 5 a) Describe how plants carry out gas exchange in the leaves. 5 b) Outline the causes and consequences of the enhanced greenhouse effect. 5 c) Explain the role of limiting factors in photosynthesis. 8 a) Outline what is meant by homeostasis. 4 b) Describe how body temperature is maintained in humans. 6 c) Explain the processes occurring in the kidney that contribute to osmoregulation. 8 a) Outline, with examples, the types of carbohydrates found in living organisms. 4 b) Describe the importance of hydrolysis in digestion. 6 c) Explain the effect of inhibitors on the activity of enzymes. 8 2013 c) d) e) 2014 f) g) h) a) Draw a labeled plan diagram to show the distribution of tissues in the leaf of a dicotyledonous plant. 4 b) Outline the metabolic processes that occur in starchy seeds during germination. 6 c) Explain the light-independent processes of photosynthesis in plants. 8 a) Draw a labeled diagram to show the structure of a motor neuron. 4 b) Explain how nerve impulses pass from one neuron to another neuron. 8 c) Outline how the rate at which the heart beats is controlled. 6 a) Describe the process of blood clotting.4 b) Factor IX is a blood clotting protein that some hemophiliacs lack. In the future, hemophilia could be treated using clotting factors synthesized by genetically modified bacteria. Outline the basic technique used for this gene transfer. 6 c) Explain how males inherit hemophilia and how females can become carriers for this condition. 8 a) Draw a simple labeled diagram to show the structure of a double stranded DNA molecule, comprising four nucleotides. 6 b) Describe the use of DNA profiling in forensic investigations. 4 c) Using a named example, discuss the effects of genetically modifying an organism. 8 a) Outline the types of evidence that can be used to support the theory of evolution. 4 b) Outline the relationship between Mendel’s law of independent assortment and meiosis. 6 c) Explain two examples of evolution in response to environmental change. 8 a) Draw a labeled diagram of the kidney and associated vessels. 5 b) Outline type II diabetes. 5 c) Explain the presence of glucose in the urine of a diabetic person and its absence in the urine of a person with type I diabetes that is being successfully treated. 8 a) Draw a labeled diagram of a mitochondrion as seen in an electron micrograph. 4 b) A supply of oxygen is needed for aerobic respiration in mitochondria. Describe the features of alveoli in human lungs that adapt them for efficient absorption of oxygen. 6 c) Explain the mechanism of ventilation of human lungs. 8 a) Draw a labeled diagram of the carbon cycle. 6 b) Outline the effect of carbon dioxide on the rate of photosynthesis and how this can be measured by oxygen release. 4 c) Carbon dioxide is released during cellular respiration. Explain anaerobic and aerobic respiration. 8